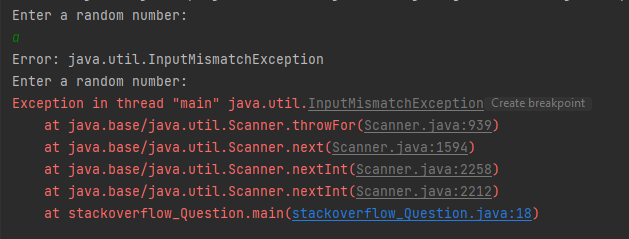
I just recently learned about the try/catch block and how once the expection is thrown the program will exit. In the photo below the code the Expection is caught once the user enters "a" instead of a random number.
Is there any way the user could reenter the value without the Expection being thrown again?
import java.util.Scanner
public class user_Num {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int random_Num = 0;
try {
System.out.println("Enter a random number:");
random_Num = input.nextInt();
if (random_Num > 0) {
System.out.println("The user entered a number that is positive.");
} else if (random_Num<0) {
System.out.println("The user entered a number that is negative");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: " e);
}
System.out.println("Enter a random number:");
random_Num = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("User Input Taken.");
}
}
Program Result:
CodePudding user response:
Yeah this is pretty easy you just have to revert back to whole code in the catch block. You could also have a thread.
import java.util.Scanner
public class user_Num{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int random_Num = 0;
Thread t1=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run()
{
System.out.println("Enter a random number:");
random_Num = input.nextInt();
if(random_Num > 0){
System.out.println("The user entered a number that is
positive.");
} else if (random_Num < 0){
System.out.println("The user entered a number that is
negative");
}
}
});
try {
t1.start();
t1.close();
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Error: " e);
System.out.println("Your input is not a number.");
t1.start();
}
}
}
}
CodePudding user response:
You have to add flag variable for findout exception is occured or not.
Here is two senario for exception occured or not:
- If exception is occured then
flagvariable is becomefalseand terminate while loop. - If exception is not occurred then
flagvariable is becometrueand you are again going to while loop.
Here dow is code:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void takeInput()
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a random number:");
int random_Num = input.nextInt();
if(random_Num > 0){
System.out.println("The user entered a number that is positive.");
} else if (random_Num < 0){
System.out.println("The user entered a number that is negative");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean flag = true;
while(flag)
{
try {
takeInput();
flag = false;
} catch (Exception e){
flag = true;
}
}
}
}