Could anyone help me to understand this code I created:
let cq = DispatchQueue(label: "downloadQueue", attributes: .concurrent)
cq.sync {
for i in 0..<10 {
sleep(2)
print(i)
}
}
print("all finished!")
And the output is serial order 1->10, with 2 sec waiting in between. In the end it will print out all finished
I understand that the the last part. However my question is:
Shouldn't concurrent queue start multiple tasks at the same time?
So my original thought was: the 1-10 printing should be done concurrently, not necessarily in the serial order.
Could anyone explain the purpose of sync call on concurrent queue and give me an example why and when we need it?
CodePudding user response:
If you want to demonstrate them running concurrently, you should dispatch the 10 tasks individually:
let cq = DispatchQueue(label: "downloadQueue", attributes: .concurrent)
for i in 0..<10 {
cq.async {
sleep(2)
print(i)
}
}
print("all finished queuing them!")
Note:
There are 10 dispatches to the concurrent queue, not one.
Each dispatched task runs concurrently with respect to other tasks dispatched to that queue (which is why we need multiple dispatches to illustrate the concurrency).
Also note that we dispatch asynchronously because we do not want to calling queue to wait for each dispatched task before dispatching the next.
You ask:
So my original thought was: the 1-10 printing should be done concurrently, not necessarily in the serial order.
Because they are inside a single dispatch, they will run as a single task, running in order. You need to put them in separate dispatches to see them run concurrently.
You go on to ask:
Could anyone explain the purpose of
synccall on concurrent queue and give me an example why and when we need it?
The sync has nothing to do with whether the destination queue is serial or concurrent. The sync only dictates the behavior of the calling thread, namely, should the caller wait for the dispatched task to finish or not. In this case, you really do not want to wait, so you should use async.
As a general rule, you should avoid calling sync unless (a) you absolutely have to; and (b) you are willing to have the calling thread blocked until the sync task runs. So, with very few exceptions, one should use async. And, perhaps needless to say, we never block the main thread for more than a few milliseconds.
While using sync on a concurrent dispatch queue is generally avoided, one example you might encounter is the “reader-writer” synchronization pattern. In this case, “reads” happen synchronously (because you need to wait the result), but “writes” happen asynchronously with a barrier (because you do not need to wait, but you do not want it to happen concurrently with respect to anything else on that queue). A detailed discussion of using GCD for synchronization (esp the reader-writer pattern), is probably beyond the scope of this question. But search the web or StackOverflow for “GCD reader-writer” and you will find discussions on the topic.)
Let us graphically illustrate my revamped rendition of your code, using 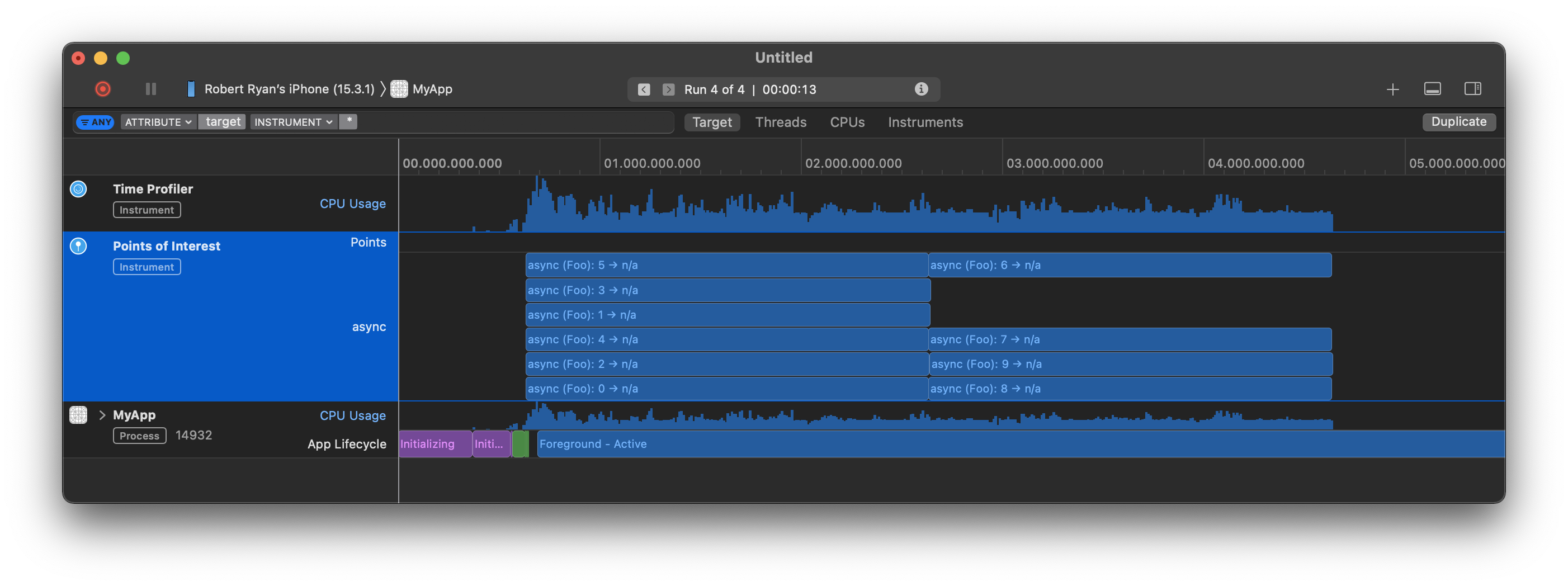
So let me draw your attention to two interesting aspects of the above:
The concurrent queue runs tasks concurrently, but because my iPhone’s CPU only has six cores, only six of them can actually run at the same time. The next four will have to wait until a core is available for that particular worker thread.
Note, this demonstration only works because I am not just calling
sleep, but rather I am spinning for the desired time interval, to more accurately simulate some slow, blocking task. Spinning is a better proxy for slow synchronous task thansleepis.This illustrates, as you noted, concurrent tasks may not appear in the precise order that they were submitted. This is because (a) they all were queued so quickly in succession; and (b) they run concurrently: There is a “race” as to which concurrently running thread gets to the logging statements (or “Points of Interest” intervals) first.
Bottom line, for those tasks running concurrently, because of races, they may not appear to run in order. That is how concurrent execution works.
CodePudding user response:
No, you have to add multiple operations to the DispatchQueue, it will then run the multiple queues in parallel.
