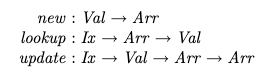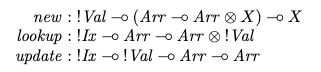I'm going through an example in A Taste of Linear Logic.
It first introduces the standard array with the usual operations defined (page 24):
Then suggests that a linear equivalent (using a linear logic for type signatures to restrict array copying) would have a slightly different type signature:
This is designed with the idea that array contains values that are cheap to copy but that the array itself is expensive to copy and thus should be passed along from use to use as a handle.
Question: The signatures for lookup and update correspond well to the standard signatures, but how do I interpret the signature for new?
In particular:
- The function new does not seem to return an array. How can I get an array to use if one is not provided?
- I think I do understand that
Arr –o Arr x Xis not derivable using linear logic and therefore a function to extract individual values without consuming the array is needed, but I don't understand why new doesn't provide that function directly
CodePudding user response:
In practical terms, this is about garbage collection.
Linear logic avoids making copies as well as leaving unused values lying around. So when you create an array with new, you also need to make sure it's eventually cleaned up again.
How can you make sure it is cleaned up? Well, in this example they do it by not giving back the array as the result, but instead “lending” it to the caller. The function Arr ⊸ Arr ⊗ X must give an array back in the end, in addition to the result you're actually interested in. It's assumed that this will be a modified form of the array you started out with. Only the X is passed back to the caller, the Arr is deallocated.