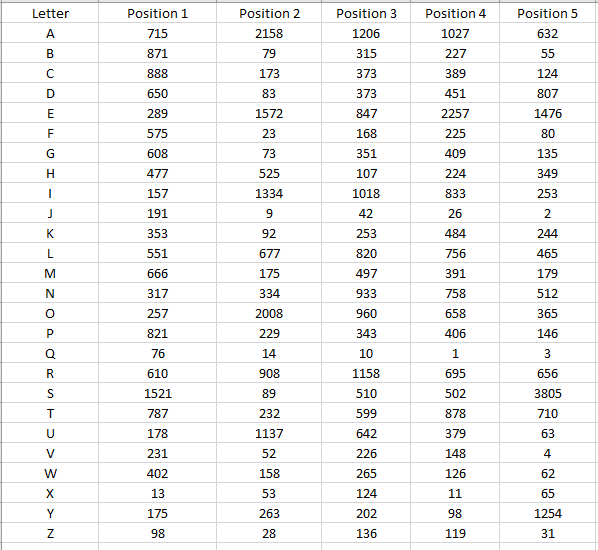
I'm having trouble figuring out how to convert my data into the X, Y, and Z axis for a a surface graph using matplotlib in python. The data is from a file that contains a list of 5 letter words and my program runs through the file and counts how may times each letter occurs in each position of a word. It is stored in 5 different dictionaries, one for each position. I'm thinking that I'll have to utilize the .keys() and .values() methods but I'm not positive.
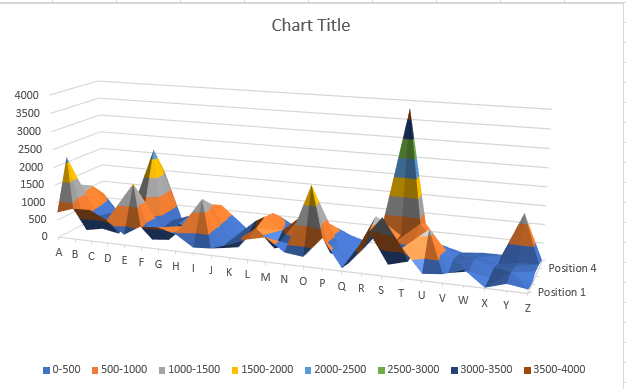
I went into excel and made the graph to show an example of what I'm trying to do.
Here is the code I have so far:
import string
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy as np
#Creates a list of the alphabet in uppercase
alphabet = string.ascii_uppercase
letter_list = list(alphabet)
#Creates dictionary for lettercount. Keys = A-Z, Values = 0
lettercount = {i: 0 for i in letter_list}
#Creates dictonaries for position frequency. Keys = A-Z, Values = 0
position1_freq = {i: 0 for i in letter_list}
position2_freq = {i: 0 for i in letter_list}
position3_freq = {i: 0 for i in letter_list}
position4_freq = {i: 0 for i in letter_list}
position5_freq = {i: 0 for i in letter_list}
with open("answers.txt") as f:
for i in f:
i = i.rstrip()
for word in i.split(" "):
for letter in range(len(word)):
#Iterates through alphabet
for j in letter_list:
#If the letter in the word = j it will add 1 to lettercount and depending on what value the indicie letter is, 1 will be added to the proper position frequency
if word[letter] == j:
lettercount[j] = 1
if letter == 0:
position1_freq[j] = 1
if letter == 1:
position2_freq[j] = 1
if letter == 2:
position3_freq[j] = 1
if letter == 3:
position4_freq[j] = 1
if letter == 4:
position5_freq[j] = 1
#Sorts the lettercount dictionary to be high to low
sort_lettercount = sorted(lettercount.items(), key = lambda x: x[1], reverse= True)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d')
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
Here is a complete example. I have used list and dictinary comprehensions since they quite common in python (good to get used to!) and the Counter class from the standard librariy. The code is therefore probably a little harder to read if you are not used to it, but the style is common in python, so I recommend learning it instead of using explicit for-loops. The Counter object is a kind of dictionary, so think of it as a dictionary. :)
I then use the .values(). function on the Counter to extract the result. I put it into a numpy array, since that is what matplotlib needs.
Finally, creating the 3d plot in matplotlib is a bit contrived. Matplotlib is not really good for categorical data (such as having letters on the X axis), nor for 3d plots with horizontal color bands (like in your excel example).
Anyways, here it is:
from string import ascii_uppercase
from collections import Counter
# a dictionary with all ascii lettters as keys, and only zeros as values
zero_counts = {c:0 for c in ascii_uppercase}
with open('answers.txt') as f:
# read the file into a list, remove trailing newlines and make sure all is uppercase
lines = [line.strip().upper() for line in f.readlines()]
# transpose the list, so that instead of having N 5-letter words, we now have 5 N-letter words
list_of_chars_per_pos = zip(*lines)
# for each of these 5 "words", count the number of occurrances of each letter
# then add these occurences into a copy of the "zero" dictionary from before
# so now we have 5 dictionaries holding the count for letter 0,1,2,3 and 4
char_counts_per_pos = [zero_counts | Counter(chars) for chars in list_of_chars_per_pos]
# matplotlib only works with numpy data structures, so lets change into that!
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(len(ascii_uppercase)) # the x axis will correspond to the letters
y = np.arange(5) # the y axis will be the positions
X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y) # create 2D arrays with the X and Y coordinates
# here we extract the data from the dictionaries using the .values() method
Z = np.array([list(dictionary.values()) for dictionary in char_counts_per_pos])
# now create the plot! create 3d axes on a new figure and draw the plot
# there is quite a bit of customization that can be done to the plot to make it look
# in whatever way you like.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.ticker import MaxNLocator, FixedLocator
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='3d')
surf= ax.plot_surface(X=X,Y=Y,Z=Z)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(FixedLocator(x))
ax.set_xticklabels(ascii_uppercase)
ax.set_box_aspect((26,5,5))
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(MaxNLocator(integer=True))
ax.set_zlabel("Counts")
ax.set_ylabel("Position")
# finally, show the plot. :)
plt.show()
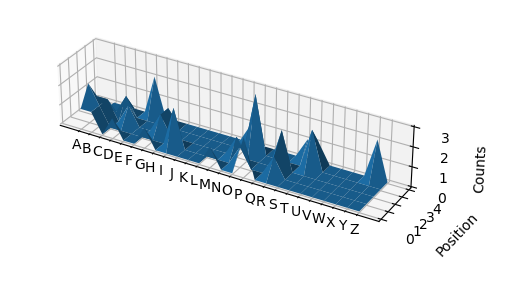
By running it on the following text file answers.txt
abbot
mince
grate
dodos
piggy
baron
party
I get the plot