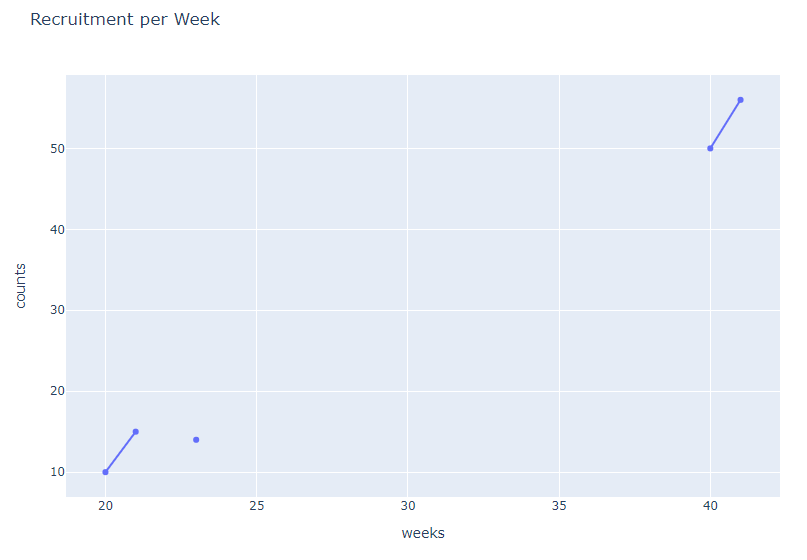
I have a dataframe with a column for weeks and data captured for each week. it looks like this
# Import pandas library
import pandas as pd
# initialize list of lists
data = [['20', 10],
['21', 15],
['23', 14],
['40', 50],
['41', 56]]
# Create the pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['weeks', 'counts'])
# print dataframe.
df
Now I am plotting a line chart with this data . Notice that from week 23 to week 40, we didnt have data. so my intention is to skip this weeks on the plot and only have a line chart of those weeks with available data.
Plotly orders everything automatically and it includes the missing weeks and this might cause problems when its being interpreted.
see what plotly does
import plotly.express as px
#df = px.data.gapminder().query("country=='Canada'")
fig = px.line(df, x="weeks", y="counts", title='Recruitment per Week')
#fig.write_image("images/Recruit.jpeg")
fig.show()
How can I have a break on the chart from week 23 to 40. Like the line chart to break in show that we didnt have data in those specific weeks.
CodePudding user response:
Do you need to repeat this often? Do you need a flexible solution or something that just works in this case? You could first check the dataframe for consecutive values, then create a new trace in the same figure for each connected period. You can also give them the same color to make it easier to read. Manually you could create a separate dataframe for each connected period and then create a trace for each dataframe.
CodePudding user response:
First, I would re-index the data so weeks with no data are accounted for.
df['weeks'] = df['weeks'].astype(int)
df = df.set_index('weeks').reindex(np.arange(df['weeks'].min(),df['weeks'].max() 1)).reset_index()
>>> df
weeks counts
0 20 10.0
1 21 15.0
2 22 NaN
3 23 14.0
4 24 NaN
5 25 NaN
6 26 NaN
7 27 NaN
8 28 NaN
9 29 NaN
10 30 NaN
11 31 NaN
12 32 NaN
13 33 NaN
14 34 NaN
15 35 NaN
16 36 NaN
17 37 NaN
18 38 NaN
19 39 NaN
20 40 50.0
21 41 56.0
fig = px.line(df,
x='weeks',
y='counts',
title='Recruitment per Week',
markers=True)
fig.show()