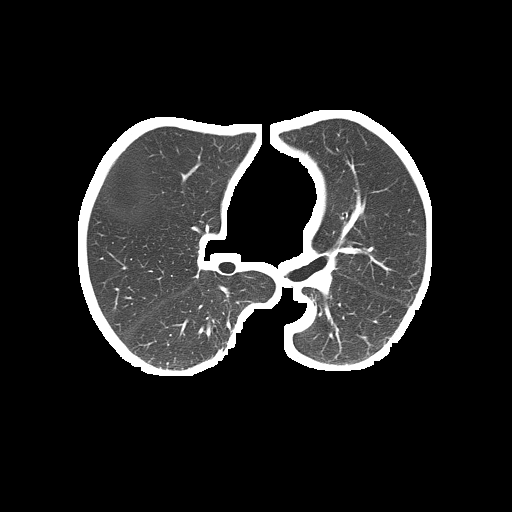
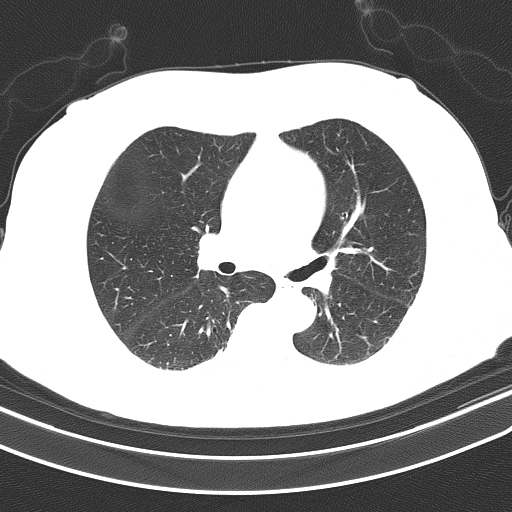
I am trying to segment lung CT images using Kmeans by using code below:
def process_mask(mask):
convex_mask = np.copy(mask)
for i_layer in range(convex_mask.shape[0]):
mask1 = np.ascontiguousarray(mask[i_layer])
if np.sum(mask1)>0:
mask2 = convex_hull_image(mask1)
if np.sum(mask2)>2*np.sum(mask1):
mask2 = mask1
else:
mask2 = mask1
convex_mask[i_layer] = mask2
struct = generate_binary_structure(3,1)
dilatedMask = binary_dilation(convex_mask,structure=struct,iterations=10)
return dilatedMask
def lumTrans(img):
lungwin = np.array([-1200.,600.])
newimg = (img-lungwin[0])/(lungwin[1]-lungwin[0])
newimg[newimg<0]=0
newimg[newimg>1]=1
newimg = (newimg*255).astype('uint8')
return newimg
def lungSeg(imgs_to_process,output,name):
if os.path.exists(output '/' name '_clean.npy') : return
imgs_to_process = Image.open(imgs_to_process)
img_to_save = imgs_to_process.copy()
img_to_save = np.asarray(img_to_save).astype('uint8')
imgs_to_process = lumTrans(imgs_to_process)
imgs_to_process = np.expand_dims(imgs_to_process, axis=0)
x,y,z = imgs_to_process.shape
img_array = imgs_to_process.copy()
A1 = int(y/(512./100))
A2 = int(y/(512./400))
A3 = int(y/(512./475))
A4 = int(y/(512./40))
A5 = int(y/(512./470))
for i in range(len(imgs_to_process)):
img = imgs_to_process[i]
print(img.shape)
x,y = img.shape
#Standardize the pixel values
allmean = np.mean(img)
allstd = np.std(img)
img = img-allmean
img = img/allstd
# Find the average pixel value near the lungs
# to renormalize washed out images
middle = img[A1:A2,A1:A2]
mean = np.mean(middle)
max = np.max(img)
min = np.min(img)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2).fit(np.reshape(middle,[np.prod(middle.shape),1]))
centers = sorted(kmeans.cluster_centers_.flatten())
threshold = np.mean(centers)
thresh_img = np.where(img<threshold,1.0,0.0) # threshold the image
eroded = morphology.erosion(thresh_img,np.ones([4,4]))
dilation = morphology.dilation(eroded,np.ones([10,10]))
labels = measure.label(dilation)
label_vals = np.unique(labels)
regions = measure.regionprops(labels)
good_labels = []
for prop in regions:
B = prop.bbox
if B[2]-B[0]<A3 and B[3]-B[1]<A3 and B[0]>A4 and B[2]<A5:
good_labels.append(prop.label)
mask = np.ndarray([x,y],dtype=np.int8)
mask[:] = 0
for N in good_labels:
mask = mask np.where(labels==N,1,0)
mask = morphology.dilation(mask,np.ones([10,10])) # one last dilation
imgs_to_process[i] = mask
m1 = imgs_to_process
convex_mask = m1
dm1 = process_mask(m1)
dilatedMask = dm1
Mask = m1
extramask = dilatedMask ^ Mask
bone_thresh = 180
pad_value = 0
img_array[np.isnan(img_array)]=-2000
sliceim = img_array
sliceim = sliceim*dilatedMask pad_value*(1-dilatedMask).astype('uint8')
bones = sliceim*extramask>bone_thresh
sliceim[bones] = pad_value
x,y,z = sliceim.shape
if not os.path.exists(output):
os.makedirs(output)
img_to_save[sliceim.squeeze()==0] = 0
im = Image.fromarray(img_to_save)
im.save(output name '.png', 'PNG')
The problem is the segmented lung still contains white borderers like this:
Segmented lung (output):
Unsegmented lung (input):
The full code can be found in Google Colab Notebook. code.
And sample of the dataset is here.
CodePudding user response:
For this problem, I don't recommend using Kmeans color quantization since this technique is usually reserved for a situation where there are various colors and you want to segment them into dominant color blocks. Take a look at this previous answer involving segmenting similar looking color areas for a typical use case. Since your CT scan images are grayscale, Kmeans would not perform very well. Here's a potential solution using simple image processing with OpenCV:
Obtain binary image. Load input image, convert to grayscale
cv2.cvtColor(), Otsu's thresholdcv2.threshold()to obtain a binary image, and find contourscv2.findContours().Create a blank mask to extract desired objects. We can use
np.zeros()to create a empty mask with the same size as the input image.Filter contours using contour area and aspect ratio. We search for the lung objects by ensuring that contours are within a specified area threshold as well as aspect ratio. We use
cv2.contourArea(),cv2.arcLength(), andcv2.approxPolyDP()for contour perimeter and contour shape approximation. If we have have found our lung object, we utilizecv2.drawContoursto fill in our mask with white to represent the objects that we want to extract.Bitwise-and mask with original image. Finally we convert the mask to grayscale and bitwise-and with
cv2.bitwise_and()to obtain our result.
Here is our image processing pipeline visualized step-by-step:
Grayscale -> Otsu's threshold
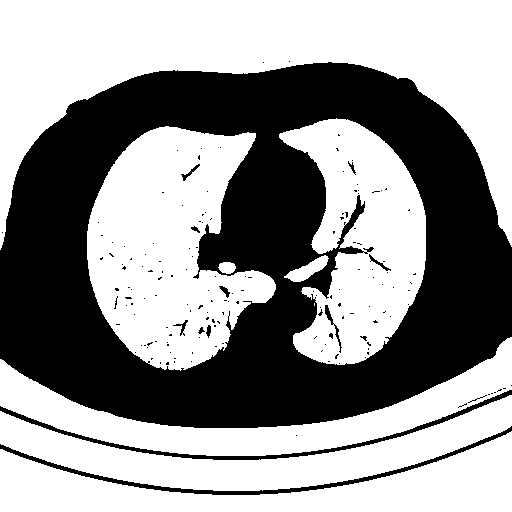
Detected objects to extract highlighted in green -> Filled mask
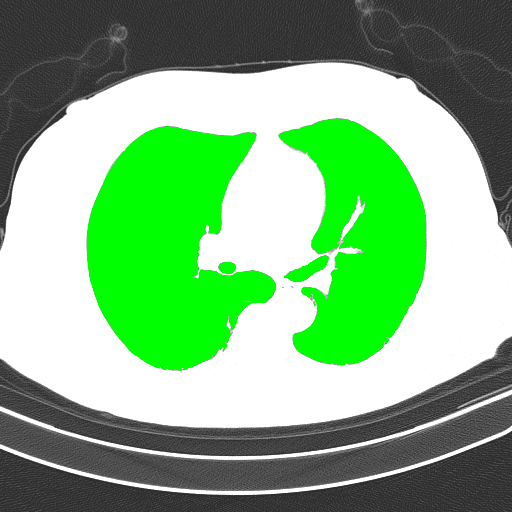

Bitwise-and to get our result -> Optional result with white background instead
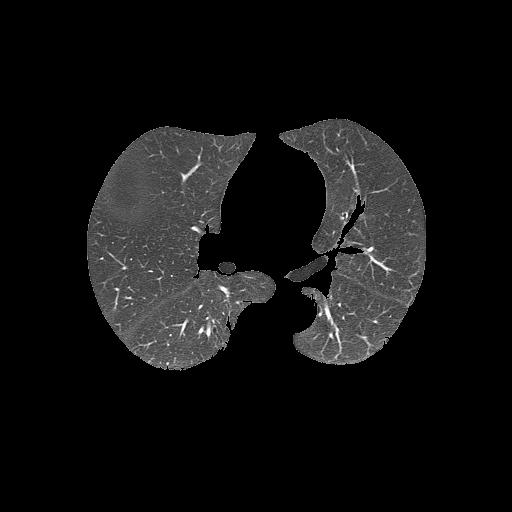
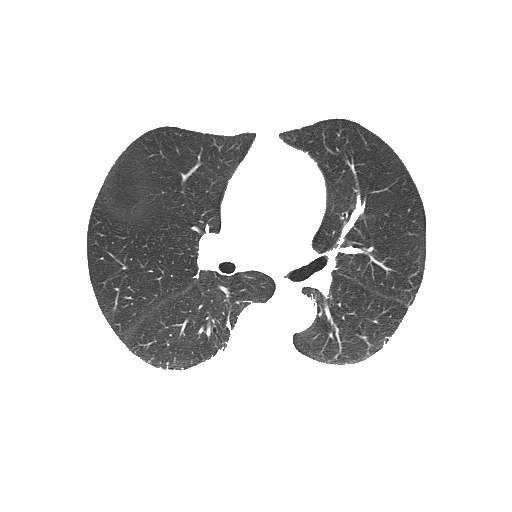
Code
import cv2
import numpy as np
image = cv2.imread('1.png')
highlight = image.copy()
original = image.copy()
# Convert image to grayscale, Otsu's threshold, and find contours
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
contours = cv2.findContours(thresh.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours = contours[0] if len(contours) == 2 else contours[1]
# Create black mask to extract desired objects
mask = np.zeros(image.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
# Search for objects by filtering using contour area and aspect ratio
for c in contours:
# Contour area
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
# Contour perimeter
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
# Contour approximation
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.035 * peri, True)
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(approx)
aspect_ratio = w / float(h)
# Draw filled contour onto mask if passes filter
# These are arbitary values, may need to change depending on input image
if aspect_ratio <= 1.2 or area < 5000:
cv2.drawContours(highlight, [c], 0, (0,255,0), -1)
cv2.drawContours(mask, [c], 0, (255,255,255), -1)
# Convert 3-channel mask to grayscale then bitwise-and with original image for result
mask = cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
result = cv2.bitwise_and(original, original, mask=mask)
# Uncomment if you want background to be white instead of black
# result[mask==0] = (255,255,255)
# Display
cv2.imshow('gray', gray)
cv2.imshow('thresh', thresh)
cv2.imshow('highlight', highlight)
cv2.imshow('mask', mask)
cv2.imshow('result', result)
# Save images
# cv2.imwrite('gray.png', gray)
# cv2.imwrite('thresh.png', thresh)
# cv2.imwrite('highlight.png', highlight)
# cv2.imwrite('mask.png', mask)
# cv2.imwrite('result.png', result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
CodePudding user response:
A simpler approach to solve this problem is using morphological erosion. Its just that than you will have to tune in threshold values