I need a function that takes as parameters an offset and a size of bits to read an int value from a byte array.
int GetInt(byte[] data, int bitOffset, int bitSize)
For example, I have the following array of bytes:
66 DC 00 00 6A DC 00 00
66 DC 00 00 58 DC 00 00
54 DC 00 00 50 DC 00 00
4C DC 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 08
F0 FF FF 9F F4 7F 20 9A
91 EB 85 88 3F 6E 00 80
3D 6E 00 80 3B 6E 00 00
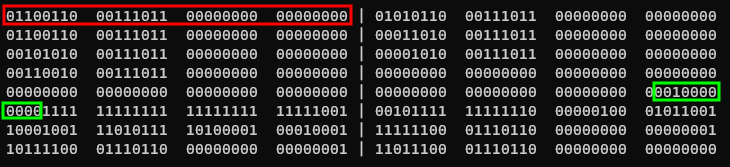
Same in bits:
01100110 00111011 00000000 00000000 01010110 00111011 00000000 00000000
01100110 00111011 00000000 00000000 00011010 00111011 00000000 00000000
00101010 00111011 00000000 00000000 00001010 00111011 00000000 00000000
00110010 00111011 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00010000
00001111 11111111 11111111 11111001 00101111 11111110 00000100 01011001
10001001 11010111 10100001 00010001 11111100 01110110 00000000 00000001
10111100 01110110 00000000 00000001 11011100 01110110 00000000 00000000
How do I most efficiently ensure that the following function has these return values?:
var a = GetInt(data, 0, 32); // a = 56422
var b = GetInt(data, 313, 11); // b = 4
EDIT: Here the bytes as an C# Array:
new byte[] { 0x66, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x6A, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x66, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x58, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x54, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x50, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x4C, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x08, 0xF0, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0x9F, 0xF4, 0x7F, 0x20, 0x9A, 0x91, 0xEB, 0x85, 0x88, 0x3F, 0x6E, 0x00, 0x80, 0x3D, 0x6E, 0x00, 0x80, 0x3B, 0x6E, 0x00, 0x00 }
EDIT 2: I have already implemented my own solution as well, with which i could take all the values for this post here. Im just very unhappy with my solution because i dont want to pass the array into a BitArray every time. To read a file, this function is called several hundred thousand times.
public static int GetdInt(this byte[] data, int bitOffset, int bitSize)
{
var bits = new BitArray(data);
var output = 0;
for(var bitIndex = 0; bitIndex < bitSize; bitIndex )
{
var bit = bits.Get(bitOffset bitIndex) ? 1 : 0;
output |= bit << bitIndex;
}
return output;
}
CodePudding user response:
C# 90 bytes
int GetInt(byte[] d,int o,int b)=>Enumerable.Range(o,b).Sum(i=>(d[i/8]>>i%8)%2>0?1<<i-o:0)
I've written this in code golfed form to poke fun at the fact that your question reads like code golf, and that you haven't shown any attempt of your own ;)
Here is a unit test for any future answerers. (OP this might be helpful to you, too):
[TestMethod]
public void Test()
{
var bytes = new byte[]
{
0x66, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x6A, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00,
0x66, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x58, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00,
0x54, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x50, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00,
0x4C, 0xDC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x08,
0xF0, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0x9F, 0xF4, 0x7F, 0x20, 0x9A,
0x91, 0xEB, 0x85, 0x88, 0x3F, 0x6E, 0x00, 0x80,
0x3D, 0x6E, 0x00, 0x80, 0x3B, 0x6E, 0x00, 0x00
};
RunTest(0, 32, 56422);
RunTest(313, 11, 4);
void RunTest(int offset, int bitSize, int expected)
{
var actual = GetInt(bytes, offset, bitSize);
Assert.AreEqual(actual, expected);
}
}
CodePudding user response:
Here is one possible strategy, reading the bytes one-by-one until enough bits have been read, and then discarding any excess. Passed the two test cases, but that's not sufficient testing IMO, do some more.
static int GetInt(byte[] data, int bitOffset, int bitSize)
{
// first chunk is special, lower bits are discarded immediately
// to prevent trying to put more than 32 bits in `result`
// when `bitSize == 32` and `bitOffset != 0`
int byteOffset = bitOffset >> 3;
int result = data[byteOffset] >> (bitOffset & 7);
int resultOffset = 8 - (bitOffset & 7);
// the "rest", whole bytes are read from data and put into their place in the result
while (resultOffset < bitSize)
{
byteOffset ;
result |= data[byteOffset] << resultOffset;
resultOffset = 8;
}
// in general too many bits have been read at this point, discard excess
return result & (int)(uint.MaxValue >> -bitSize);
}
There are other possible strategies. For example, reading a whole int or long with the BitConverter class (or other tricks) and then doing some shifting and masking to extract the target range of bits from that. That has the potential to be more efficient, but has some unfortunate details to take care of when the target range doesn't cross the end of the array but the byte-aligned integer that contains them would.
The way the excess bits are discarded at the end doesn't work properly when bitSize = 0, which I did not think is interesting to support, but could be done easily by handling that as a special case. Unlike (1 << bitSize) - 1, the way I used does work for 32 bits.