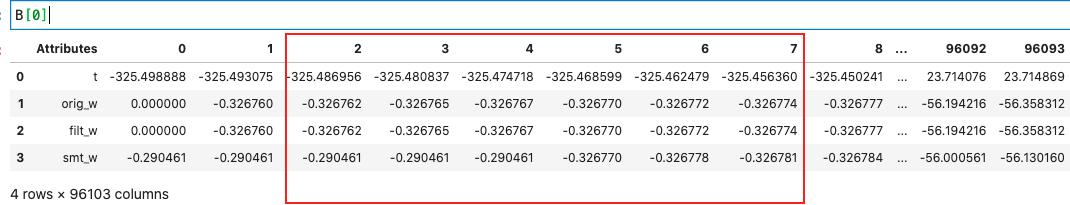
I have a big pandas DF (4 X 96103). Based on some conditions on values in first row, I want to extract a subset of the DF to a smaller DF_subset. For a single case this can be done many ways and wont harm computationally. But I will need to apply this operation of thousands of files (the same condition and the same operation). What is the most efficient way of this application. Below is a snippet of what I have done,
tt = []
x1=[]
x2=[]
x3=[]
for i in range(np.shape(DF)[1]):
if ((float(DF.iloc[0,i]) > -5.0) and (float(DF.iloc[0,i])) < 15.0):
tt.append(DF.iloc[0,i] )
x1.append(DF.iloc[1,i] )
x2.append(DF.iloc[2,i] )
x3.append(DF.iloc[3,i] )
X = (np.concatenate((tt,x1,x2,x3),axis=0))
X = pd.DataFrame(np.reshape(X,(4,-1)))
The original DF looks like the following and the red marked zone is an example of how I want the DF_subset to be
CodePudding user response:
You need to transpose the df then select by conditions. Use:
df = DF.T
df[(df[0].astype(float)) > -5.0)&(df.iloc[0].astype(float)) < 15.0)]
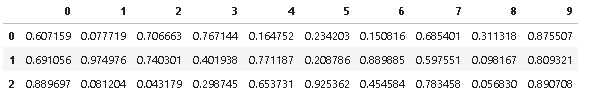
Example: input df:
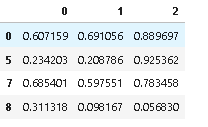
Ooutput df:
Example code:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(3,10))
df2 = df.T
df2[(df2[0]>.2)&(df2[0]<.7)]