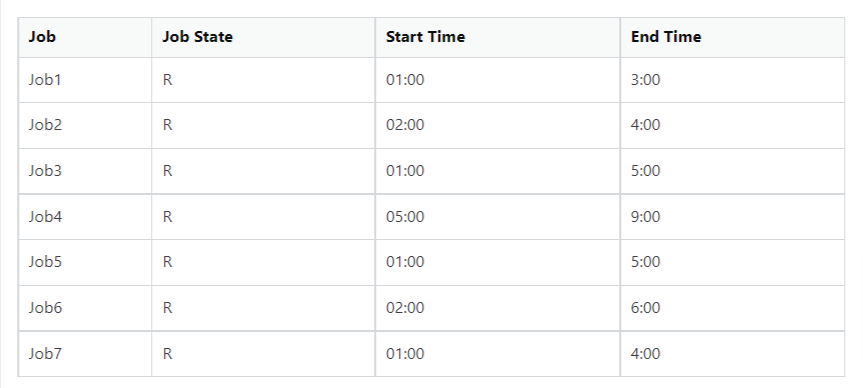
I have this table with millions of records:
I want to get the sum of all running jobs from Start Time to End Time. For example query 1:
Between 1:00 and 4:00 how many jobs were running?
Then here the answer will be 3 (Job1, Job2 & Job7).
I can use joins but want the approach that takes least time for millions of records.
CodePudding user response:
You can write a subquery that gets your job COUNT between your start and end times along with a GROUP_CONCAT to group all of your jobs in a single, comma delimited row:
SELECT jobs AS "Jobs", job_count AS "Job Count"
FROM
(
SELECT
1,
GROUP_CONCAT(job SEPARATOR ', ') as jobs,
COUNT(job) AS job_count
FROM
sample_table
WHERE
start_time >= '1:00'
AND
end_time <= '4:00'
GROUP BY
1
) a
Result:
| Jobs | Job Count |
|---|---|
| Job1, Job2, Job7 | 3 |
Alternatively, you can use a CTE:
WITH cte AS (SELECT
1,
GROUP_CONCAT(job SEPARATOR ', ') as jobs,
COUNT(job) AS job_count
FROM
sample_table
WHERE
start_time >= '1:00'
AND
end_time <= '4:00'
GROUP BY
1
) SELECT jobs AS "Jobs", job_count AS "Job Count" FROM cte
Result:
| Jobs | Job Count |
|---|---|
| Job1, Job2, Job7 | 3 |
db<>fiddle here.
Notes:
I used a dummy value of
1for the grouping which is why I used asubqueryandCTE, if you don't mind outputting the column you can remove thesubqueryorCTE.You can add a
DISTINCTandORDER BYattributes to theGROUP_CONCATbut this will likely impact your performance.
GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT job ORDER BY job ASC SEPARATOR ', ')
- Since you're dealing with a large dataset, I would ensure your table is properly
indexed. I'm not sure what your key columns are but setting upindexeswill speed up the query. See How MySQL Uses Indexes.