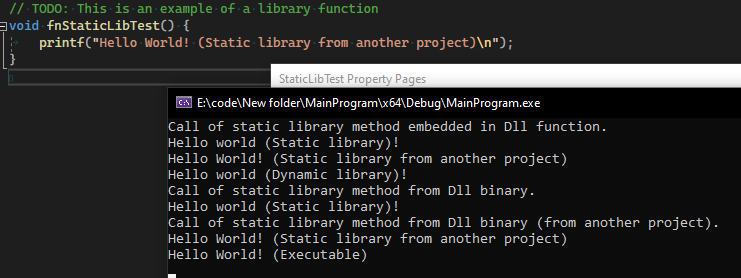
I have created example of using static libraries. The goal is this functionality:
- DllTestFunctDll.dll links static_lib.lib (contains fnStaticLibrary())
- example.exe links DllTestFunctDll.dll (contains dllTestFunct())
- main() calls directly fnStaticLibrary() and dllTestFunct().
- dllTestFunct() calls directly fnStaticLibrary().
I don't understand one thing, this works only if fnStaticLibrary() is inside same project as main() and dllTestFunct().
If I create another solution that
- DllTestFunctDll.dll links also static_lib.lib (contains fnStaticLibTest())
- main() newly also calls directly fnStaticLibTest().
- dllTestFunct() newly also calls directly fnStaticLibTest().
dllTestFunct() is able to call fnStaticLibTest() and main() is unable to call fnStaticLibTest() due to linker. But I am able to call fnStaticLibTest() inside dllTestFunct().
I used dumpbin to see what functions are exported:
dumpbin /EXPORTS "C:\\path\\DllTestFunctDll.dll"
Output:
ordinal hint RVA name
1 0 00001000 ?dllTestFunct@@YAXXZ = ?dllTestFunct@@YAXXZ (void __cdecl DllTestFunct(void))
2 1 00001070 ?fnStaticLibrary@@YAXXZ = ?fnStaticLibrary@@YAXXZ (void __cdecl fnStaticLibrary(void))
You can see that fnStaticLibTest() is missing inside the output.
In both static lib projects I export function by "__declspec(dllexport) ".
I assume that the problem is inside the Visual Studio. Do you know how to solve it?
Thank you in advance for your answers.
CodePudding user response:
An object module is added from a .lib, if it is required. If the dll does not call (or reference) any item in a compilation unit (c/cpp file), it won't be added to the dll