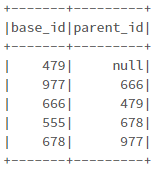
My input table looks like below
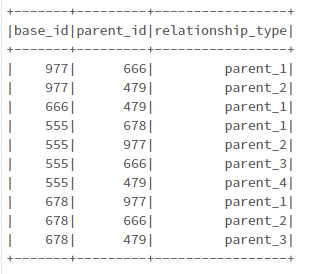
From this table, I have to take each base_id and find out the parent hierarchy. My output table should be like below
Here, for each base_id, the parent (parent_1), grand parent (parent_2)...(parent_n) Has to be calculated. Note that different base_id can have different hierarchy depth and the maximum level of depth is unknown.
I've written a script for this that I'm attaching below. It's working but the problem with my code is - I'm running a for loop for each base_id to find out its hierarchy. This is not very optimized since the no of base_ids can be 1 million plus. And God knows how much time it will take to run against Million ids.
from pyspark.sql.types import StructType, StructField, StringType, IntegerType
import pyspark.sql.functions as F
from functools import reduce
from pyspark.sql import DataFrame
data2 = [('479', None),
('977', '666'),
('666', '479'),
('555', '678'),
('678', '977'),
]
schema = StructType([
StructField("base_id", StringType(), True),
StructField("parent_id", StringType(), True)
])
base_df = spark.createDataFrame(data=data2, schema=schema)
base_df.show()
def id_parent_relation():
itself_df = (
base_df
.filter(F.col("parent_id").isNull())
.selectExpr(
"base_id",
"base_id as parent_id",
"'itself' as retion_type"
)
)
related_df = base_df.filter(F.col("parent_id").isNotNull())
df_list = []
id_list = related_df.select("base_id").rdd.flatMap(lambda x: x).collect()
# print(id_list)
for base_id in id_list:
checker = True
iteration = 1
new_df = related_df.filter(F.col("base_id") == base_id)
while checker:
if iteration == 1:
new_df = new_df.withColumn("relationship_type", F.lit("parent_1"))
else:
new_df = (
new_df
.withColumnRenamed("base_id", "base_id_new")
.withColumnRenamed("parent_id", "parent_id_new")
)
new_df = (
new_df
.join(
related_df,
on=(related_df["base_id"] == new_df["parent_id_new"]),
how="left"
)
.select(
F.lit(base_id).alias("base_id"),
F.col("parent_id").alias("parent_id"),
)
.withColumn("relationship_type", F.lit("parent_{}".format(iteration)))
)
if new_df.filter(F.col("parent_id").isNotNull()).rdd.isEmpty():
checker = False
else:
iteration = 1
df_list.append(new_df)
union_df = reduce(DataFrame.unionAll, df_list)
union_df.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
id_parent_relation()
I was hoping to somehow avoid the loops so that the script can be run for million records.
Please help me in this and thanks in advance!!!
CodePudding user response:
I am no PySpark expert, so please feel free to criticize my
suggestion.
The join part should be fine, but not sure how the stacking step will perform with high number of ids.
# Data from original post
df0 = base_df.alias("df0")
# Keep tracks of joins number
i = 1
# Performs join as many times as necessary
while (df0.filter(~F.isnull(F.col("df" str(i - 1) ".parent_id"))).count() > 0):
# Create new alias
df = base_df.alias("df" str(i))
# Join
df0 = df0.join(df, F.col("df" str(i - 1) ".parent_id") == F.col("df" str(i) ".base_id"), "left")
i = 1
# Delete singletons (479 in exemple)
df0 = df0.where(~F.isnull(F.col("df0.parent_id")))
# Create stack expression
stack_expr = ""
for col in range(1, i):
stack_expr = f" df0.base_id, df{col}.base_id, 'parent_{col}',"
# Remove last ,
stack_expr = stack_expr[:-1]
# Stack to display columns as rows
df0.selectExpr("stack(" str(i) ", " stack_expr ") as (base_id, parent_id, relation_type)") \
.where("parent_id is not null") \
.show()
CodePudding user response:
To my knowledge you cannot resolve a graph (transitive closure) with a single query. You need to run join multiple times (number of loop cycles is log(max_depth)).
Here is a trivial example in spark examples showing how to resolve a graph iteratively with exit condition checking whether any new connection have been found.