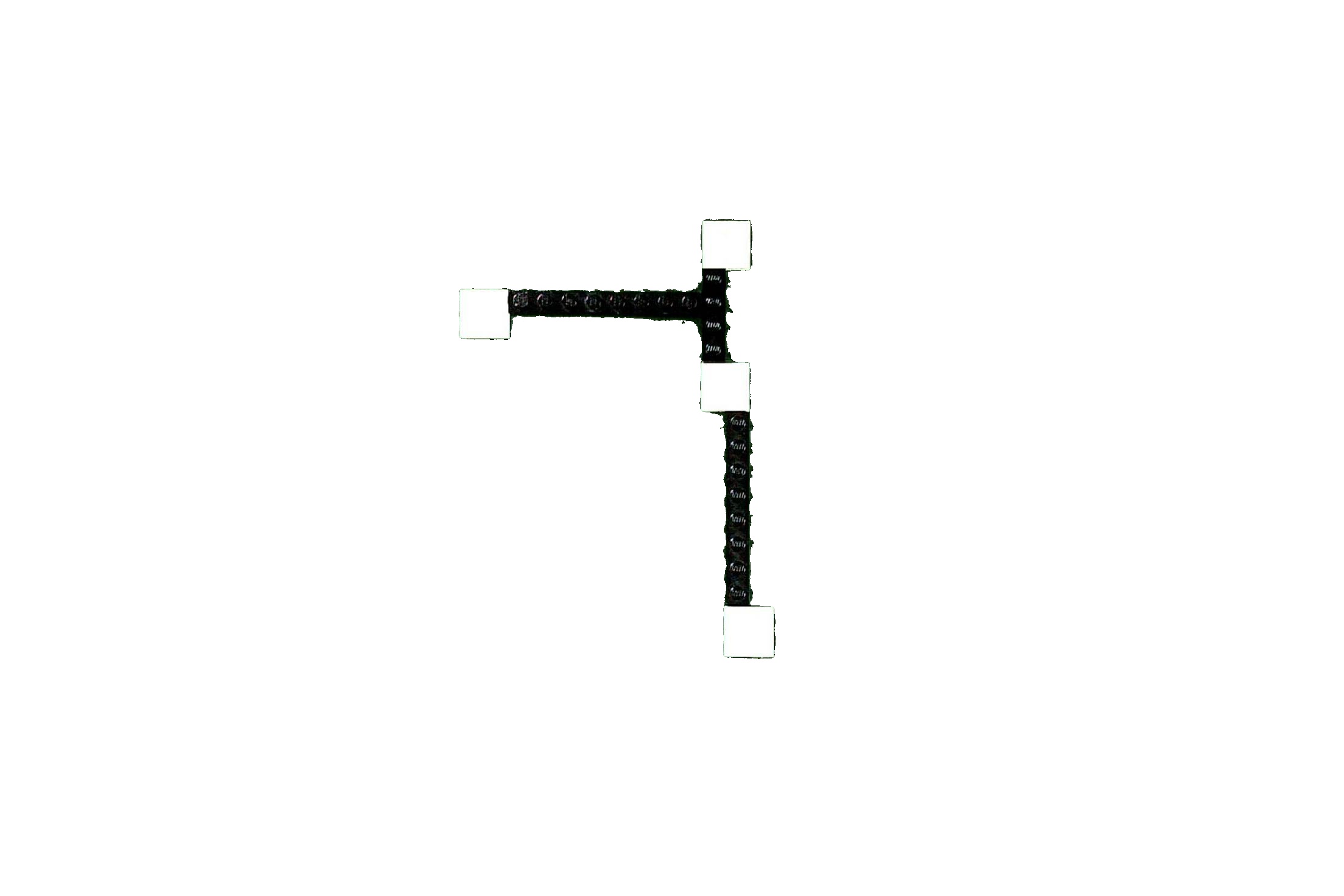
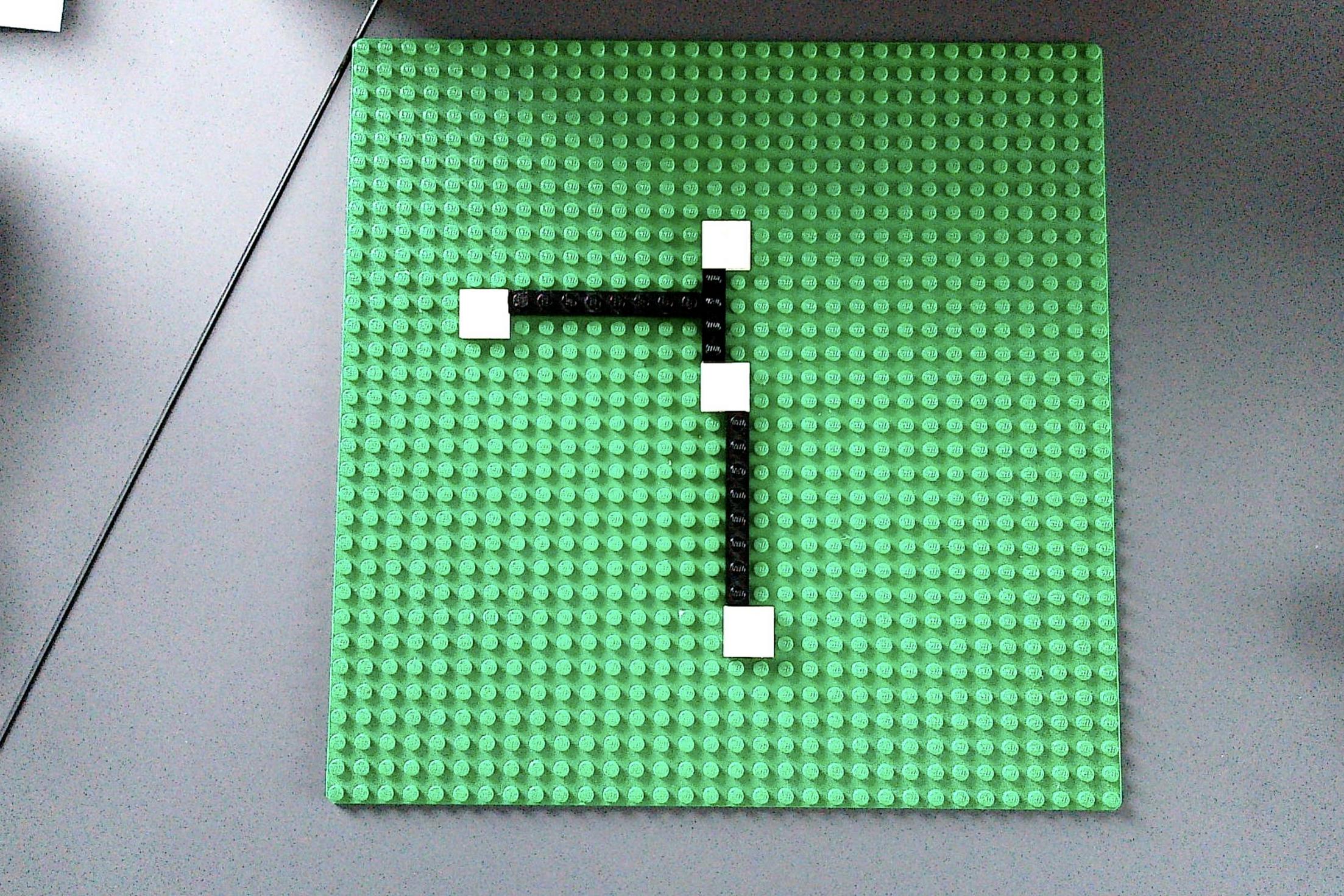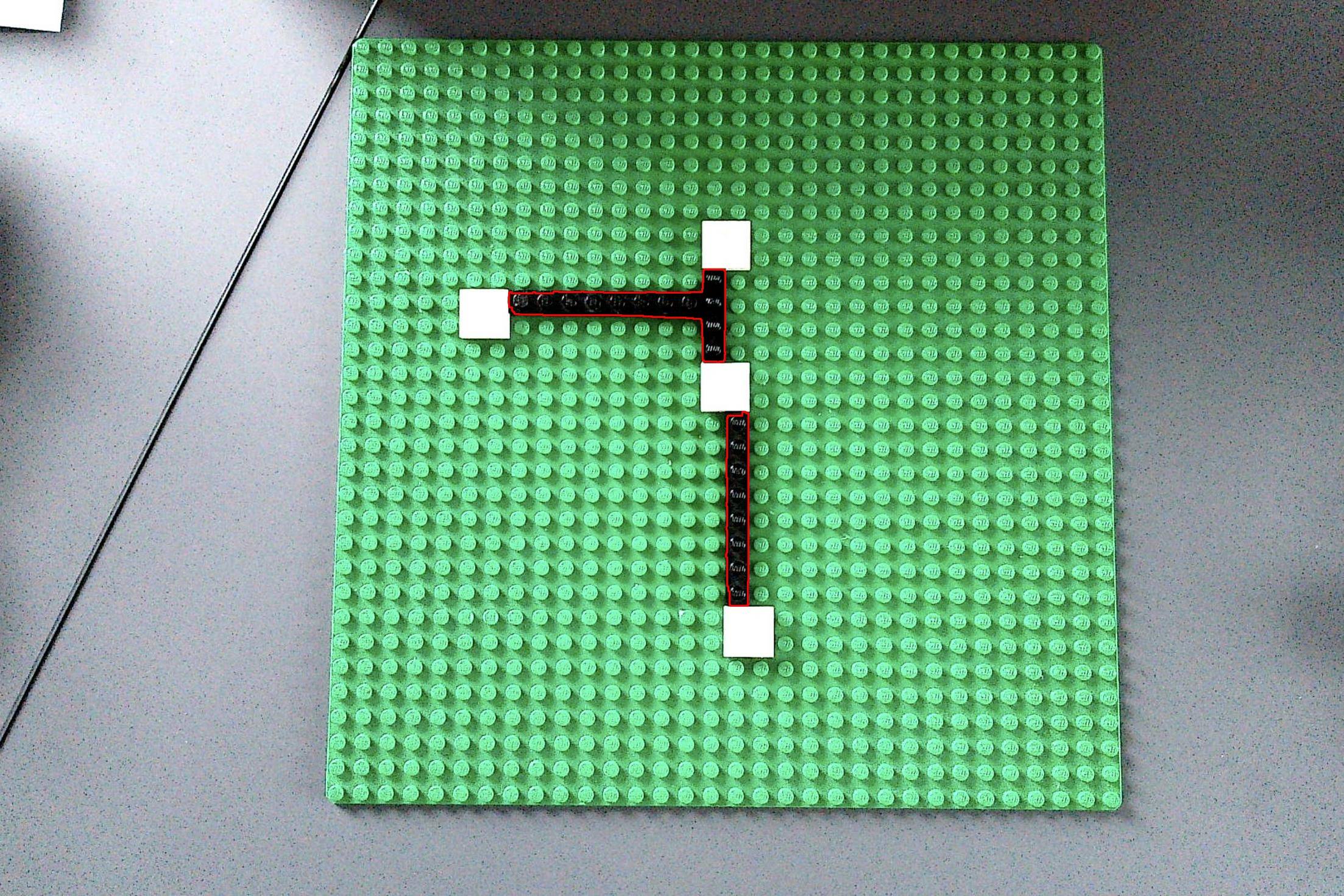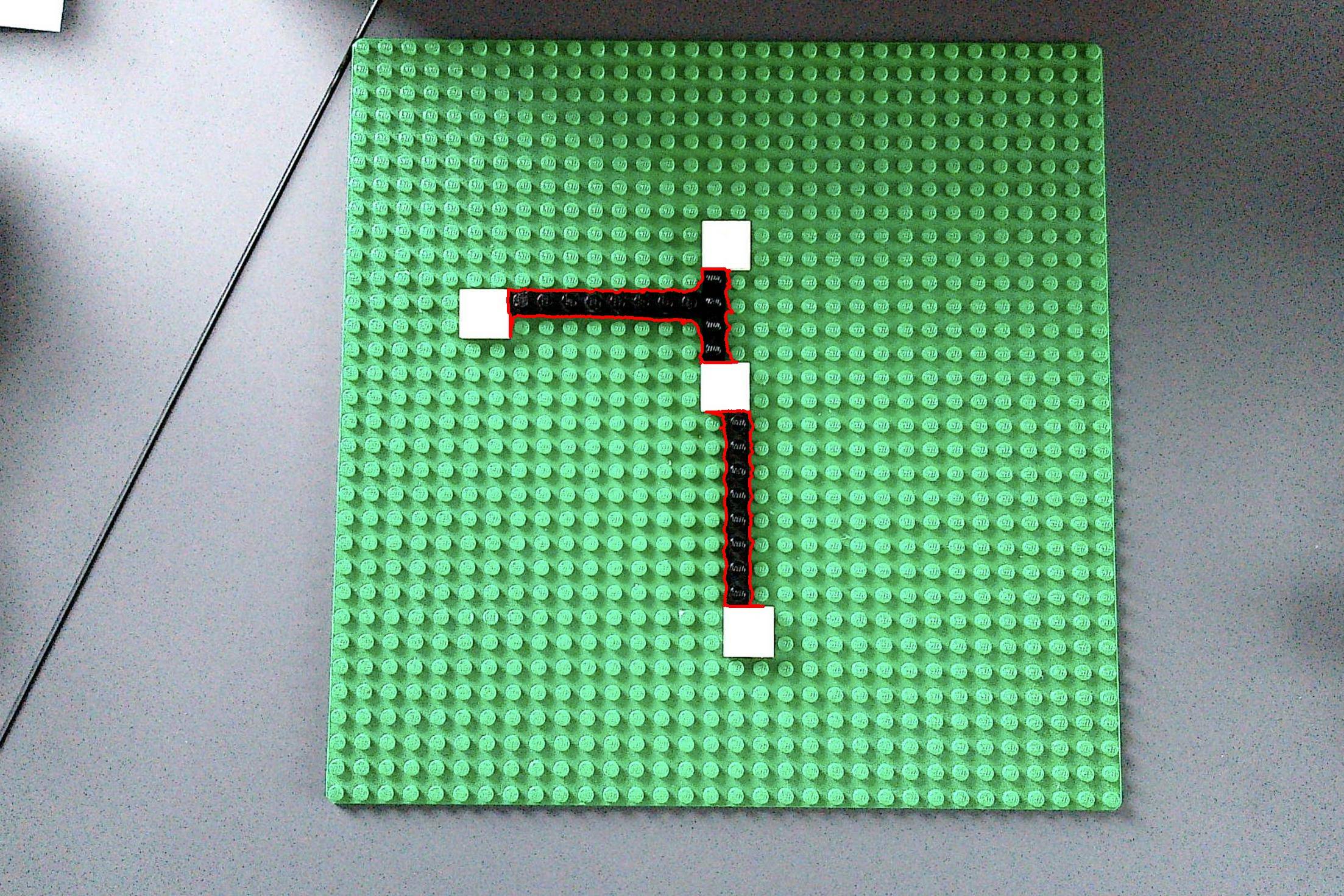I have the following image of a lego board with some bricks on it
Now I am trying to detect the thick black lines (connecting the white squares) with OpenCV. I have already experimented a lot with HoughLinesP, converted the image to gray or b/w before, applied blur, ... Nonthing led to usable results.
# Read image
img = cv2.imread('image.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# Resize Image
img = cv2.resize(img, (0,0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
# Initialize output
out = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# Median blurring to get rid of the noise; invert image
img = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
# Adaptive Treshold
bw = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,\
cv2.THRESH_BINARY,15,8)
# HoughLinesP
linesP = cv2.HoughLinesP(bw, 500, np.pi / 180, 50, None, 50, 10)
# Draw Lines
if linesP is not None:
for i in range(0, len(linesP)):
l = linesP[i][0]
cv2.line(out, (l[0], l[1]), (l[2], l[3]), (0,0,255), 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
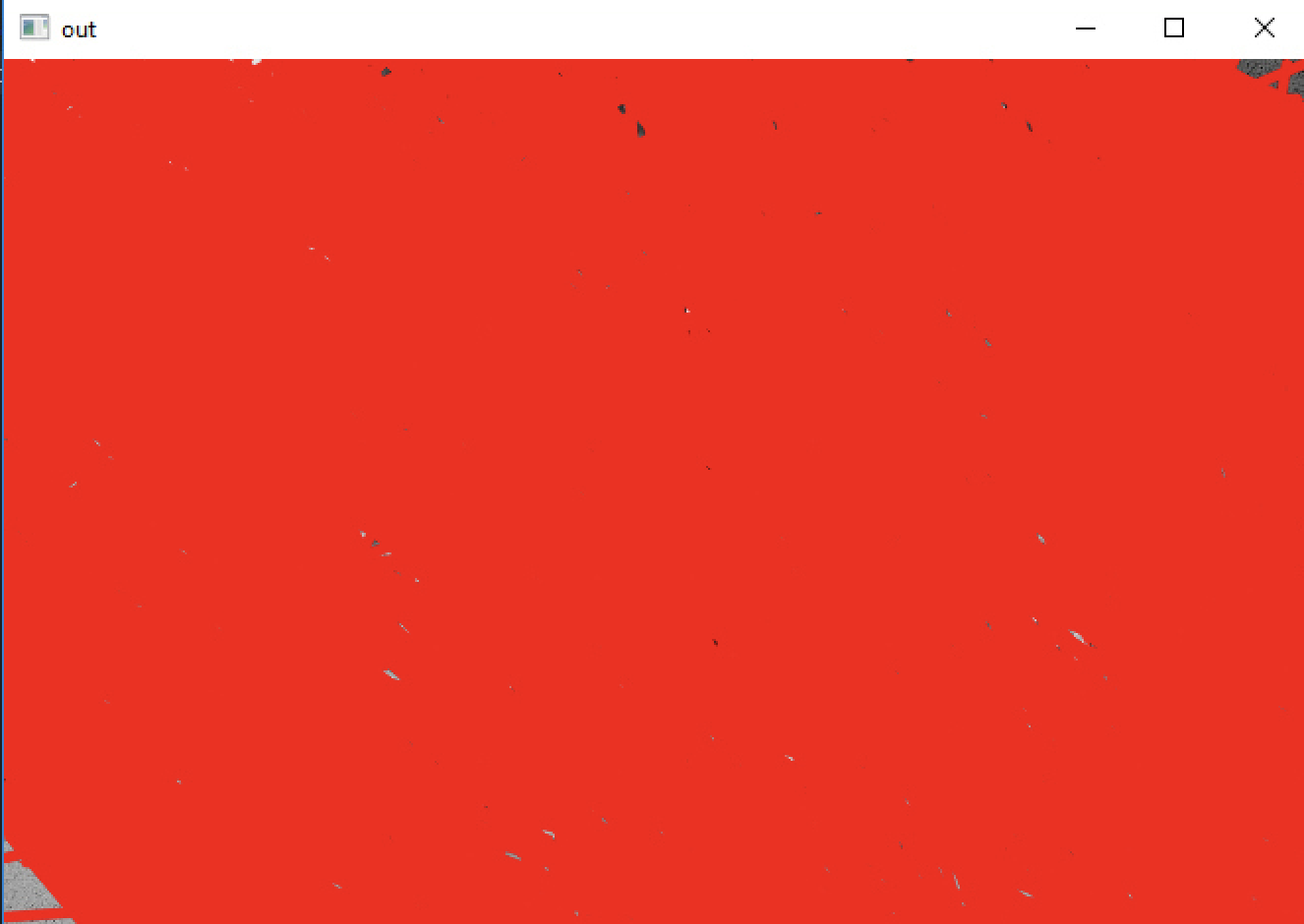
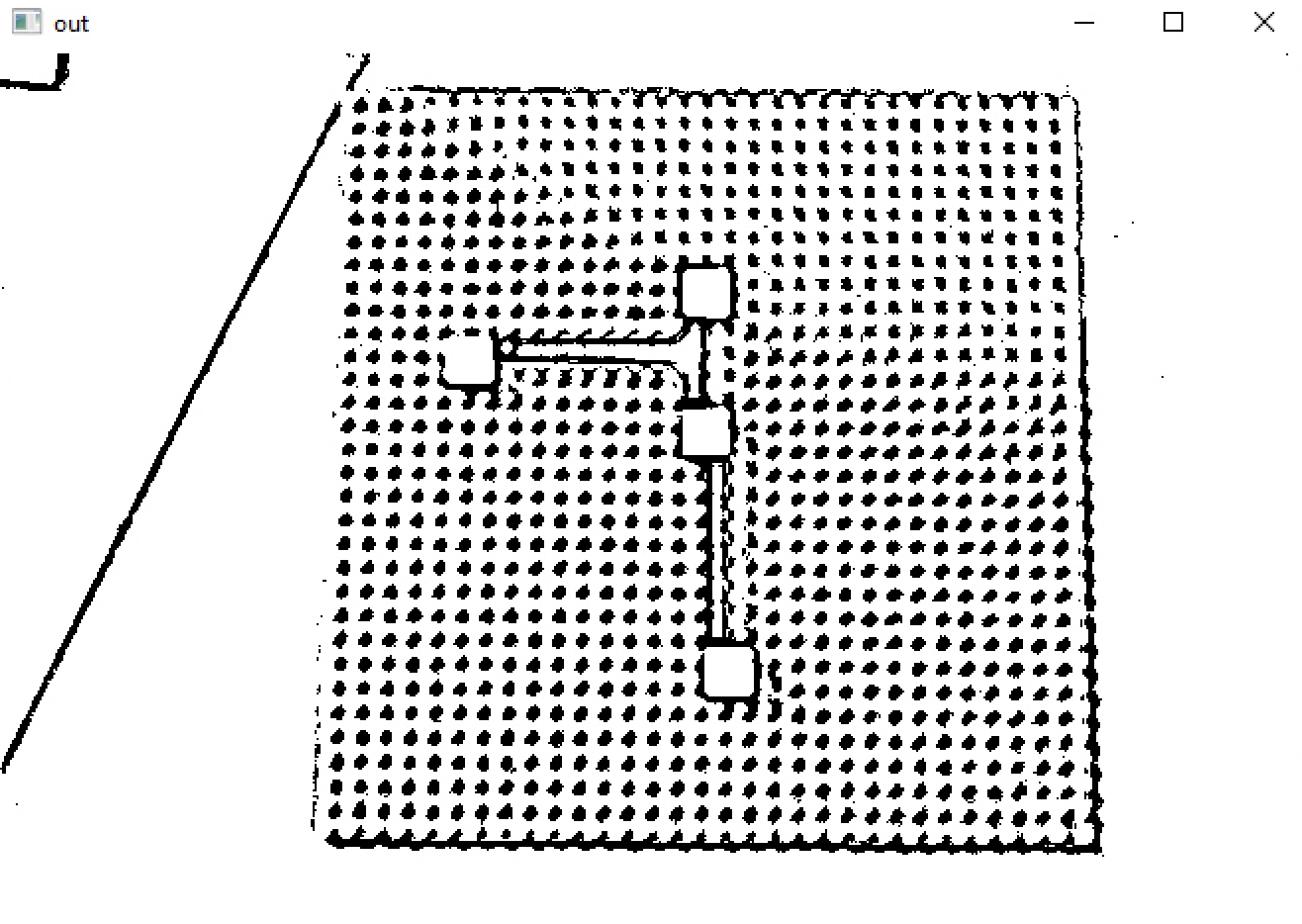
The adaptive treshold lets you see edges quite well, but with HoughLinesP you don't get anything usable out of it
What am I doing wrong?
CodePudding user response:
Here is one way to do that in Python/OpenCV.
- Read the image
- Apply median blur
- Threshold on black color using cv2.inRange()
- Apply morphology to clean it up
- Get contours and filter on area
- Draw contours on input
- Save the result
Input:
import cv2
import numpy as np
# read image
img = cv2.imread('black_lines.jpg')
# median blur
median = cv2.medianBlur(img, 5)
# threshold on black
lower = (0,0,0)
upper = (15,15,15)
thresh = cv2.inRange(median, lower, upper)
# apply morphology open and close
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3,3))
morph = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (29,29))
morph = cv2.morphologyEx(morph, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# filter contours on area
contours = cv2.findContours(morph, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours = contours[0] if len(contours) == 2 else contours[1]
result = img.copy()
for c in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area > 1000:
cv2.drawContours(result, [c], -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# save result
cv2.imwrite("black_lines_threshold.jpg", thresh)
cv2.imwrite("black_lines_morphology.jpg", morph)
cv2.imwrite("black_lines_result.jpg", result)
# view result
cv2.imshow("threshold", thresh)
cv2.imshow("morphology", morph)
cv2.imshow("result", result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
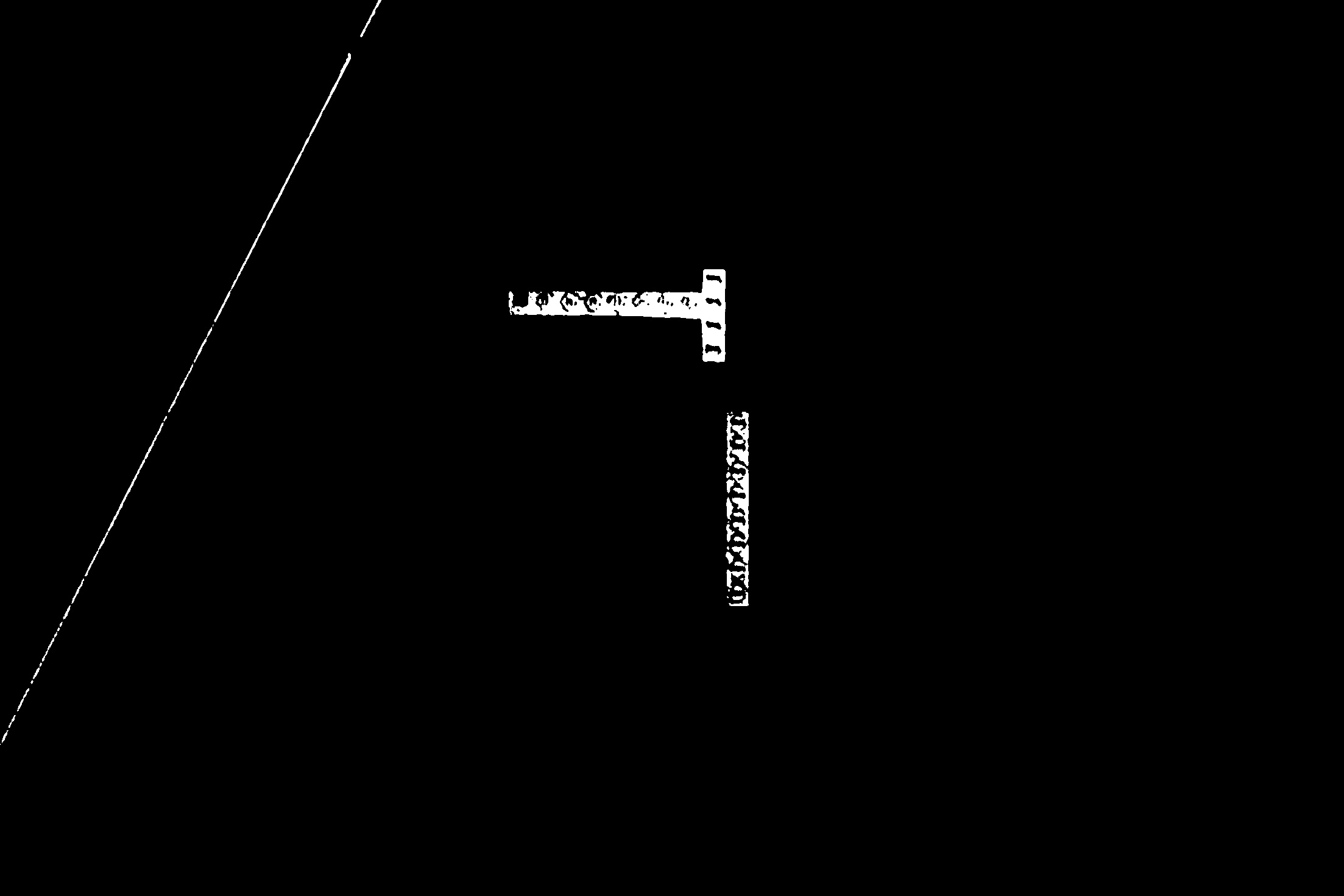
Threshold image:
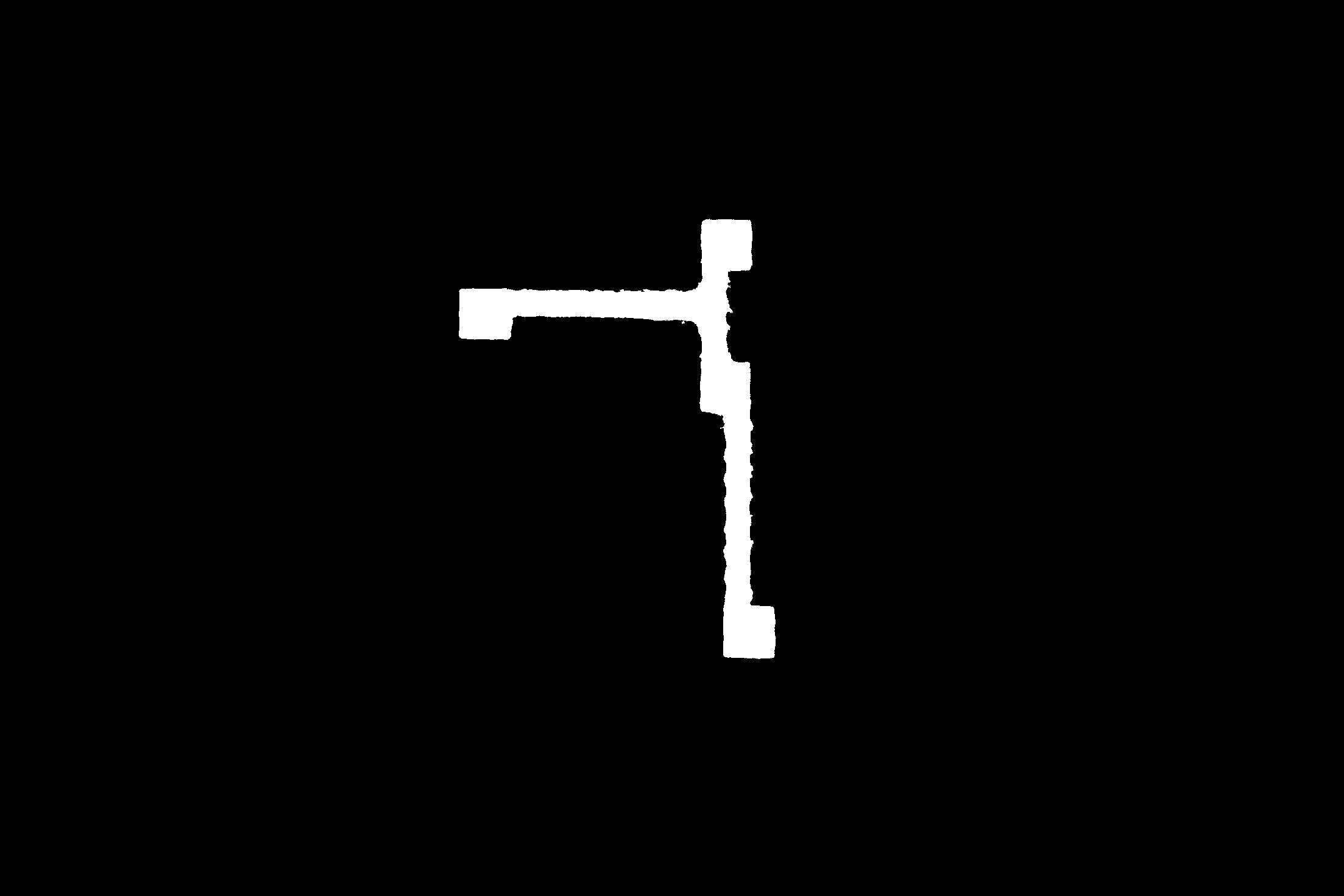
Morphology image:
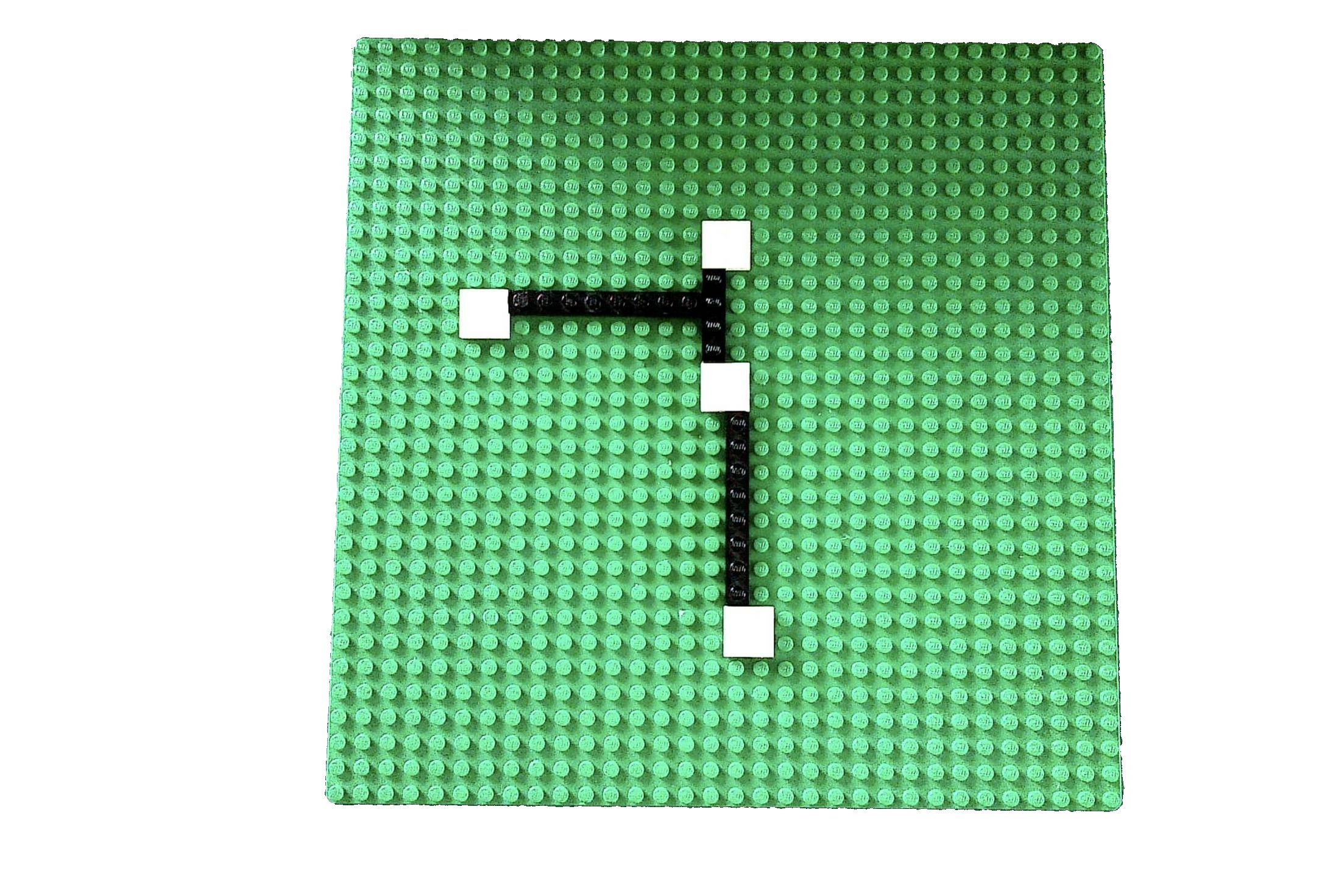
Result:
CodePudding user response:
Here I am presenting a repeated segmentation approach using color.
This answer is based on the usage of 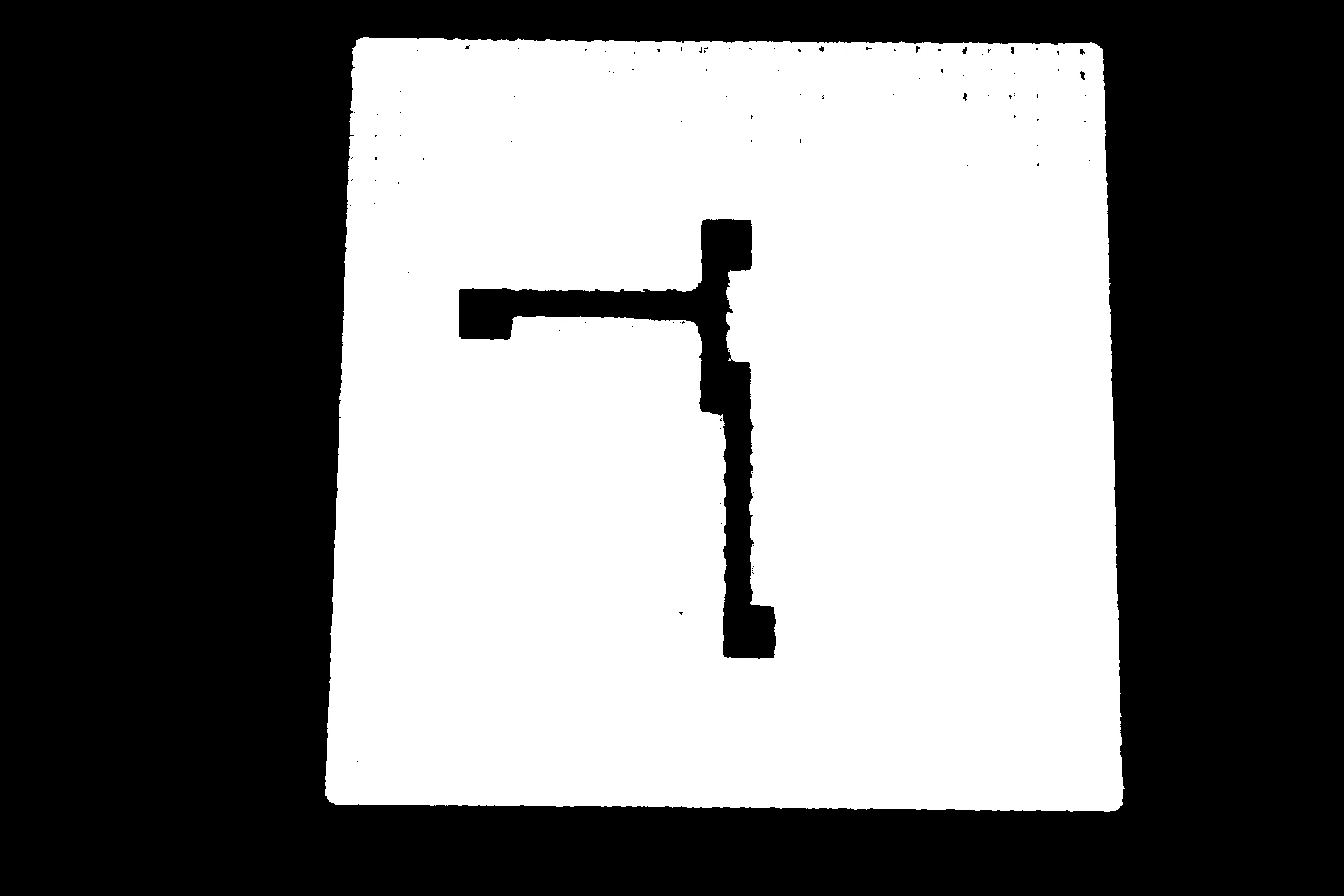
# function to obtain the largest contour in given image after filling it
def get_region(image):
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(image, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
c = max(contours, key = cv2.contourArea)
black = np.zeros((image.shape[0], image.shape[1]), np.uint8)
mask = cv2.drawContours(black,[c],0,255, -1)
return mask
mask = get_region(th)
# turning the region outside the green block white
green_block = cv2.bitwise_and(img, img, mask = mask)
green_block[black==0]=(255,255,255)
2. Segmenting the road
- To get an approximate region of the road, I subtracted the
maskandth.
cv2.subtract() performs arithmetic subtraction, where cv2 will take care of negative values.
road = cv2.subtract(mask,th)
# `road` contains some unwanted spots/contours which are removed using the function "get_region"
only_road = get_region(road)
Masking only the road segment with the original image gives
road_colored = cv2.bitwise_and(img, img, mask = only_road)
road_colored[only_road==0]=(255,255,255)
From the above image only the black regions (road) are present, which is easy to segment:
# converting to grayscale and applying threshold
th2 = cv2.threshold(road_colored[:,:,1],127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# using portion of the code from fmw42's answer, to get contours above certain area
contours = cv2.findContours(th2, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours = contours[0] if len(contours) == 2 else contours[1]
result = img.copy()
for c in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area > 1000:
cv2.drawContours(result, [c], -1, (0, 0, 255), 4)
Note:
To clean up the end result, you can apply morphological operations on th2 before drawing contours.