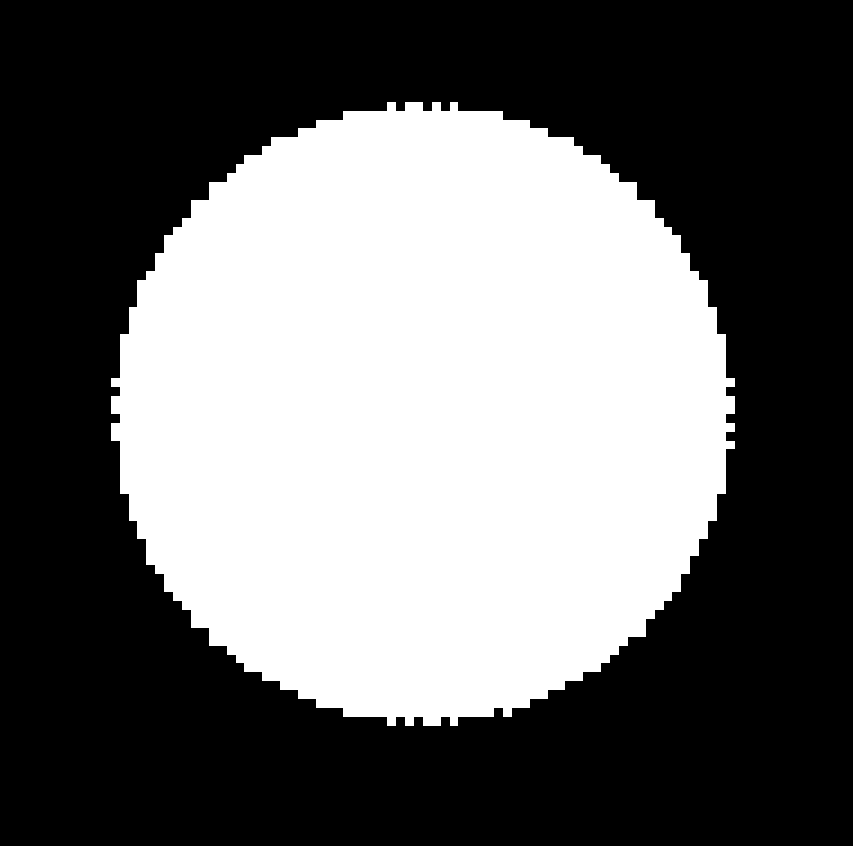
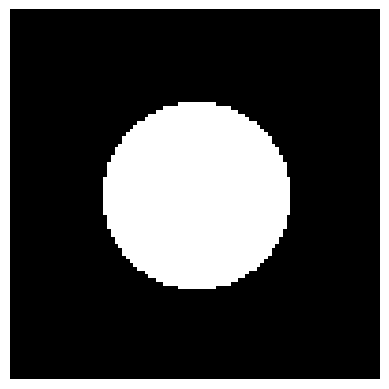
I am creating binary images (i.e., with only black and white and no other colors) of different shapes using matplotlib and PIL libraries. I have constraints on the number of pixels as 64x64, and the image has to be binary. At this low pixel range, I am getting pixelated images as shown below. I am searching for an approach where I can minimize the protrusions of white pixels and make their variation more uniform and gradual.
I have used the following piece of code to generate this image.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import io
from PIL import Image
def get_image_array(_fig):
io_buffer = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(io_buffer, format="raw")
io_buffer.seek(0)
_image_array = np.reshape(
np.frombuffer(io_buffer.getvalue(), dtype=np.uint8),
newshape=(int(_fig.bbox.bounds[3]), int(_fig.bbox.bounds[2]), -1)
)
io_buffer.close()
return _image_array
def draw_box_and_circle(bbox, xc, yc, r, pixels=(100, 100), angular_parts=100):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(pixels[0]*0.01, pixels[1]*0.01))
fig.add_axes(plt.Axes(fig, [0., 0., 1., 1.]))
# draw bbox
x0, y0, x1, y1 = bbox
plt.fill([x0, x1, x1, x0], [y0, y0, y1, y1], color='0')
# draw circle
theta = np.linspace(0.0, 2.0*np.pi, angular_parts)
x = xc (r*np.cos(theta))
y = yc (r*np.sin(theta))
plt.fill(x, y, color='1')
#
plt.axis('off')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.xlim([BBOX[0], BBOX[2]])
plt.ylim([BBOX[1], BBOX[3]])
image_array = get_image_array(fig)
print(image_array.shape)
image = Image.fromarray(image_array)
image.save("before_conversion.png")
image = image.convert(mode="1")
image.save("after_conversion.png")
print(np.array(image).shape)
return
BBOX = (0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
draw_box_and_circle(BBOX, 0.5, 0.5, 0.25)
CodePudding user response:
You probably want to disable dithering in the conversion from RGB, use:
image = image.convert(mode="1", dither=0)
You could also consider generating a binary shape directly, instead of "thresholding" the anti-aliassed shape from Matplotlib.
For example using something like:
xc = 0.5
yc = 0.5
r = 0.25
n_pixels = 100
dxy = 1/n_pixels
hdxy = dxy/2
yy, xx = np.mgrid[hdxy:1-hdxy:dxy, hdxy:1-hdxy:dxy]
# subtract the center
xx = xx - xc
yy = yy - yc
# treshold distance from center to create
# the (binary) circle
circle = np.sqrt(xx**2 yy**2) <= r
circle = (circle*255).astype(np.uint8)
And plot the array with plt.imshow(circle, resample="nearest") instead. It might give you finer control at the pixel level. Relying on Matplotlibs anti-aliassing might make your solution backend specific?