I have a dataframe as below:
import pandas as pd
# sample data
# sample data
data = {'RowName': ['A1', 'A2', 'A3'], '20/09/21 (LP%)': [120, 0, 0], '20/09/21 (Vol)': [13, 1, 31], '20/09/21 (OI)': [0, 0, 0], '21/09/21 (LP%)': [135.0, 143.43, 143.43], '21/09/21 (Vol)': [68.6, 63.81, 58.1], '21/09/21 (OI)': [0, 0, 0], '22/09/21 (LP%)': [130, 0, 0], '22/09/21 (Vol)': [0, 0, 0], '22/09/21 (OI)': [75, 80, 85]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# display(df)
RowName 20/09/21 (LP%) 20/09/21 (Vol) 20/09/21 (OI) 21/09/21 (LP%) 21/09/21 (Vol) 21/09/21 (OI) 22/09/21 (LP%) 22/09/21 (Vol) 22/09/21 (OI)
0 A1 120 13 0 135.00 68.60 0 130 0 75
1 A2 0 1 0 143.43 63.81 0 0 0 80
2 A3 0 31 0 143.43 58.10 0 0 0 85
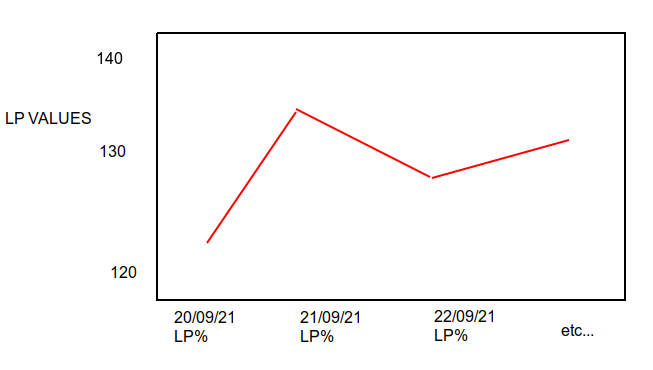
Using matplotlib and the following dataframe in pandas, is there a way to plot:
x axis : columns that have
(LP%)in them - take the date and use each of these columns as a point on the x-axisI have selected columns using this:
df2 = df.filter(regex='LP%')y axis : the actual value for row A1 only
Something like this:
CodePudding user response:
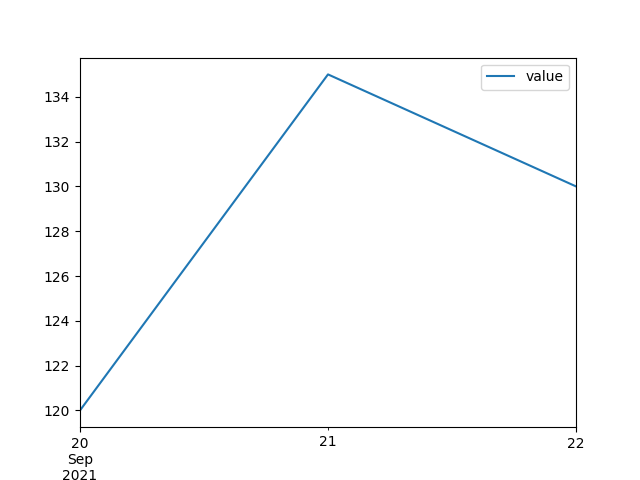
You need to reshape your dataframe firstly. Starting from a dataframe like this:
RowName 20/09/21 (LP%) 20/09/21 (Vol) 20/09/21 (OI) 21/09/21 (LP%) 21/09/21 (Vol) 21/09/21 (OI) 22/09/21 (LP%) 22/09/21 (Vol) 22/09/21 (OI)
0 A1 120 13 0 135.00 68.60 0 130 0 75
1 A2 0 1 0 143.43 63.81 0 0 0 80
2 A3 0 31 0 143.43 58.10 0 0 0 85
You can re-shape with:
# row filter
df = df.iloc[:1, :]
# column filter and transpose
df = df[[col for col in df.columns if '(LP%)' in col]].T
# convert column name to datetime value
df.index = pd.to_datetime(df.index.map(lambda x: x.split(' ')[0]))
# pass a sting as label
df.columns = ['value']
Then you can simply plot with:
df.plot()
plt.show()
Complete Code
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = pd.read_csv(r'data/data.csv')
df = df.iloc[:1, :]
df = df[[col for col in df.columns if '(LP%)' in col]].T
df.index = pd.to_datetime(df.index.map(lambda x: x.split(' ')[0]))
df.columns = ['value']
df.plot()
plt.show()
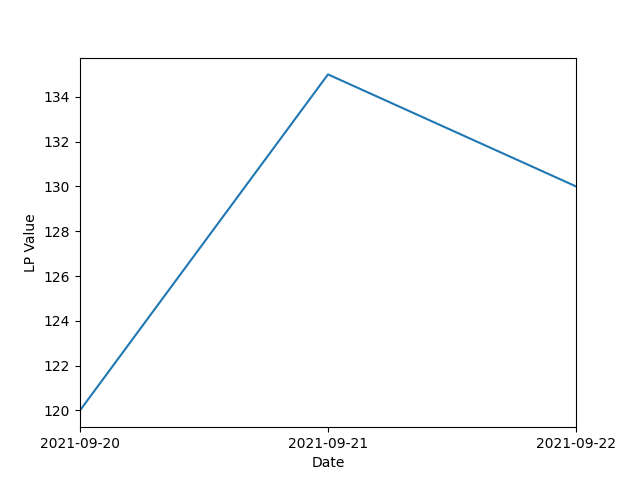
You can further customize datetime axis with:
import matplotlib.dates as md
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(df.index, df['value'])
ax.set_xlabel('Date')
ax.set_ylabel('LP Value')
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(md.DayLocator(interval = 1))
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(md.DateFormatter('%Y-%m-%d'))
plt.setp(ax.xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation = 0)
ax.set_xlim([df.index[0], df.index[-1]])
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
Looking at your dataframe (assume it is named df), I think the quickest way to do this is to transpose it, seeing as you want to use rows as columns:
df_trans = df.transpose() #or df.T
df_trans.plot.line(x='RowName', y='A1', color='red')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.show()
Maybe you want to rename the 'Rowname' column:
df_trans.rename({0: 'LP'}, axis=1)
df_trans.plot.line(x='LP', y='A1', color='red')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
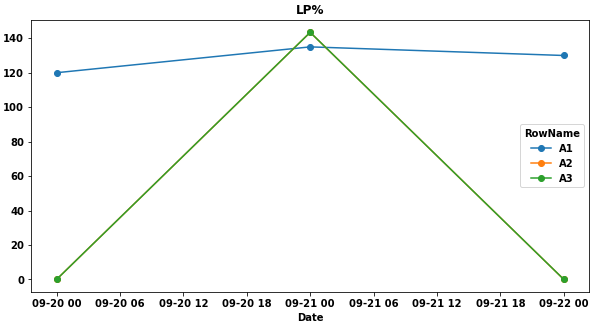
- The issue with the current implementation is you only get a result for
'A1'and then presumably you have repeat the code to get the other data. 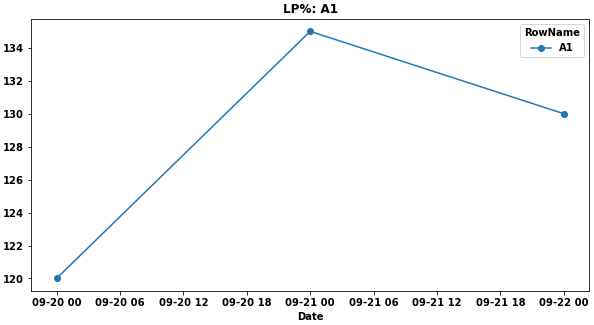
# or all 3 dlp.plot(rot=0, figsize=(10, 5), marker='o', title='LP%')- The
'A3'line covers the'A2'line because the data is the same
# specify the kind parameter for a bar plot dlp.plot(kind='bar', rot=0, figsize=(10, 5), title='LP%')- The