Recently I ran into a unique behavior of Pandas DataFrames, which I am trying to understand.
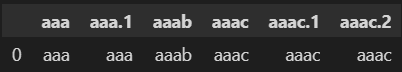
If we use the following code:
col_headers = ['aaa', 'aaa.1', 'aaab', 'aaac', 'aaac.1', 'aaac.2']
data = ['aaa', 'aaa', 'aaab', 'aaac', 'aaac', 'aaac']
df = pd.DataFrame(data=[pd.Series(data)], dtype=object)
df.columns = col_headers
we get the desired results
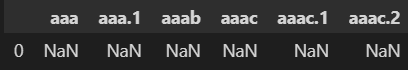
However, if we specify the columns directly in the DataFrame initialization like this:
col_headers = ['aaa', 'aaa.1', 'aaab', 'aaac', 'aaac.1', 'aaac.2']
data = ['aaa', 'aaa', 'aaab', 'aaac', 'aaac', 'aaac']
df = pd.DataFrame(data=[pd.Series(data)], columns = col_headers, dtype=object)
we get a DataFrame with NaN values
What causes this to happen?
CodePudding user response:
If you are supplying the columns param in pd.DataFrame function, you will have to convert the data to a list. Because pd.Series contains index names which is treated as header for the input data and when you supply the column param alongwith, it tries to look for those index names which has been provided in the columns list and since it does not find any, it inserts nan for those columns.
df = pd.DataFrame(data = [data], columns = col_headers, dtype=object)
data can contain ndarray , Iterable, dict, or DataFrame. Dict can contain Series, arrays, constants, dataclass or list-like objects. If data is a dict, column order follows insertion-order. If a dict contains Series which have an index defined, it is aligned by its index.
Because when you use series, your data contains column labels(like below)
[pd.Series(data)]
[0 aaa
1 aaa
2 aaab
3 aaac
4 aaac
5 aaac
dtype: object]
If data contains column labels, it will perform column selection instead.
For POC,
Renaming col_headers
You can try naming the column header as numbers and do similarly like you are doing now, the row insertion should work fine now.
col_headers = [0,1,2,3,4,5]
df = pd.DataFrame(data=[pd.Series(data)], columns = col_headers, dtype=object)
df
Output :
0 1 2 3 4 5
0 aaa aaa aaab aaac aaac aaac
Renaming Pandas Series Index
Similarly, it should work when you rename the index of the series with your column name.
data_series = pd.Series(data)
index_ = ['aaa', 'aaa.1', 'aaab', 'aaac', 'aaac.1', 'aaac.2']
data_series.index = index_
df = pd.DataFrame(data=[pd.Series(data_series)], columns = col_headers, dtype=object)
Output :
aaa aaa.1 aaab aaac aaac.1 aaac.2
0 aaa aaa aaab aaac aaac aaac