I am writing a piece of simulation software in python using pandas, here is my problem:
Imagine you have two pandas dataframes dfA and dfB with numeric columns A and B respectively. Both dataframes have a different number of rows denoted by n and m. Let's assume that n > m. Moreover, dfA includes a binary column C, which has m times 1, and the rest 0. Assume both dfA and dfB are sorted.
My question is, in order, I want to add the values in B to the values in column A if column C == 0.
In the example n = 6, m = 3.
Example data:
dataA = {'A': [7,7,7,7,7,7],
'C': [1,0,1,0,0,1]}
dfA = pd.Dataframe(dataA)
dfB = pd.Dataframe([3,5,4], columns = ['B'])
Example pseudocode: DOES NOT WORK
if dfA['C'] == 1:
dfD['D'] = dfA['A']
else:
dfD['D'] = dfA['A'] dfB['B']
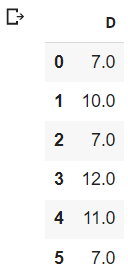
Expected result:
dfD['D']
[7,10,7,12,11,7]
I can only think of obscure for loops with index counters for each of the three vectors, but I am sure that there is a faster way by writing a function and using apply. But maybe there is something completely different that I am missing.
*NOTE: In the real problem the rows are not single values, but row vectors of equal length. Moreover, in the real problem it is not just simple addition but a weighted average over the two row vectors
CodePudding user response:
The accepted answer is pretty clever. I am just showing an alternative way if you would like to do it using loops:
# Create an empty df
dfD = pd.DataFrame()
# Create Loop
k = 0
for i in range(len(dfA)):
if dfA.loc[i, "C"] == 1:
dfD.loc[i, "D"] = dfA.loc[i, "A"]
else:
dfD.loc[i, "D"] = dfA.loc[i, "A"] dfB.loc[k, "B"]
k = k 1
# Show results
dfD
CodePudding user response:
You can use:
m = dfA['C'].eq(1)
dfA['C'] = dfA['A'].where(m, dfA['A'] dfB['B'].set_axis(dfA.index[~m]))
Or:
dfA.loc[m, 'C'] = dfA.loc[m, 'A']
dfA.loc[~m, 'C'] = dfB['B'].values
Output:
A C
0 7 7
1 7 10
2 7 7
3 7 12
4 7 11
5 7 7