I know this is a general question, but I have the following code in my app.js
app.post('/data', (req, res) =>{
const file = req.files.filename;
const nose = [];
const filename = file.name;
file.mv('./excel/' filename, (err)=>{
if(err){
console.log(err)
} else{
const result = importExcel({
sourceFile: './excel/' filename,
header: {rows:1},
columnToKey :{A:'Dimension', B:'Category', C:'Subcategory',D:'Factor', E:'Context', F:'Date',G:'Indicator', H:'Formula',I:'FoundValue'},
sheets:['data']
})
for(var i=0; result.data.length > i; i ){
nose.push(result.data[i].Dimension,
result.data[i].Category)
}
res.send(nose)
console.log(nose ' = Total data ' nose.length);
}
})
})
Here is my data.ejs in the part of the button for sending data
<form action="/data" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div style="float:right">
<input style="margin-top:6%;" type="file" name="filename">
<button style="float:right" type="submit" ><i ></i></button>
</div>
<div style="margin-left: 0px; margin-right: 0px!important;">
Right now it looks visually like this; 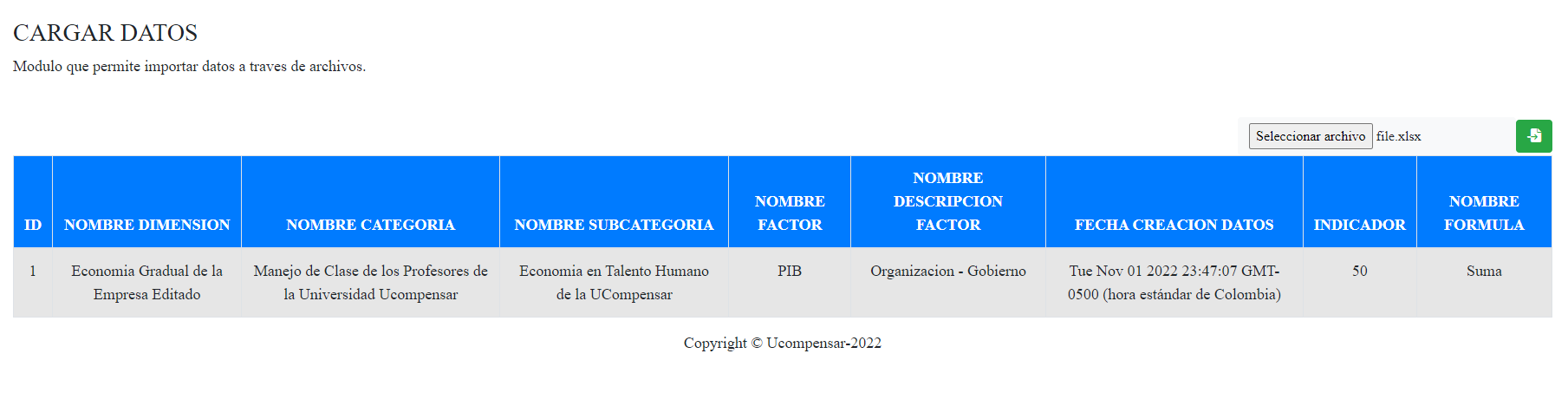
And my data is displayed like this;
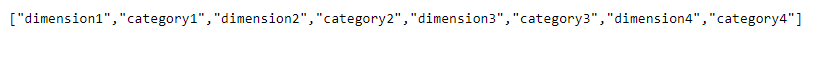
Which is fine, because that's what my excel looks like;

Context: I need to send that .json data in app.js to my MySQL database using Nodejs but I don't know how to send that data to my database table, I've seen that they use multer,sequelize, etc. I don't know if that's the way or there are easier ways to understand for a newbie like me.
I also have an app. get, like this;
app.get('/data', (req, res) =>{
connection.query('SELECT c.data_id, d.dimension_name, cc.category_name, s.subcategory_name, f.factor_name,f.factor_description,c.date_creation_data, c.Indicator,ff.formula_name FROM data_load c INNER JOIN dimensions d ON c.dimension_id = d. id_dimensions INNER JOIN categories cc ON c.id_categories = cc.id_categories INNER JOIN subcategory s ON c.id_subcategories = s.id_subcategories INNER JOIN factors f ON c.id_factor = f.id_factor INNER JOIN formulas ff ON c.id_formula = ff.id_formula;',
function(error, results){
if(error){
console.log(error)
} else{
res.render('./data', {
results:results
})
}
})
})
My table, too, as you noticed in app.get has several INNER JOIN, so this is my table at present;
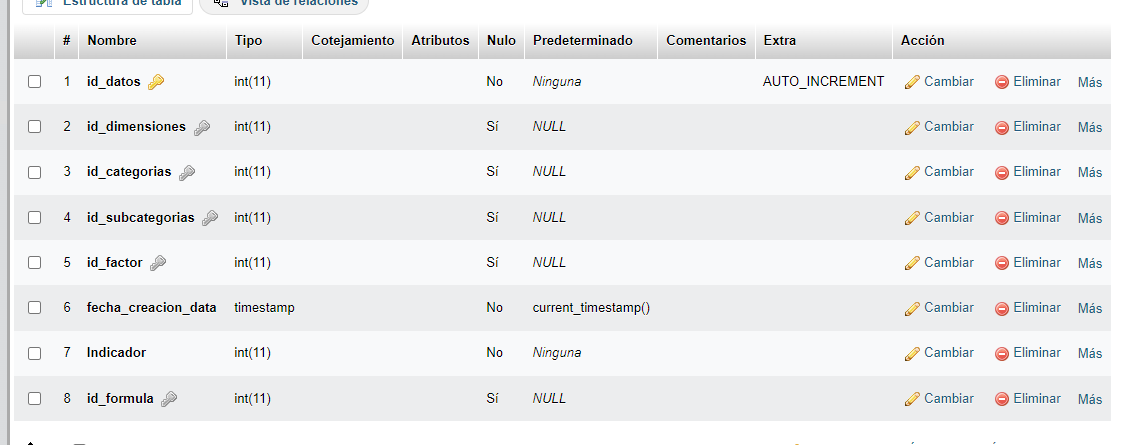
CREATE TABLE `carga_datos` (
`id_datos` int(11) NOT NULL,
`id_dimensiones` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`id_categorias` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`id_subcategorias` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`id_factor` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`fecha_creacion_data` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT current_timestamp(),
`Indicador` int(11) NOT NULL,
`id_formula` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
ALTER TABLE `carga_datos`
ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id_datos`),
ADD KEY `id_dimensiones` (`id_dimensiones`),
ADD KEY `id_categorias` (`id_categorias`),
ADD KEY `id_subcategorias` (`id_subcategorias`),
ADD KEY `id_factor` (`id_factor`),
ADD KEY `id_formula` (`id_formula`);
ALTER TABLE `carga_datos`
MODIFY `id_datos` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, AUTO_INCREMENT=2;
ALTER TABLE `carga_datos`
ADD CONSTRAINT `carga_datos_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`id_dimensiones`) REFERENCES `dimensiones` (`id_dimensiones`),
ADD CONSTRAINT `carga_datos_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`id_categorias`) REFERENCES `categorias` (`id_categorias`),
ADD CONSTRAINT `carga_datos_ibfk_3` FOREIGN KEY (`id_subcategorias`) REFERENCES `subcategoria` (`id_subcategorias`),
ADD CONSTRAINT `carga_datos_ibfk_4` FOREIGN KEY (`id_factor`) REFERENCES `factores` (`id_factor`),
ADD CONSTRAINT `carga_datos_ibfk_5` FOREIGN KEY (`id_formula`) REFERENCES `formulas` (`id_formula`);
COMMIT;
Please help, I don't know what to do,
Thanks in advance :(
CodePudding user response:
I suggest using sequelize for your data models. This example should get you on your way.
You create and update tables via migrations, then run them via your console:
'use strict';
module.exports = {
up: (queryInterface, Sequelize) => {
return queryInterface.createTable('carga_datos', {
id: {
allowNull: false,
autoIncrement: true,
primaryKey: true,
type: Sequelize.INTEGER
},
id_datos: {
allowNull: false,
type: Sequelize.INTEGER
},
id_dimensiones: {
allowNull: true,
type: Sequelize.INTEGER
},
id_categorias: {
allowNull: true,
type: Sequelize.INTEGER
},
id_subcategorias: {
allowNull: true,
type: Sequelize.INTEGER
},
createdAt: {
allowNull: false,
type: Sequelize.DATE
},
updatedAt: {
allowNull: false,
type: Sequelize.DATE
}
})
},
down: (queryInterface, Sequelize) => {
return queryInterface.dropTable('carga_datos');
}
};
You will define your model schemas like this:
'use strict';
module.exports = (sequelize, DataTypes) => {
var carga_datos = sequelize.define('carga_datos', {
id: {
allowNull: false,
autoIncrement: true,
primaryKey: true,
type: DataTypes.INTEGER
},
id_datos: {
allowNull: false,
type: DataTypes.INTEGER
},
id_dimensiones: {
allowNull: true,
type: DataTypes.INTEGER
},
id_categorias: {
allowNull: true,
type: DataTypes.INTEGER
},
id_subcategorias: {
allowNull: true,
type: DataTypes.INTEGER
},
createdAt: {
allowNull: false,
type: DataTypes.DATE
},
updatedAt: {
allowNull: false,
type: DataTypes.DATE
}
})
carga_datos.associate = function (models) {
}
return carga_datos;
}
When you want to create a new entry in your database, you will use:
const datos = await carga_datos.create({
id_datos: req.body.id_datos,
id_dimensiones: req.body.id_dimensiones
})
Pay attention to the types when writing models and migrations, they may get confused. Good luck!
