I want to create a randomized bool array with a given length a given number of True values efficiently in Python. I could not find a single command to do so, the following does what I want (twice). Is there anything more elegant way to do it?
import numpy as np
def randbool(length,numtrue):
index_array=np.random.choice(length,numtrue,replace=False)
bool_array=np.zeros(length,dtype=bool)
bool_array[index_array]=True
return(bool_array)
def randbool2(length,numtrue):
bool_array=np.hstack((np.tile(True,numtrue),np.tile(False,length-numtrue)))
np.random.shuffle(bool_array)
return(bool_array)
print(randbool(5,2))
print(randbool2(5,2))
CodePudding user response:
Still another option:
def randbool(l,n):
return np.random.permutation(l)<n
np.random.permutation randomly permute np.arange(l).
CodePudding user response:
Another suggestion:
def randbool3(length, numtrue):
return np.random.choice(length, length, replace=False) < numtrue
Similar in efficiency to the first approach but a bit shorter in code
CodePudding user response:
Both of your examples have small n and is therefore in the regime where native Python code can be faster than Numpy. For example, given:
from random import shuffle
def randbool4(length, numtrue):
arr = [False] * length
arr[:numtrue] = [True] * numtrue
shuffle(arr)
return arr
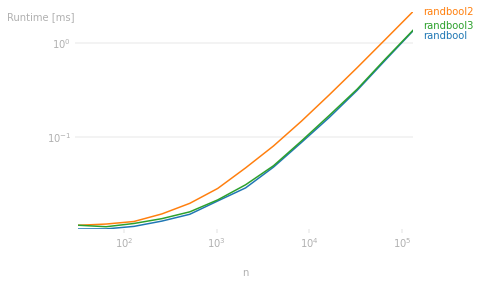
I can execute randbool4(5,2) in ~4µs. Your variants take ~30µs and mozway's are similar, while obchardon's Numpy variant takes only ~6µs which is surprisingly close.
Obviously when n gets large then Numpy's native kernels of win, but thought it worth pointing out.