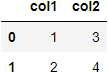
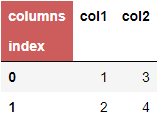
I understand to access the top left cell of a dataframe we need to use df.columns.name and I can see the pandas document on styling provides example to style row/column headers with apply_index (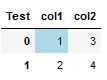
Change the # within the function for font color or both.
To see the steps within the function check:
print(pd.DataFrame('', index=df.index, columns=df.columns))
print(df.iloc[0,0])
To assing a color to a specific index you can use 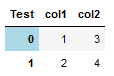
CodePudding user response:
Option 1. Cell is empty
Trick is to look at the output for print(df.style.set_table_styles().to_html()):
<thead>
<tr>
<th > </th>
<th id="T_d7719_level0_col0" >col1</th>
...
</tr>
</thead>
Notice: <th > </th>. We can access these class names and set the format. E.g. in this case, we access blank (level0 applying to all of level0, i.e. all cols and index too).
df.style.set_table_styles(
[{'selector': '.blank',
'props': [('background-color', 'IndianRed'),
('color', 'white')]
}]
)
Result:
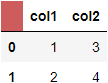
Option 2. Either df.columns.name or df.index.name, or both. One style to entire cell.
In either scenario, we will need .index_name instead of .blank. E.g.
df.columns.name = 'columns'
df.style.set_table_styles(
[{'selector': '.index_name',
'props': [('background-color', 'IndianRed'),
('color', 'white')]
}]
)
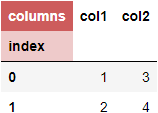
Result:
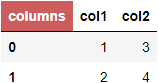
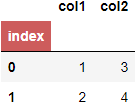
Option 3. df.columns.name and df.index.name, different styles.
This one is a little more tricky, as we will need to add tr:nth-child(1) for columns.name and tr:nth-child(2) for index.name.
# just setting col and index name immediately inside `pd.DataFrame`
df = pd.DataFrame([[1,3],[2,4]],
columns=pd.Index(['col1','col2'], name='columns'),
index=pd.Index([0,1], name='index'))
df.style.set_table_styles(
[{'selector': 'tr:nth-child(1) .index_name',
'props': [('background-color', 'IndianRed'),
('color', 'white')]
}, {'selector': 'tr:nth-child(2) .index_name',
'props': [('background-color', '#EECACA'),
('color', 'black')]
}]
)