Some time ago I asked how to draw UI block in 
but I don't understand where is my left ui block with 4 different labels and how to make stackview ui proportionally filled. I mean that I don't need to huge left view, I need it about 10% of the main stackview. I tried to make it in such way:
leftStack.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.heightAnchor, multiplier: 0.1).isActive = true
but it does not help me. I will need like 10% of the left block and 90% of main block with the image. I thought it is possible to set proportions for the views inside the stackview
CodePudding user response:
The problem you are running into is related to how transforms and auto-layout interact - or, perhaps better said, don't interact.
There are various ways to get around this... thinking about your end-goal, let's create a UIView subclass with a label that will auto-adjust itself when transformed based on the label's frame.
So, custom class:
class MyCustomLabelView: UIView {
// public properties to replicate UILabel
// add any additional if needed
public var text: String = "" {
didSet { theLabel.text = text }
}
public var textColor: UIColor = .black {
didSet { theLabel.textColor = textColor }
}
public var font: UIFont = .systemFont(ofSize: 17.0) {
didSet { theLabel.font = font }
}
public var textAlignment: NSTextAlignment = .left {
didSet { theLabel.textAlignment = textAlignment }
}
override var backgroundColor: UIColor? {
didSet {
theLabel.backgroundColor = backgroundColor
super.backgroundColor = .clear
}
}
private let theLabel = UILabel()
public func rotateTo(_ d: Double) {
if let v = subviews.first {
// set the rotation transform
if d == 0 {
self.transform = .identity
} else {
self.transform = CGAffineTransform(rotationAngle: d)
}
// remove the label
v.removeFromSuperview()
// tell it to layout itself
v.setNeedsLayout()
v.layoutIfNeeded()
// get the frame of the label
// apply the same transform
let r = v.frame.applying(self.transform)
wC.isActive = false
hC.isActive = false
// add the label back
addSubview(v)
// set self's width and height anchors
// to the width and height of the label
wC = self.widthAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: r.width)
hC = self.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: r.height)
// apply the new constraints
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
v.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.centerXAnchor),
v.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.centerYAnchor),
wC, hC
])
}
}
private var wC: NSLayoutConstraint!
private var hC: NSLayoutConstraint!
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
commonInit()
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: coder)
commonInit()
}
private func commonInit() {
backgroundColor = .clear
theLabel.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
addSubview(theLabel)
wC = self.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: theLabel.widthAnchor)
hC = self.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: theLabel.heightAnchor)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
theLabel.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: centerXAnchor),
theLabel.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: centerYAnchor),
wC, hC,
])
}
}
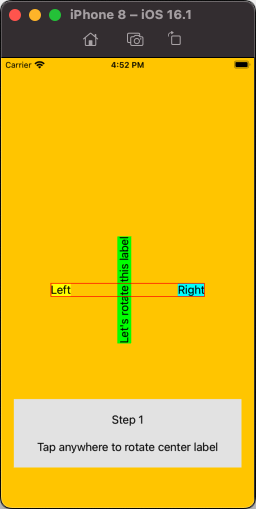
and the same controller as Step1 but we'll use three MyCustomLabelView instead of three UILabel:
class Step2VC: UIViewController {
let leftLabel = MyCustomLabelView()
let centerLabel = MyCustomLabelView()
let rightLabel = MyCustomLabelView()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.backgroundColor = .systemYellow
let mainStackView = UIStackView()
mainStackView.axis = .horizontal
mainStackView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(mainStackView)
let g = view.safeAreaLayoutGuide
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
mainStackView.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.centerXAnchor),
mainStackView.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.centerYAnchor),
])
// add three labels to the stack view
leftLabel.textAlignment = .center
leftLabel.text = "Left"
leftLabel.backgroundColor = .yellow
centerLabel.textAlignment = .center
centerLabel.text = "Let's rotate this label"
centerLabel.backgroundColor = .green
rightLabel.textAlignment = .center
rightLabel.text = "Right"
rightLabel.backgroundColor = .cyan
mainStackView.addArrangedSubview(leftLabel)
mainStackView.addArrangedSubview(centerLabel)
mainStackView.addArrangedSubview(rightLabel)
// outline the stack view so we can see its frame
mainStackView.layer.borderColor = UIColor.red.cgColor
mainStackView.layer.borderWidth = 1
// info label
let iLabel = UILabel()
iLabel.backgroundColor = UIColor(white: 0.9, alpha: 1.0)
iLabel.numberOfLines = 0
iLabel.textAlignment = .center
iLabel.text = "\nStep 2\n\nTap anywhere to rotate center label\n"
iLabel.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(iLabel)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
iLabel.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.bottomAnchor, constant: -60.0),
iLabel.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.centerXAnchor),
iLabel.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.widthAnchor, multiplier: 0.9),
])
}
override func touchesBegan(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
if centerLabel.transform == .identity {
centerLabel.rotateTo(-.pi * 0.5)
} else {
centerLabel.rotateTo(0)
}
}
}
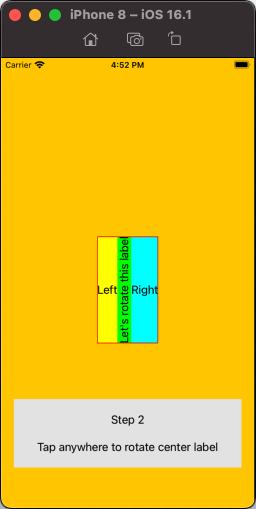
Now when we rotate the center label (view), we get this:
So, to get the full layout you're looking for, we'll create a custom view that contains the "left-side" labels (in a couple stack views), and an image view, a stack view for the bottom labels, and an "outer" stack view to hold everything together.
Custom "left-side" class:
class MyCustomView: UIView {
public var titleText: String = "" {
didSet { titleLabel.text = titleText }
}
public func addLabel(_ v: UIView) {
labelsStack.addArrangedSubview(v)
}
public func rotateTo(_ d: Double) {
// get the container view (in this case, it's the outer stack view)
if let v = subviews.first {
// set the rotation transform
if d == 0 {
self.transform = .identity
} else {
self.transform = CGAffineTransform(rotationAngle: d)
}
// remove the container view
v.removeFromSuperview()
// tell it to layout itself
v.setNeedsLayout()
v.layoutIfNeeded()
// get the frame of the container view
// apply the same transform as self
let r = v.frame.applying(self.transform)
wC.isActive = false
hC.isActive = false
// add it back
addSubview(v)
// set self's width and height anchors
// to the width and height of the container
wC = self.widthAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: r.width)
hC = self.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: r.height)
// apply the new constraints
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
v.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.centerXAnchor),
v.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.centerYAnchor),
wC, hC
])
}
}
// our subviews
private let outerStack = UIStackView()
private let titleLabel = UILabel()
private let labelsStack = UIStackView()
private var wC: NSLayoutConstraint!
private var hC: NSLayoutConstraint!
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
commonInit()
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: coder)
commonInit()
}
private func commonInit() {
// stack views and label properties
outerStack.axis = .vertical
outerStack.distribution = .fillEqually
labelsStack.axis = .horizontal
labelsStack.distribution = .fillEqually
titleLabel.textAlignment = .center
titleLabel.backgroundColor = .lightGray
titleLabel.textColor = .white
// add title label and labels stack to outer stack
outerStack.addArrangedSubview(titleLabel)
outerStack.addArrangedSubview(labelsStack)
outerStack.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
addSubview(outerStack)
wC = self.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: outerStack.widthAnchor)
hC = self.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: outerStack.heightAnchor)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
outerStack.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.centerXAnchor),
outerStack.centerYAnchor.constraint(equalTo: self.centerYAnchor),
wC, hC,
])
}
}
and an example controller:
class Step3VC: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.backgroundColor = .systemYellow
guard let img = UIImage(named: "testPic") else {
fatalError("Need an image!")
}
// create the image view
let imgView = UIImageView()
imgView.contentMode = .scaleToFill
imgView.backgroundColor = .systemBlue
imgView.image = img
// create the "main" stack view
let mainStackView = UIStackView()
mainStackView.axis = .horizontal
// create the "right-side" stack view
let rightSideStack = UIStackView()
rightSideStack.axis = .vertical
// create the "bottom labels" stack view
let bottomLabelsStack = UIStackView()
bottomLabelsStack.distribution = .fillEqually
// add the image view and bottom labels stack view
// to the right-side stack view
rightSideStack.addArrangedSubview(imgView)
rightSideStack.addArrangedSubview(bottomLabelsStack)
// create the custom "left-side" view
let myView = MyCustomView()
// add views to the main stack view
mainStackView.addArrangedSubview(myView)
mainStackView.addArrangedSubview(rightSideStack)
// add main stack view to view
mainStackView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(mainStackView)
let g = view.safeAreaLayoutGuide
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
// constrain Top/Leading/Trailing
mainStackView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.topAnchor, constant: 20.0),
mainStackView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.leadingAnchor, constant: 20.0),
mainStackView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.trailingAnchor, constant: -20.0),
// main stack view height will be determined by its subviews
])
// setup the left-side custom view
myView.titleText = "Gefährdung"
let titles: [String] = [
"keine / gering", "mittlere", "erhöhte", "hohe",
]
let colors: [UIColor] = [
UIColor(red: 0.863, green: 0.894, blue: 0.527, alpha: 1.0),
UIColor(red: 0.942, green: 0.956, blue: 0.767, alpha: 1.0),
UIColor(red: 0.728, green: 0.828, blue: 0.838, alpha: 1.0),
UIColor(red: 0.499, green: 0.706, blue: 0.739, alpha: 1.0),
]
for (c, t) in zip(colors, titles) {
myView.addLabel(colorLabel(withColor: c, title: t, titleColor: .black))
}
// rotate the left-side custom view 90-degrees counter-clockwise
myView.rotateTo(-.pi * 0.5)
// setup the bottom labels
let colorDictionary = [
"Red":UIColor.systemRed,
"Green":UIColor.systemGreen,
"Blue":UIColor.systemBlue,
]
for (myKey,myValue) in colorDictionary {
bottomLabelsStack.addArrangedSubview(colorLabel(withColor: myValue, title: myKey, titleColor: .white))
}
// info label
let iLabel = UILabel()
iLabel.backgroundColor = UIColor(white: 0.9, alpha: 1.0)
iLabel.numberOfLines = 0
iLabel.textAlignment = .center
iLabel.text = "\nStep 3\n"
iLabel.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(iLabel)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
iLabel.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.bottomAnchor, constant: -60.0),
iLabel.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.centerXAnchor),
iLabel.widthAnchor.constraint(equalTo: g.widthAnchor, multiplier: 0.9),
])
}
func colorLabel(withColor color:UIColor, title:String, titleColor:UIColor) -> UILabel {
let newLabel = UILabel()
newLabel.backgroundColor = color
newLabel.text = title
newLabel.textAlignment = .center
newLabel.textColor = titleColor
return newLabel
}
}
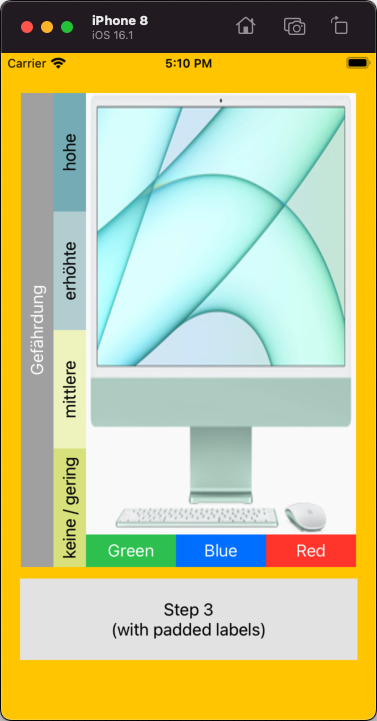
The result:
To improve the visual a bit, I wanted a little "padding" on the labels... so, I used this simple label subclass:
class PaddedLabel: UILabel {
var padding: UIEdgeInsets = .zero
override func drawText(in rect: CGRect) {
super.drawText(in: rect.inset(by: padding))
}
override var intrinsicContentSize : CGSize {
let sz = super.intrinsicContentSize
return CGSize(width: sz.width padding.left padding.right, height: sz.height padding.top padding.bottom)
}
}
Replaced the colorLabel(...) func with this:
func colorLabel(withColor color:UIColor, title:String, titleColor:UIColor) -> UILabel {
let newLabel = PaddedLabel()
newLabel.padding = UIEdgeInsets(top: 6, left: 8, bottom: 6, right: 8)
newLabel.backgroundColor = color
newLabel.text = title
newLabel.textAlignment = .center
newLabel.textColor = titleColor
return newLabel
}
and get this final result:
CodePudding user response:
First, create the two child stack views and configure them as desired. For example:
let stackView1 = UIStackView()
stackView1.axis = .vertical
stackView1.alignment = .fill
stackView1.distribution = .fillEqually
let stackView2 = UIStackView()
stackView2.axis = .vertical
stackView2.alignment = .fill
stackView2.distribution = .fillEqually
Next, create the horizontal stack view and add the two child stack views as arranged subviews:
let horizontalStackView = UIStackView()
horizontalStackView.axis = .horizontal
horizontalStackView.alignment = .fill
horizontalStackView.distribution = .fillEqually
horizontalStackView.addArrangedSubview(stackView1)
horizontalStackView.addArrangedSubview(stackView2)
Finally, add the horizontal stack view to your view hierarchy and configure its constraints as desired. For example:
view.addSubview(horizontalStackView)
horizontalStackView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
horizontalStackView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor).isActive = true
horizontalStackView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor).isActive = true
horizontalStackView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.topAnchor).isActive = true
horizontalStackView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.bottomAnchor).isActive = true
This will create a horizontal stack view with two child stack views that are arranged side-by-side, filling the entire width of the parent view. You can then add views to the child stack views as needed to create your layout.