So I'm trying to add a header to a csv file dynamically. My current code looks like the following:
import csv
from datetime import datetime
import pandas as pd
rows = []
with open(r'Test_Timestamp.csv', 'r', newline='') as file:
with open(r'Test_Timestamp_Result.csv', 'w', newline='') as file2:
reader = csv.reader(file, delimiter=',')
for row in reader:
rows.append(row)
file_write = csv.writer(file2)
for val in rows:
current_date_time = datetime.now().replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)
val.insert(0, current_date_time)
file_write.writerow(val)
Currently how this works is it inserts a new timestamp at column A which is exactly what I want it to do, as I want everything to be pushed as I'll be working with csv files with various different number of columns.
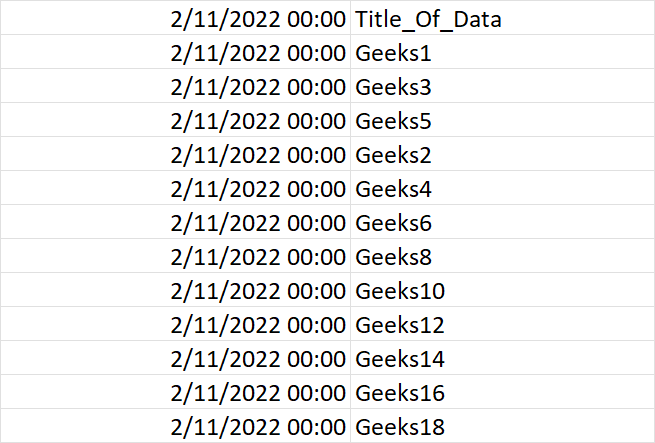
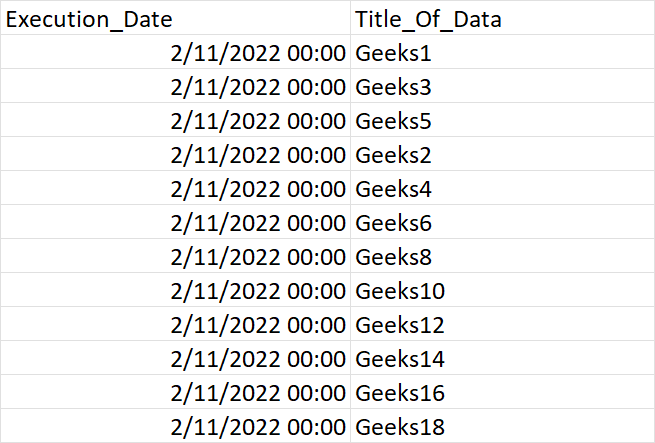
What I'm having trouble with is, how am I able to add a column header? Currently a timestamp is created next to the header. I would want to create a new header named: Execution_Date
I have looked at pandas as a solution but from the documentation I've seen the examples given looks like its a set of column headers already pre-determined. I've tried inserting a column header with df.insert(0, "Execution_Date", current_date_time) but gives me an error when trying to accomplish this.
I know I'm fairly close to doing this but I'm running into errors. Is there a way to do this dynamically so it automatically does this with various different csv files and number of different columns in each csv file, etc.? The current output looks like:
What I want the final result to look like is:
Any help with this would be greatly appreciated! I'm going to continue to see if I can solve this in the meantime, but I'm at a wall with how to proceed.
CodePudding user response:
If the end result is something that excel can read like maybe a csv you can likely bypass pandas altogether:
Edit: adding support for existing titles
Given a simple csv like:
Title,Other
Geeks1,foo
Geeks2,bar
Then you might use:
import contextlib
import csv
from datetime import datetime
with contextlib.ExitStack() as stack:
file_in = open('Test_Timestamp.csv', "r", encoding="utf-8")
file_out = open('Test_Timestamp_Result.csv', "w", encoding="utf-8", newline="")
reader = csv.reader(file_in, delimiter=',')
writer = csv.writer(file_out)
writer.writerow(["Execution_Date"] next(reader))
writer.writerows(
[datetime.now().replace(hour=0, minute=0, second=0, microsecond=0)] row
for row in reader
)
to give you a file like:
Execution_Date,Title,Other
2022-02-11 00:00:00,Geeks1,foo
2022-02-11 00:00:00,Geeks2,bar
CodePudding user response:
One way is to do this is to utilize to.csv()?
Example:
# importing python package
import pandas as pd
# read contents of csv file
file = pd.read_csv("gfg.csv")
print("\nOriginal file:")
print(file)
# adding header
headerList = ['id', 'name', 'profession']
# converting data frame to csv
file.to_csv("gfg2.csv", header=headerList, index=False)
# display modified csv file
file2 = pd.read_csv("gfg2.csv")
print('\nModified file:')enter code here
print(file2)