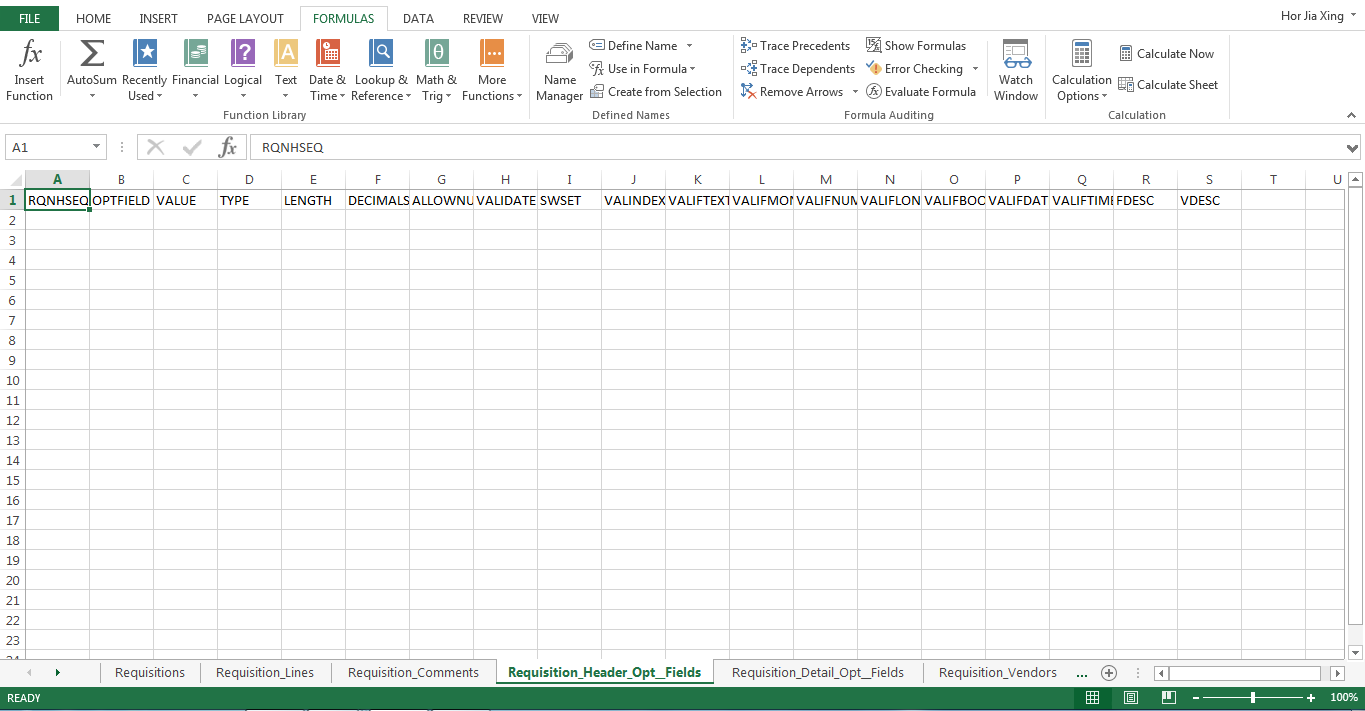
My task is to import the data from the test_import table into multiple sheets of the same excel workbook. What I am trying to achieve is to fill up specific cells in the selected sheet with selected data columns that I have in my MS SQL database through VB.NET.
I am currently undergoing my internship in a company and I never learn VB.NET before. However, my employer had assigned me this task. Hence, finding sources from internet and YouTube are my only option to self-learn VB.NET. Will be appreciate if there are source code or advice that could help me on my task!
Dim oExcel As Object
oExcel = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
Dim oBook As Excel.Workbook
Dim oSheet As Excel.Worksheet
oBook = oExcel.Workbooks.Add
If oExcel.Application.Sheets.Count() < 1 Then
oSheet = CType(oBook.Worksheets.Add(), Excel.Worksheet)
Else
oSheet = oExcel.Worksheets(1)
End If
oSheet.Name = "Requisition_Vendors"
oSheet.Range("A1").Value = "RQNHSEQ"
oSheet.Range("B1").Value = "VDCODE"
oSheet.Range("C1").Value = "CURRENCY"
oSheet.Range("D1").Value = "RATE"
oSheet.Range("E1").Value = "SPREAD"
oSheet.Range("F1").Value = "RATETYPE"
oSheet.Range("G1").Value = "RATEMATCH"
oSheet.Range("H1").Value = "RATEDATE"
oSheet.Range("I1").Value = "RATEOPER"
If oExcel.Application.Sheets.Count() < 2 Then
oSheet = CType(oBook.Worksheets.Add(), Excel.Worksheet)
Else
oSheet = oExcel.Worksheets(2)
End If
oSheet.Name = "Requisition_Detail_Opt__Fields"
oSheet.Range("A1").Value = "RQNHSEQ"
oSheet.Range("B1").Value = "RQNLREV"
oSheet.Range("C1").Value = "OPTFIELD"
oSheet.Range("D1").Value = "VALUE"
oSheet.Range("E1").Value = "TYPE"
oSheet.Range("F1").Value = "LENGTH"
oSheet.Range("G1").Value = "DECIMALS"
oSheet.Range("H1").Value = "ALLOWNULL"
oSheet.Range("I1").Value = "VALIDATE"
oSheet.Range("J1").Value = "SWSET"
oSheet.Range("K1").Value = "VALINDEX"
oSheet.Range("L1").Value = "VALIFTEXT"
oSheet.Range("M1").Value = "VALIFMONEY"
oSheet.Range("N1").Value = "VALIFNUM"
oSheet.Range("O1").Value = "VALIFLONG"
oSheet.Range("P1").Value = "VALIFBOOL"
oSheet.Range("Q1").Value = "VALIFDATE"
oSheet.Range("R1").Value = "VALIFTIME"
oSheet.Range("S1").Value = "FDESC"
oSheet.Range("T1").Value = "VDESC"
If oExcel.Application.Sheets.Count() < 3 Then
oSheet = CType(oBook.Worksheets.Add(), Excel.Worksheet)
Else
oSheet = oExcel.Worksheets(3)
End If
oSheet.Name = "Requisition_Header_Opt__Fields"
oSheet.Range("A1").Value = "RQNHSEQ"
oSheet.Range("B1").Value = "OPTFIELD"
oSheet.Range("C1").Value = "VALUE"
oSheet.Range("D1").Value = "TYPE"
oSheet.Range("E1").Value = "LENGTH"
oSheet.Range("F1").Value = "DECIMALS"
oSheet.Range("G1").Value = "ALLOWNULL"
oSheet.Range("H1").Value = "VALIDATE"
oSheet.Range("I1").Value = "SWSET"
oSheet.Range("J1").Value = "VALINDEX"
oSheet.Range("K1").Value = "VALIFTEXT"
oSheet.Range("L1").Value = "VALIFMONEY"
oSheet.Range("M1").Value = "VALIFNUM"
oSheet.Range("N1").Value = "VALIFLONG"
oSheet.Range("O1").Value = "VALIFBOOL"
oSheet.Range("P1").Value = "VALIFDATE"
oSheet.Range("Q1").Value = "VALIFTIME"
oSheet.Range("R1").Value = "FDESC"
oSheet.Range("S1").Value = "VDESC"
If oExcel.Application.Sheets.Count() < 4 Then
oSheet = CType(oBook.Worksheets.Add(), Excel.Worksheet)
Else
oSheet = oExcel.Worksheets(4)
End If
oSheet.Name = "Requisition_Comments"
oSheet.Range("A1").Value = "RQNHSEQ"
oSheet.Range("B1").Value = "RQNCREV"
oSheet.Range("C1").Value = "RQNCSEQ"
oSheet.Range("D1").Value = "COMMENTTYP"
oSheet.Range("E1").Value = "COMMENT"
If oExcel.Application.Sheets.Count() < 5 Then
oSheet = CType(oBook.Worksheets.Add(), Excel.Worksheet)
Else
oSheet = oExcel.Worksheets(5)
End If
oSheet.Name = "Requisition_Lines"
oSheet.Range("A1").Value = "RQNHSEQ"
oSheet.Range("B1").Value = "RQNLREV"
oSheet.Range("C1").Value = "RQNLSEQ"
oSheet.Range("D1").Value = "RQNCSEQ"
oSheet.Range("E1").Value = "OEONUMBER"
oSheet.Range("F1").Value = "VDCODE"
oSheet.Range("G1").Value = "ITEMNO"
oSheet.Range("H1").Value = "LOCATION"
oSheet.Range("I1").Value = "ITEMDESC"
oSheet.Range("J1").Value = "EXPARRIVAL"
oSheet.Range("K1").Value = "VENDITEMNO"
oSheet.Range("L1").Value = "HASCOMMENT"
oSheet.Range("M1").Value = "ORDERUNIT"
oSheet.Range("N1").Value = "OQORDERED"
oSheet.Range("O1").Value = "HASDROPSHI"
oSheet.Range("P1").Value = "DROPTYPE"
oSheet.Range("Q1").Value = "IDCUST"
oSheet.Range("R1").Value = "IDCUSTSHPT"
oSheet.Range("S1").Value = "DLOCATION"
oSheet.Range("T1").Value = "DESC"
oSheet.Range("U1").Value = "ADDRESS1"
oSheet.Range("V1").Value = "ADDRESS2"
oSheet.Range("W1").Value = "ADDRESS3"
oSheet.Range("X1").Value = "ADDRESS4"
oSheet.Range("Y1").Value = "CITY"
oSheet.Range("Z1").Value = "STATE"
oSheet.Range("AA1").Value = "ZIP"
oSheet.Range("AB1").Value = "COUNTRY"
oSheet.Range("AC1").Value = "PHONE"
oSheet.Range("AD1").Value = "FAX"
oSheet.Range("AE1").Value = "CONTACT"
oSheet.Range("AF1").Value = "EMAIL"
oSheet.Range("AG1").Value = "PHONEC"
oSheet.Range("AH1").Value = "FAXC"
oSheet.Range("AI1").Value = "EMAILC"
oSheet.Range("AJ1").Value = "MANITEMNO"
oSheet.Range("AK1").Value = "CONTRACT"
oSheet.Range("AL1").Value = "PROJECT"
oSheet.Range("AM1").Value = "CCATEGORY"
oSheet.Range("AN1").Value = "UNITCOST"
oSheet.Range("AO1").Value = "UCISMANUAL"
oSheet.Range("AP1").Value = "CPCOSTTOPO"
oSheet.Range("AQ1").Value = "EXTENDED"
oSheet.Range("AR1").Value = "DISCOUNT"
oSheet.Range("AS1").Value = "DISCPCT"
oSheet.Range("AT1").Value = "UNITWEIGHT"
oSheet.Range("AU1").Value = "EXTWEIGHT"
oSheet.Range("AV1").Value = "WEIGHTUNIT"
oSheet.Range("AW1").Value = "WEIGHTCONV"
oSheet.Range("AX1").Value = "DEFUWEIGHT"
oSheet.Range("AY1").Value = "DEFEXTWGHT"
oSheet.Range("AZ1").Value = "NETXTENDED"
oSheet.Range("BA1").Value = "DETAILNUM"
If oExcel.Application.Sheets.Count() < 6 Then
oSheet = CType(oBook.Worksheets.Add(), Excel.Worksheet)
Else
oSheet = oExcel.Worksheets(6)
End If
oSheet.Name = "Requisitions"
oSheet.Range("A1").Value = "RQNHSEQ"
oSheet.Range("B1").Value = "ISPRINTED"
oSheet.Range("C1").Value = "DATE"
oSheet.Range("D1").Value = "RQNNUMBER"
oSheet.Range("E1").Value = "VDCODE"
oSheet.Range("F1").Value = "VDNAME"
oSheet.Range("G1").Value = "ONHOLD"
oSheet.Range("H1").Value = "ORDEREDON"
oSheet.Range("I1").Value = "EXPARRIVAL"
oSheet.Range("J1").Value = "EXPIRATION"
oSheet.Range("K1").Value = "DESCRIPTIO"
oSheet.Range("L1").Value = "REFERENCE"
oSheet.Range("M1").Value = "COMMENT"
oSheet.Range("N1").Value = "REQUESTBY"
oSheet.Range("O1").Value = "DOCSOURCE"
oSheet.Range("P1").Value = "STCODE"
oSheet.Range("Q1").Value = "STDESC"
oSheet.Range("R1").Value = "APPROVER"
oSheet.Range("S1").Value = "ENTEREDBY"
oSheet.Range("T1").Value = "HASJOB"
oSheet.Range("U1").Value = "DETAILNEXT"
Dim requisitions As Worksheet = oBook.Sheets("Requisitions")
Dim range1 As Range = CType(requisitions.Range("$A:$U"), Range)
range1.Name = "Requisitions"
Dim requisitionLines As Worksheet = oBook.Sheets("Requisition_Lines")
Dim range2 As Range = CType(requisitionLines.Range("$A:$BA"), Range)
range2.Name = "Requisition_Lines"
Dim requisitionComments As Worksheet = oBook.Sheets("Requisition_Comments")
Dim range3 As Range = CType(requisitionComments.Range("$A:$E"), Range)
range3.Name = "Requisition_Comments"
Dim requisitionHOF As Worksheet = oBook.Sheets("Requisition_Header_Opt__Fields")
Dim range4 As Range = CType(requisitionHOF.Range("$A:$S"), Range)
range4.Name = "Requisition_Header_Opt__Fields"
Dim requisitionDOF As Worksheet = oBook.Sheets("Requisition_Detail_Opt__Fields")
Dim range5 As Range = CType(requisitionDOF.Range("$A:$T"), Range)
range5.Name = "Requisition_Detail_Opt__Fields"
Dim requisitionVendors As Worksheet = oBook.Sheets("Requisition_Vendors")
Dim range6 As Range = CType(requisitionVendors.Range("$A:$I"), Range)
range6.Name = "Requisition_Vendors"
Dim SaveFileDialog1 As New SaveFileDialog()
SaveFileDialog1.Filter = "Execl files (*.xlsx)|*.xlsx"
SaveFileDialog1.FilterIndex = 2
SaveFileDialog1.RestoreDirectory = True
If SaveFileDialog1.ShowDialog() = DialogResult.OK Then
oSheet.SaveAs(SaveFileDialog1.FileName)
MsgBox("Excel File Created Successfully!")
Else
Return
End If
oBook.Close()
oExcel.Quit()
End Sub
Actually I had wrote a code to create excel file that looks the same like the excel file shown in png. I want to be able to import selected row only into selected cell respectively in the excel file. For example, I want to insert data in "ProjectCode" from sql into "RQNHSEQ" column in excel, data in "ItemCode" from sql into "Type" column in excel.
Sorry if I accidentally mislead about the goal of my task.
CodePudding user response:
Here's a VBA solution to import data from SQL Server, to Excel.
Sub ADOExcelSQLServer()
' Carl SQL Server Connection
'
' FOR THIS CODE TO WORK
' In VBE you need to go Tools References and check Microsoft Active X Data Objects 2.x library
'
Dim Cn As ADODB.Connection
Dim Server_Name As String
Dim Database_Name As String
Dim User_ID As String
Dim Password As String
Dim SQLStr As String
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Set rs = New ADODB.Recordset
Server_Name = "EXCEL-PC\SQLEXPRESS" ' Enter your server name here
Database_Name = "NORTHWND" ' Enter your database name here
User_ID = "" ' enter your user ID here
Password = "" ' Enter your password here
SQLStr = "SELECT * FROM [Customers]" ' Enter your SQL here
Set Cn = New ADODB.Connection
Cn.Open "Driver={SQL Server};Server=" & Server_Name & ";Database=" & Database_Name & _
";Uid=" & User_ID & ";Pwd=" & Password & ";"
rs.Open SQLStr, Cn, adOpenStatic
' Dump to spreadsheet
For iCols = 0 To rs.Fields.Count - 1
Worksheets("Sheet1").Cells(1, iCols 1).Value = rs.Fields(iCols).Name
Next
With Worksheets("sheet1").Range("a2:z500") ' Enter your sheet name and range here
'.ClearContents
.CopyFromRecordset rs
End With
' Tidy up
rs.Close
Set rs = Nothing
Cn.Close
Set Cn = Nothing
End Sub
After importing data from the first table...
move the focus to another table
SQLStr = "SELECT * FROM [Customers]"
select a new worksheet...
With Worksheets("sheet1").Range("a2:z500")
You could create a SProc to do essentially the same thing; export to Excel, and call the SProc with VBA.
CodePudding user response:
The following shows how to read data from an SQL Server database and use Excel Interop to insert it into an Excel workbook. It's been tested with Excel 2016.
Note: It is recommended to enable 
Alternatively, open a cmd window and type the following:
sc query type=service | find /i "sql"
See here for more information.
Add Reference (Microsoft Excel xx.x Object Library)
- In VS menu, click Project
- Select Add Reference...
- Select COM
- Select Microsoft Excel xx.x Object Library (ex: Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library)
- Click OK
Add Reference (System.Configuration)
- In VS menu, click Project
- Select Add Reference...
- Select Assemblies
- Check System.Configuration
- Click OK
Open Solution Explorer
- In VS menu, click View
- Select Solution Explorer
Add connection string(s) to the App.Config file
- In Solution Explorer, double-click App.Config to open it
App.config:
Note: The Server and Database need to be changed for your environment. For more information about connection strings, see here.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="ConnectionStringWindowsAuthentication" connectionString="Server='.\SQLExpress'; Database='Testing'; Trusted_Connection=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
<add name="ConnectionStringSqlServerAuthentication" connectionString="Server=.\SQLExpress; Database=Testing; User Id=|Username|; Password=|UserPassword|;" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
<startup>
<supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.8" />
</startup>
</configuration>
Create a class (name: Helper.vb)
Note: The code below can be adapted for use in your application (it will need to be modified for your environment). Start by checking the 'ToDo' items in the code below. Function GetExcelColumnName is adapted from here.
Imports System.Configuration
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
Imports Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel
Public Class Helper
Private _connectionStr As String = String.Empty
Sub New()
'Windows authentication - get connection string from App.config
_connectionStr = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings("ConnectionStringWindowsAuthentication").ConnectionString
End Sub
Sub New(username As String, userPassword As String)
'SQL Server authentication - get connection string from App.config
_connectionStr = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings("ConnectionStringSqlServerAuthentication").ConnectionString.Replace("|Username|", username).Replace("|UserPassword|", userPassword)
End Sub
Private Function CreateExcelWorkbook(filename As String, dt As DataTable) As String
Dim oMissing As Object = System.Reflection.Missing.Value
Dim excelApp As Excel.Application = Nothing
Dim excelWorkbook As Excel.Workbook = Nothing
Dim excelWorksheet As Excel.Worksheet = Nothing
Dim styleDate As Excel.Style = Nothing
Dim previousWorksheet As Excel.Worksheet = Nothing
Try
'create New instance
excelApp = New Excel.Application()
'suppress displaying alerts (such as prompting to overwrite existing file)
excelApp.DisplayAlerts = False
'set Excel visability
excelApp.Visible = True
'disable user control while modifying the Excel Workbook
'to prevent user interference
'only necessary if Excel application Visibility property = true
'excelApp.UserControl = false
'add workbook
'adding a Workbook also adds a default Worksheet named "Sheet1"
excelWorkbook = excelApp.Workbooks.Add()
If excelWorkbook IsNot Nothing AndAlso excelWorkbook.Sheets.Count > 0 Then
'set value
previousWorksheet = CType(excelWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1"), Excel.Worksheet)
End If
'add a worksheet after the existing worksheet; excelWorksheet will be the new Worksheet
excelWorksheet = CType(excelWorkbook.Sheets.Add(After:=previousWorksheet), Excel.Worksheet)
'ToDo: set to desired name
excelWorksheet.Name = "My Sheet Name"
'indices are 1-based in Excel: (row, column)
'A1 = Cells(1,1); B1 = Cells(1, 2)
'
'excelWorksheet.Cells(1, "A") = "Project Code"
'excelWorksheet.Cells(1, "B") = "Item Code"
'
'excelWorksheet.Cells(1, 1) = "Project Code"
'excelWorksheet.Cells(1, 2) = "Item Code"
'
'excelWorksheet.Range("A1").Value = "Project Code"
'excelWorksheet.Range("A2").Value = "Item Code"
'add column headers using the database column names
For j As Integer = 0 To dt.Columns.Count - 1
'add 1 to get excel column number; Excel indices start at 1
Dim excelColNum As Integer = j 1
'set value - column header
excelWorksheet.Cells(1, excelColNum) = dt.Columns(j).ColumnName
'Debug.WriteLine($"Column Name: '{dt.Columns(j).ColumnName}' Data Type: '{dt.Columns(j).DataType.ToString()}'")
'get range for column
Dim rng As Excel.Range = CType(excelWorksheet.Cells(1, excelColNum), Excel.Range).EntireColumn
'set data type for column
'ToDo: change as desired
If dt.Columns(j).DataType.ToString() = "System.DateTime" Then
rng.NumberFormat = "yyyy\-mm\-dd;@"
ElseIf dt.Columns(j).DataType.ToString() = "System.Int32" Then
rng.NumberFormat = 0
ElseIf dt.Columns(j).DataType.ToString() = "System.Decimal" Then
rng.NumberFormat = "0.00"
End If
Next
'set values in Excel using data from database
'ToDo: add desired code
For i As Integer = 0 To dt.Rows.Count - 1
Dim excelRowNum As Integer = i 2 'headers are in row 1 so data starts in row 2
For j As Integer = 0 To dt.Columns.Count - 1
Dim excelColNum As Integer = j 1
If dt(i)(dt.Columns(j).ColumnName) IsNot Nothing AndAlso dt(i)(dt.Columns(j).ColumnName) IsNot DBNull.Value Then
'set cell value
excelWorksheet.Cells(excelRowNum, excelColNum) = dt(i)(dt.Columns(j).ColumnName).ToString()
End If
Next
Next
'Sheet1 can be deleted
If excelWorkbook IsNot Nothing AndAlso excelWorkbook.Sheets.Count > 0 Then
excelWorksheet = CType(excelWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1"), Excel.Worksheet)
'delete existing worksheet
excelWorksheet.Delete()
End If
If excelApp IsNot Nothing AndAlso excelWorkbook IsNot Nothing Then
'save Workbook - if file exists, overwrite it
excelWorkbook.SaveAs(filename, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value, System.Reflection.Missing.Value)
End If
Return ($"Operation successfully completed. Created '{filename}'.")
Catch ex As Exception
Debug.WriteLine("Error (CreateExcelWorkbook): " & ex.Message)
Throw ex
Finally
If excelWorkbook IsNot Nothing Then
excelWorkbook.Close()
'release resources
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.FinalReleaseComObject(excelWorkbook)
excelWorksheet = Nothing
excelWorkbook = Nothing
End If
If excelApp IsNot Nothing Then
excelApp.Quit()
'release all resources
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.FinalReleaseComObject(excelApp)
End If
End Try
Return "Operation not successful"
End Function
Public Function Create(filename As String) As String
Dim dt As DataTable = GetDataSqlServer()
Return CreateExcelWorkbook(filename, dt)
End Function
Private Function GetDataSqlServer() As DataTable
Dim dt As DataTable = New DataTable()
Using con As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection(_connectionStr)
'open
con.Open()
Using da As SqlDataAdapter = New SqlDataAdapter("SELECT * from Project", con)
'get data from database
da.Fill(dt)
Return dt
End Using
End Using
End Function
Private Function GetExcelColumnName(excelColumnNumber As Integer) As String
'get column letter from column number
'ex: given column number '1', returns 'A'
Dim d As Integer = excelColumnNumber
Dim m As Integer = 0
Dim name As String = String.Empty
Do While d > 0
m = (d - 1) Mod 26
name = Chr(65 m) name
d = CInt((d - m) / 26)
Loop
Return name
End Function
End Class
Usage:
Note: The following code assumes that there is a Button (name: btnRun) on the form and the Click event handler has been added.
Private _helper As Helper = Nothing
...
Private Sub btnRun_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnRun.Click
Using sfd As SaveFileDialog = New SaveFileDialog()
sfd.Filter = "Execl files (*.xlsx)|*.xlsx"
sfd.RestoreDirectory = True
sfd.FileName = "Test.xlsx"
If sfd.ShowDialog() = DialogResult.OK Then
Dim result As String = _helper.Create(sfd.FileName)
Debug.WriteLine($"{result}")
End If
End Using
End Sub
Resources
- Connection Strings
- Connection Strings and Configuration Files
- ConfigurationManager Class
- Set data type like number, text and date in excel column using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel in c#
- How to convert a column number (e.g. 127) into an Excel column (e.g. AA)
- Range.NumberFormat
- Number Format Codes
- Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel Namespace
- System.Data.SqlClient Namespace
- SqlConnection Class
- SqlDataAdapter Class
- SqlCommand Class
- SQL Server Data Types