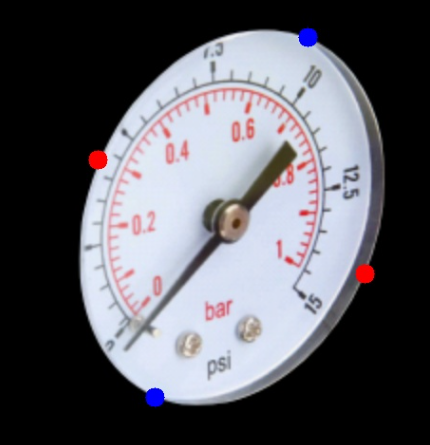
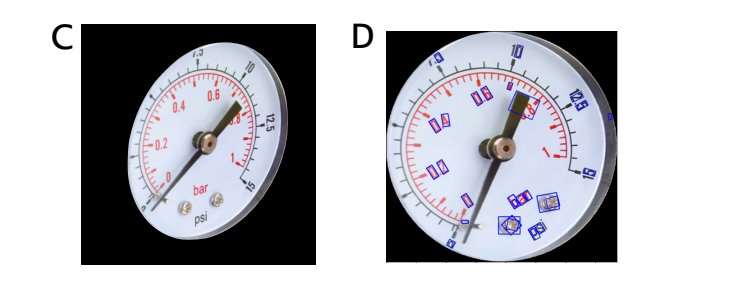
im currently trying to implement a paper of reading pressure gauges. There is a step where i dont know what to do. It says: "The display contour is then rotated to vertically align the long axis of the ellipse and inscribed in a rectangle used to crop the gauge image." So im not sure how i can rotate this image vertically, for better understanding i will show you a example what the current image is and what it needs to be.
Im currently at step C and need to get the image in position of step D. The text detection in the example is currently not important.
At the moment i have the correct contours and ellipse for the display.
(cnts, boundingBoxes) = sort_contours(cnts)
#find correct contours and fitellipse
if len(cnts) != 0:
for i in range(len(cnts)):
if len(cnts[i]) >= 5: #if contours has more than 5 points
# cv2.drawContours(image,cnts[0],-1,(150,10,255),3)
ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(cnts[i])
finalElps.append(ellipse) #(centx,centy), (width,height), angle
for i in range(len(finalElps)):
centx = finalElps[i][0][0]
centy = finalElps[i][0][1]
eWidth = finalElps[i][1][0]
eHeight = finalElps[i][1][1]
sfRes = Sf(eWidth, eHeight)
cfRes = Cf(centx, imgCenterX, centy, imgCenterY)
afRes = Af(eWidth,eHeight,imgWidth,imgHeight)
print("SF: " str(sfRes) "| " "CF: " str(cfRes) "| Af: " str(afRes))
if(sfRes < 0.4 and cfRes < 6 and afRes < 0.9):
print(finalElps[i])
cv2.ellipse(image, finalElps[i], (255,0,0), 2)
plt.imshow(image)
sfRes, cfRes and afRes are just calculations to find the right ellipse.
What should be my next step to reach the vertical rotation? I think the correct name for it is "image rectification" but im not 100% sure about it
CodePudding user response:
Here is how to get the image D from the image C:
- Find the binary mask
- Find an ellipse (center, width, height, angle)
- Find 4 points on opposite sides of the ellipse
- Use these 4 points to get perspective transform that can be used to warp the rotated gauge image to rectangular image. The final result:
Code:
import cv2
import numpy as np
image = cv2.imread("gauge.png")
# find the parameters of the ellipse
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
mask = cv2.threshold(gray, 10, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
points = np.stack(np.nonzero(mask.T)).T
hull = cv2.convexHull(points)
(cx, cy), (width, height), angle = cv2.fitEllipse(hull)
# for visualization
# cv2.ellipse(image, (int(cx), int(cy)), (int(width/2), int(height/2)), angle, 0, 360, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# find the points on the opposite sides of the ellipse
# define rectangular homogenuous coordinates and rotate them using a rotation matrix
mat = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cx, cy), -angle, 1)
mat = np.vstack((mat, [0, 0, 1]))
coords = np.array(
[
[cx width // 2, cy, 1],
[cx - width // 2, cy, 1],
[cx, cy height // 2, 1],
[cx, cy - height // 2, 1],
]
)
points = (mat @ coords.T)[:2].T # drop the homogenuos part
# for visualization
# for px, py in points.astype(int)[:2]:
# cv2.circle(image, (px, py), 10, (0, 0, 255), -1)
# for px, py in points.astype(int)[2:]:
# cv2.circle(image, (px, py), 10, (255, 0, 0), -1)
# define points on the target image to which the ellipse points should be mapped
size = 300
target = np.float32(
[
[size, size // 2],
[0, size // 2],
[size // 2, size],
[size // 2, 0],
]
)
mat = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points.astype(np.float32), target)
rect_image = cv2.warpPerspective(image, mat, (size, size))
cv2.imwrite("rect_gauge.png", rect_image)