A one-dimensional array:
1, the array declaration
Byte [] arrByte;
Int [] arrInt;
Char [] arrChar;
String [] arrStr;
Note: String arrStr1 []; Support on syntax, but don't write
2, array initialization
(1) static initialization
ArrByte=new byte [] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Or an array variable declaration and initial enter a complete statement
Byte [] arrByte1=new byte [] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
(2) dynamic initialization
ArrInt=new int [4].
Or an array variable declaration and initial enter a complete statement
Int [] arrInt=new int [4].
3, assignment and values
(1) manual assignment
ArrInt [0]=1; ArrInt [1]=2; ArrInt [2]=3;
(2) the traversal assignment
for(int i=0; i
ArrInt [I]=I;
}
(3) traversal values
For (int I=0; i
System. The out. Println (arrInt [I]);
}
A two-dimensional array:
Two-dimensional array declaration, initialization and reference similar to the one dimensional array:
* the sample code: *
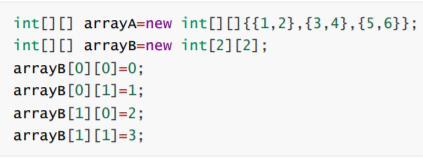
Note: the Java language, a two-dimensional array is considered an array of arrays, array space is not continuous distribution, so does not require a two-dimensional array of each dimension the same size,

CodePudding user response:
Learning, very goodCodePudding user response:
Writing is very good oh
