I'm using an Excel table to sum some values. On a certain column, I want a running total (that is, a sum of all values previous and up to the current row). Doing that on ranges is easy, all I need to do is use an absolute cell address for the start of the range (using the $ notation) and use a relative address for the current row.
However, using tables, things get messy - the notation for ranges in tables use the [[]] syntax. Is there a way to denote a range beginning at the top of the column until the current row?
CodePudding user response:
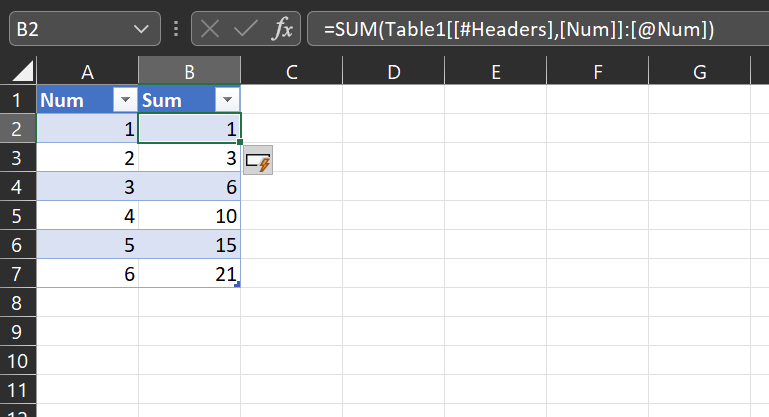
Use the Header as your starting point:
=SUM(Table1[[#Headers],[Num]]:[@Num])
CodePudding user response:
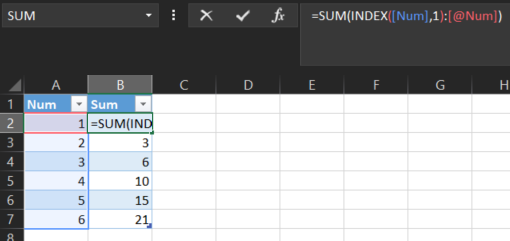
I suggest you go with @ScottCraner but another option is:
=SUM(INDEX([Num],1):[@Num])
This can also be adapted to allow you to sum to any row, not just the current one. e.g. to sum the first 3 rows:
=SUM(INDEX([Num],1):INDEX([Num],3))
CodePudding user response:
You want a separate column with the totals up to this row? That is the previous total plus the current value.
Or, assuming column A has the values and B has the running total :
- cell B1 =A1
- cell B2 =B1 A2
- and copy that formula down as far as you need