I have many text files in a very specific format that need to be read into a csv. I can not seem to figure out how to get all the data in the format that I want in my csv. I can get the file name and the header for the sheet, but none of the data is active in the sheet. The text file is as follows:
ID 0x20f7
City Metropolitian
Time_taken (min) 42.000000
My texts files like this:
0.txt,
1.txt,
3.txt,
5.txt,
6.txt,
9.txt,
10.txt
I tried like this:
csvout = pd.DataFrame()
file_list = glob.glob(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "dataset/train/", "*.txt"))
for filename in file_list:
data = pd.read_csv(filename, sep=' ', index_col=0, header=None).T
csvout = csvout.append(data)
csvout.to_csv("train.csv")
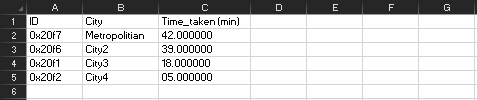
I need a output like this:
ID City Time_taken (min)
0x20f7 Metropolitian 42.00000
0
CodePudding user response:
CodePudding user response:
So the input text files contain a list of key values, like a dictionary? And each file should result in one record in the output dataframe, right? You could do something like this:
import pandas as pd
import os
import glob
# create empty dataframe
csvout = pd.DataFrame(columns = ["ID", "City", "Time_taken (min)"])
# get list of files
file_list = glob.glob(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "dataset/train/", "*.txt"))
for filename in file_list:
# next file/record
mydict = {}
with open(filename) as datafile:
# read each line and split on " " space
for line in datafile:
# Note: partition result in 3 string parts, "key", " ", "value"
# array slice third parameter [::2] means steps= 2
# so only take 1st and 3rd item
name, var = line.partition(" ")[::2]
mydict[name.strip()] = var.strip()
# put dictionary in dataframe
csvout = csvout.append(mydict, ignore_index=True)
# write to csv
csvout.to_csv("train.csv", sep=";", index=False)