I was simply trying out this code which is saw in a tutorial
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 34;
int *ptra = &a;
printf("%d\n", ptra);
return 0;
}
Here when I run this code I get a number as an output. The number was 6422216.
What does this number stand for ?
(I was trying to learn pointer arithmetics)
CodePudding user response:
It is the address of your variable a
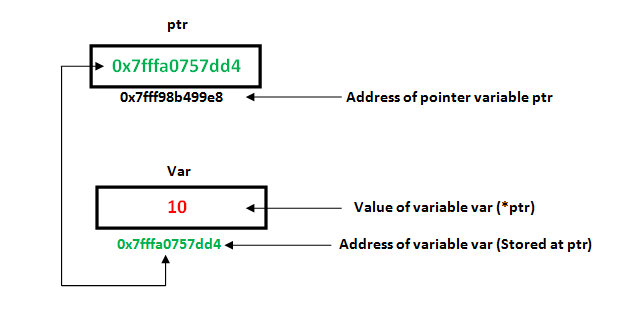
let's understand using the above diagram where int a=10 is referred using pointer ptr
int a=10;
int *ptr=&a;
printf("%d",(void *)ptr); //10 which is value of variable
printf("%p",ptr); //0x7fffa0757dd4 which is the address of variable Var
CodePudding user response:
Your program prints out the memory address of where the integer a is stored and I'll explain why but firstly you need to know what the symbols stand for.
* - is used to declare a pointer and when placed before a address it will give you what is stored at that address
& - will give you the address of the variable written after it
So, first you assign the integer a value of 34
int a = 34;
Then you create a pointer of a integer called ptra and assign it the memory address of where the integer a is stored
int *ptra = &a;
And finally you print the value of ptra which is the memory address of where the integer a is stored
printf("%d\n", ptra);
If you would wan to print out the value of a through the integer, then you should replace ptra with *ptra in the printf function.
CodePudding user response:
The behavior of the code sample is actually undefined because you pass a value of type int * where printf expects an int as the argument for conversion %d.
The code may be corrected as printf("%p\n", (void *)ptra); or possibly printf("%llu\n", (long long)ptra);
The value printed is the address of the variable a, which is system specific and may change from one run of the program to another, as is the case on OS/X that implements address space randomisation to increase the difficulty for hackers to exploit some program flaws.