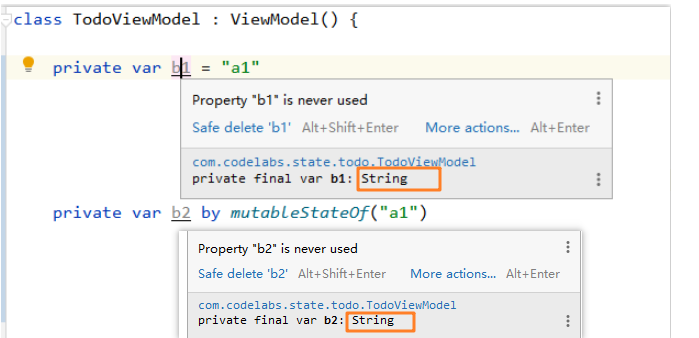
There are two variables b1 and b2 in Code A. It seems that there are all String variable, as you can see in Image A.
Question 1: What are the differences between private var b1 = "a1" and private var b2 by mutableStateOf("a1")?
Code A
class TodoViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var b1 = "a1"
private var b2 by mutableStateOf("a1")
BTW
Question 2: Image B is from the 
And more
Question 3: In the article, why doesn't the author use private var currentEditPosition = mutableStateOf(-1) instead of private var currentEditPosition1 by mutableStateOf(-1)?
CodePudding user response:
mutableStateOf is an observable state holder, changes to its value notify its observers. In a sense you can think of it as similar to LiveData.
You can use mutableStateOf when you want your UI to react to changes to your state, if you have a composable that reads your b2 value, as in this example
Text(
text = b2.value
)
then by changing your mutableStateOf the text composable will automatically recompose and update its content.
CodePudding user response:
b1 is a regular String that when the value changed the composables that using the variable will not recomposed or updating automatically.
b2 is actually a MutableState<String> which is when the value changed any composables that using it will be automatically recomposed.
You can not see the difference between it because you're using Kotlin delegate by for assigning the b2 variable. If you use = for assigning a variable with mutableStateOf you should use variable.value to get and set the value.