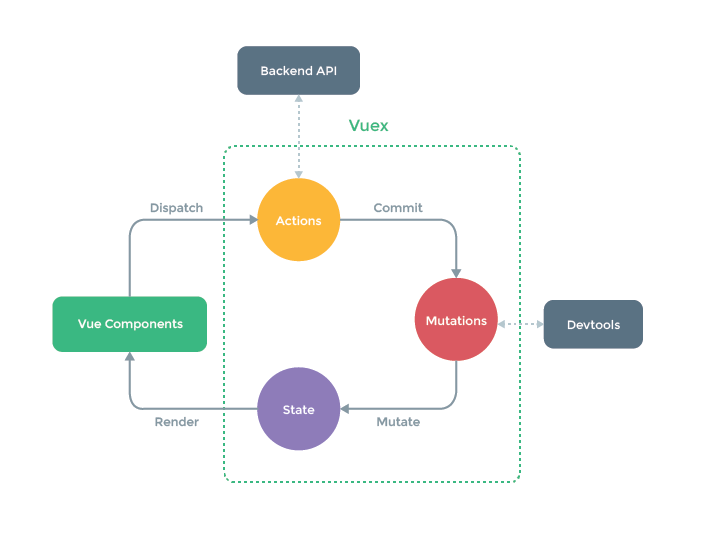
I am trying to set my state to the data I'm getting from my API with a GETTER in the store.
during the mounted() lifecyclehook trigger the GETTER getProducts() which looks like this:
export const getters = {
async getProducts() {
axios.get('/api/products')
.then(res => {
var data = res.data
commit('setProducts', data)
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}
}In the GETTER I try to trigger a MUTATION called setProducts() which looks like this:
export const mutations = {
setProducts(state, data) {
state.products = data
}
}But when I run this I get the error ReferenceError: commit is not defined in my console. So obviously what goes wrong is triggering the MUTATION but after looking for 2 days straight on the internet I still couldn't find anything.
I also tried replacing commit('setProducts', data) with:
this.setProducts(data)
setProducts(data)
Which all ended with the error "TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'setProducts')"
CodePudding user response:
If your function getProduct is defined in a Vue component, you have to access the store like this :
this.$store.commit('setProducts', data)
If your function is not defined in a Vue component but in an external javascript file, you must first import your store
import store from './fileWhereIsYourStore.js'
store.commit('setProducts', data)
If your getters export is literally the definition of your store's getters, you can use the solution of importing the store first, but you should know that it is clearly not a good practice to make commits in getters. There must be a better solution to your problem.
EDIT : To answer your comment, here's how you could do it:
// Your store module
export default {
state: {
products: []
},
mutations: {
SET_PRODUCTS(state, data) {
state.products = data
}
},
actions: {
async fetchProducts(store) {
await axios.get('/api/products')
.then(res => {
var data = res.data
store.commit('SET_PRODUCTS', data)
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}
}
}
Now, you can fetch products and populate your store in each of your components like this :
// A random Vue Component
<template>
</template>
<script>
export default {
async mounted() {
await this.$store.dispatch('fetchProducts')
// now you can access your products like this
console.log(this.$store.state.products)
}
}
</script>
I didn't tested this code but it should be ok.
CodePudding user response:
Only actions do have commit in their context as you can see here.
Getters don't have commit.
Otherwise, you could also use mapActions (aka import { mapActions } from 'vuex'), rather than this.$store.dispatch (just a matter of style, no real difference at the end).
Refactoring your code to have an action as Julien suggested is a good solution because this is how you should be using Vuex.
Getters are usually used to have some state having a specific structure, like sorted alphabetically or alike. For common state access, use the regular state or the mapState helper.