Need a fix for Multiple Searched Elements (Not getting the right index)
the attached image below is the expected output and the output I'm having
Expected Output

Actual output
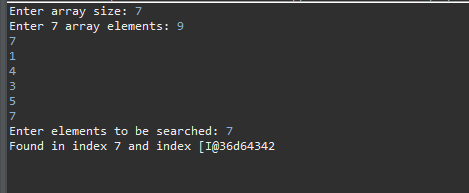
I am getting the wrong Index when running the program I hope someone can help
Thank you!
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Multiple Search Elements {
public static boolean verify;
public static int arrayElements (int value, int [] a)
{
int index = 0;
for ( int i=0; i<a.length; i )
{
if (a[i] == value)
{
index = i;
verify = true;
}
}
return index;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter array size: ");
int array_length = sc.nextInt();
int [] array = new int[array_length];
System.out.println("Enter " array_length " array elements: ");
for(int i=0; i<array_length; i )
{
array[i] =sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.print("Enter elements to be searched: ");
int element = sc.nextInt();
int index = arrayElements(element, array);
if (verify)
{
System.out.println("Found in index " element " and index " array);
}
else
{
System.out.print("Element not found");
}
}
}
CodePudding user response:
Consider returning a List of all the found positions:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class MultipleSearchElements {
public static List<Integer> getElementPositions(int[] array, int target) {
List<Integer> elementPositions = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i ) {
if (array[i] == target) {
elementPositions.add(i);
}
}
return elementPositions;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter array size: ");
int arrayLength = sc.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[arrayLength];
System.out.printf("Enter %d array elements: ", arrayLength);
for (int i = 0; i < arrayLength; i ) {
array[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.printf("%nEnter element to be searched: ");
int element = sc.nextInt();
List<Integer> elementPositions = getElementPositions(array, element);
if (!elementPositions.isEmpty()) {
System.out.printf("Found in index %s%n", elementPositions.stream()
.map(Object::toString)
.collect(Collectors.joining(" and index ")));
} else {
System.out.print("Element not found");
}
}
}
Example Usage:
Enter array size: 7
Enter 7 array elements: 9 7 1 4 3 5 7
Enter element to be searched: 7
Found in index 1 and index 6
CodePudding user response:
You're just not printing the good thing, print index
System.out.println("Found in index " element " and index " index);
Then no need of verify, the convention would be to use a specific value (if possible) here use -1
public static int arrayElements(int value, int[] a) {
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ) {
if (a[i] == value) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
return index;
}
With a solution to read numbers on one line
int array_length = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int[] array = new int[array_length];
System.out.println("Enter " array_length " array elements: ");
String[] numbers = sc.nextLine().split("\\s ");
for (int i = 0; i < array_length; i ) { // use array_length in case there is too much numbers given
array[i] = Integer.parseInt(numbers[i]);
}
System.out.print("Enter elements to be searched: ");
int element = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
int index = arrayElements(element, array);
if (index != -1) {
System.out.println("Found in index " element " and index " index);
} else {
System.out.print("Element not found");
}
