u <- rnorm(10000)
v <- rnorm(10000)
# `outer`
system.time(mat1 <- outer(u, v , `<`))
user system elapsed
1.80 1.34 3.32
# `for` loop
system.time({
mat2 <- matrix(NA, nrow = length(u), ncol = length(v))
for(i in seq_along(v)) {
mat2[, i] <- u < v[i]
}
})
user system elapsed
0.97 0.02 1.01
identical(mat1, mat2)
# [1] TRUE
CodePudding user response:
If you use bench::press() with the four options set out you can get a sense of the trade-off between memory and speed described by David Arenburg in the comments. I like 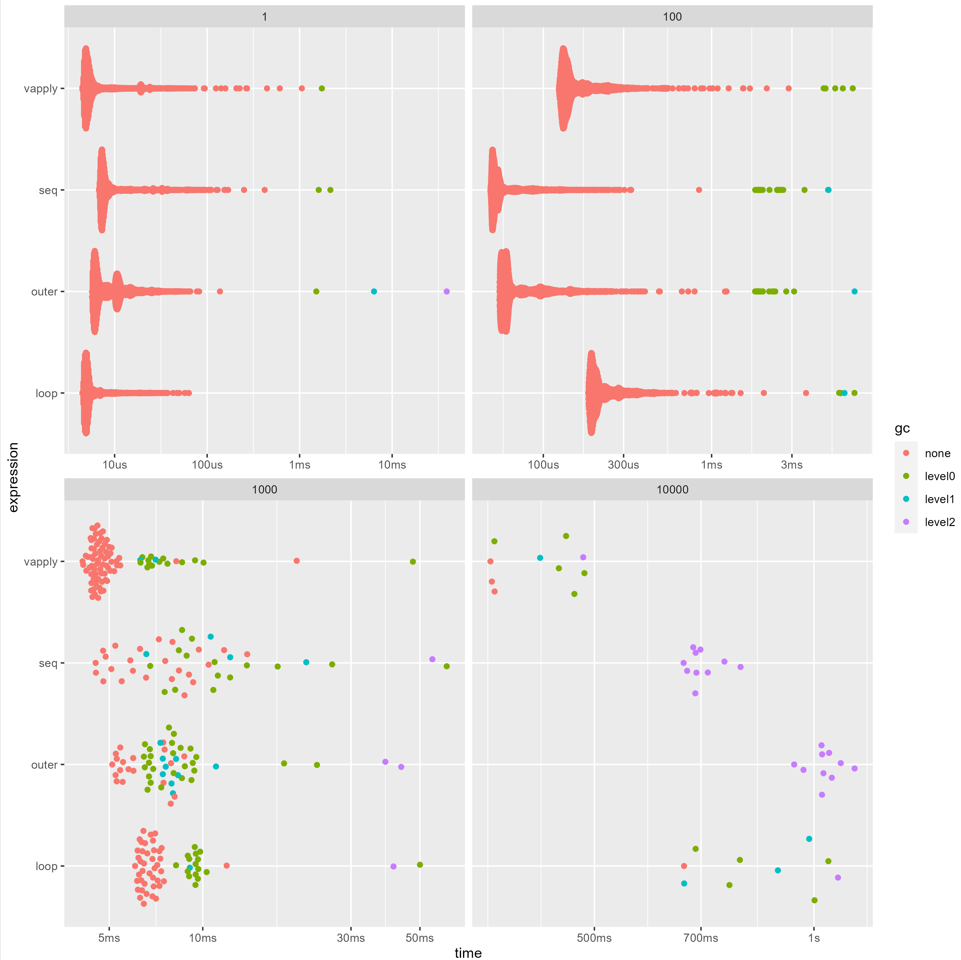
With 100 rows, vapply is slower than the other methods, and there's no difference in gc() calls (garbage collection).
However, once the data is larger than that, we can see that vapply() does a lot less garbage collection and is a lot faster.
Similarly, in the final facet (1e4 rows and columns), we can see that the for loop has less garbage collection and tends to be faster than outer().
Code to generate this:
sizes <- c(1, 1e2, 1e3, 1e4)
results <- bench::press(
size = sizes,
{
set.seed(1)
u <- rnorm(size)
v <- rnorm(size)
bench::mark(
min_iterations = 10,
check = FALSE,
outer = {
mat <- outer(u, v, `<`)
},
loop = {
mat <- matrix(NA, nrow = length(u), ncol = length(v))
for (i in seq_along(v)) {
mat[, i] <- u < v[i]
}
mat
},
vapply = {
mat <- vapply(seq_along(v), \(i) u < v[i], logical(length(u)))
},
seq = {
mat <- as.matrix(
`<`(
rep(u, times = ceiling(length(v) / length(u))),
rep(v, rep.int(length(u), length(v)))
),
nrow = length(u)
)
}
)
}
)
ggplot2::autoplot(results)
ggplot2::facet_wrap(ggplot2::vars(size),scales="free_x")
Disclaimer: These are the results on one machine (an unremarkable fairly old laptop). I didn't get the same magnitude of discrepancy between outer() and the for loop as you did so your results may differ.
CodePudding user response:
Not an answer just a benchmark with 100 repetitions, with two additional codes provided in the comments
library(microbenchmark)
microbenchmark(
"outer"={
mat1 <- outer(u, v , `<`)
},
"loop"={
mat2 <- matrix(NA, nrow = length(u), ncol = length(v))
for(i in seq_along(v)) {
mat2[, i] <- u < v[i]
}
},
"rep"={
mat3 <- matrix(
`<`(rep(u, times = ceiling(length(v)/length(u))), rep(v, rep.int(length(u), length(v)))),
nrow = length(u), ncol = length(v)
)
},
"vapply"={
mat4 <- vapply(seq_along(v), function(i) u < v[i], logical(length(u)))
},
times=100
)
Unit: milliseconds
expr min lq mean median uq max neval cld
outer 699.9203 876.1811 1071.5173 1010.6888 1191.9587 2913.109 100 c
loop 528.7204 620.2197 714.3295 668.7907 763.5013 1164.178 100 b
rep 627.0500 730.9696 964.0966 838.9883 984.2554 9111.802 100 c
vapply 338.7537 395.2330 478.9374 441.3241 517.2067 1011.938 100 a
