I am doing CRUD operations using __rowid__ which comes default with the sqlite table. I don't have separate columns for ID's in any of my tables.
My create, read and delete operations are done.
I am searching the database by customer's name.
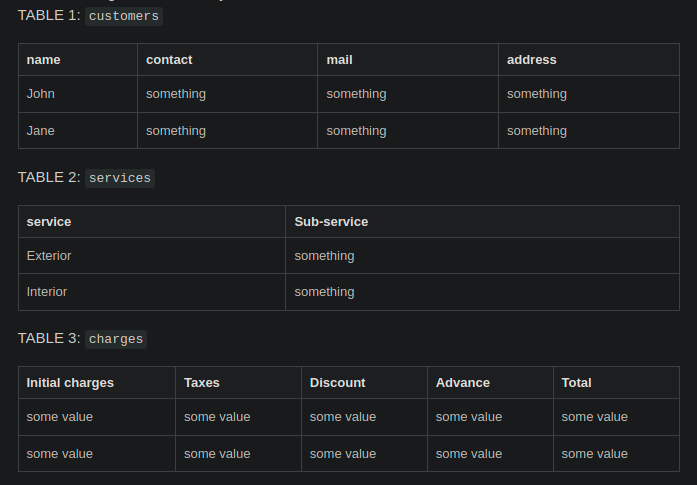
TABLES
UPDATE query for the customers table
cursor.execute("""
SELECT * FROM customers
WHERE name = ?""", (name_variable.get(),))
cursor.execute("""
UPDATE customers SET
'contact' = ?,
'mail' = ?,
'address' = ?
WHERE name = ?
""",
(
contact_variable.get(),
mail_variable.get(),
address_variable.get(),
name_variable.get()
)
)
My issue is with updating the services & charges table.
What I want is if user changes John's information then how do I UPDATE only John's data to these two tables using __rowid__. I don't understand how to execute that query.
(I am using sqlite3 version 3.31.1 on Ubuntu 20.04).
CodePudding user response:
According to the schema you have shown there is no relationship between Customers, Services and Charges so updating a Customer has no bearing on the other tables. As such you probably want a relationship and the implication of you saying
then how do I UPDATE only John's data to these two tables using rowid
The answer to that is the rowid column, as there are not relationships, does not do anything other than uniquely identify a row in the respective tables.
So first you need to define the relationships which will require either
- a column in each of the two tables (services and charges) to cater for a parent (customer) with children (services will be children of a customer and charges will be children of a customer) aka two one (customer) to many (services and charges) relationship, or
- a mapping reference table if you need a many-many relationship.
Typically the most efficient way of mapping/reference/relating/linking/associating children to parents is to utilises the always present (but normally hidden) rowid by aliasing it to column name (e.g. id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY).
As such you probably want you table definitions to be something like:-
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS customers (
customer_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
contact TEXT,
mail TEXT,
address TEXT
);
- the customer_id is an alias of the rowid column
then :-
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS services (
serviceid INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
service TEXT, subservice TEXT,
customer_id INTEGER REFERENCES customers(customer_id) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE
);
- the service_id column is an alias of the rowid column
- the customer_id column references the parent, i.e. the customer to whom the services belongs to.
- the REFERENCES keyword along with the table and the associated column defines a constraint that says the customer_id column MUST be a value that exists in the customer_id column of the customers table (i.e. a Foreign Key constraint (rule)).
then :- - The ON DELETE CASCADE says that if a parent is deleted then all the children of the parent are to be deleted down from the parent. - The ON UPDATE is similar but cascades any change to the customer_id column in the customers table.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS charges (
initialcharges REAL,
taxes REAL,
discount REAL,
advance REAL,
total REAL,
customer_id INTEGER REFERENCES customers(customer_id) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE
);
- Similar to services
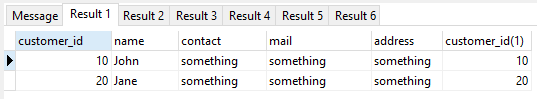
Now say you then insert some (2) customers (noting that for the demo specific customer_id vales are specified rather than allowing them to be auto generated) using :-
INSERT OR IGNORE INTO customers VALUES
(10,'John','something','something','something')
,(20,'Jane','something','something','something')
;
and then use :-
SELECT *,rowid FROM customers;
Then :-
- note that rowid is displayed as customer_id(1) as it now has customer_id as it's alias and that it exactly matches the value of the customer_id column.
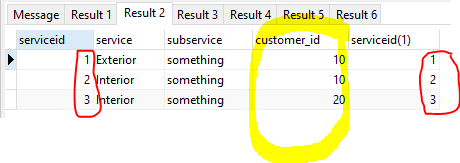
Now we add some rows the the services table using:-
INSERT INTO services (service,subservice,customer_id) VALUES
('Exterior','something',10)
,('Interior','something',10)
,('Interior','something',20)
;
- Note how the customer_id is a value from the customer_id column of the customers table and hence how you relate each services row to ONE customer.
using: -
SELECT *,rowid FROM services;
results in :-
- again the rowid matches it's alias BUT both columns are both just a unique identifier of the row in the services table it has no meaning to the relationship between a service row and it's parent customer (hence why the rowid is of no use for what you want).
- the important row, relationship wise, is the customer_id row which specifies the parent.
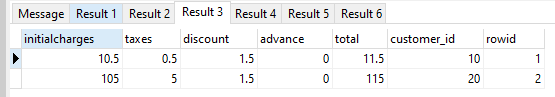
Similarly for the charges table :-
INSERT INTO charges (initialcharges,taxes,discount,advance,total,customer_id) VALUES
(10.50,0.50,1.5,0,11.50,10),
(105.00,05.00,1.5,0,115,20)
;
SELECT *,rowid FROM charges;
Now say you used-
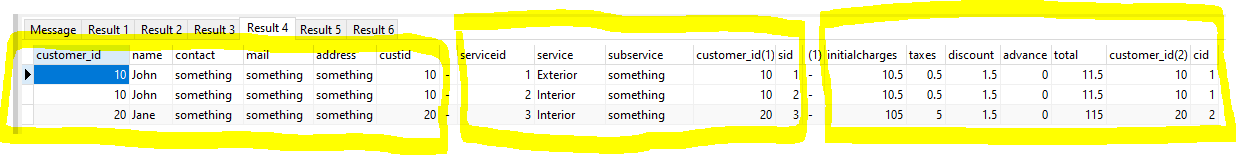
SELECT customers.*,customers.rowid AS custid,' - ' AS ' ', services.*,services.rowid AS sid,' - ' AS ' ',charges.*,charges.rowid AS cid
FROM customers
JOIN services ON services.customer_id = customers.customer_id
JOIN charges ON charges.customer_id = customers.customer_id
;
then you get :-
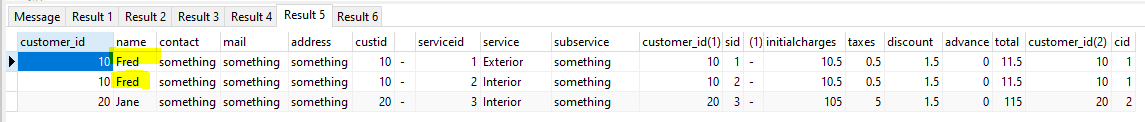
If the name of John were changed to Fred using :-
UPDATE customers SET name = 'Fred' WHERE name = 'John';
Then as the John (now Fred) is accessed from the specific row it's change will be seen without any special processing in future queries e.g.
SELECT customers.*,customers.rowid AS custid,' - ' AS ' ', services.*,services.rowid AS sid,' - ' AS ' ',charges.*,charges.rowid AS cid
FROM customers
JOIN services ON services.customer_id = customers.customer_id
JOIN charges ON charges.customer_id = customers.customer_id
;
now results in :-
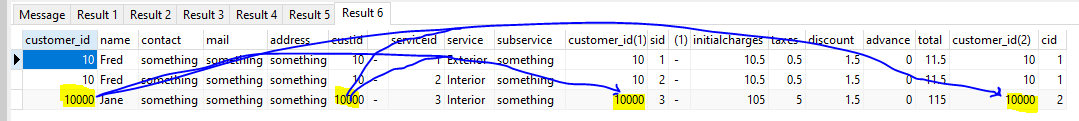
However, say the id for Jane were changed to 10000 using:-
UPDATE customers SET customer_id = 10000 WHERE customer_id = 20;
Then using the same query results in:-
i.e the ne value (10000) has automatically been applied to the children (not that you would likely change the customer_id often).
NOTE if you updated a child's column (if it did not violate the FK constraint) then that change IS NOT propagated to the parent. The parent would be switched.
Deletion works in a similar way, Delete the parent and the children will be deleted. Delete an child and just that child is child.
So with something like above, all you need to do is update whatever you need to update.
- NOTE the above may or may not reflect actually what you want, it is rather a demonstration of the principle.