I am trying to read and store the values of a text file in a variable so that I can covert that text file into CSV file afterwards. But I am getting this error that the file is not found. I used the exact path by right clicking on the text file and select copy path. Still getting this error. Any idea on how to fix this
Here is the Code
import pandas as pd
import csv
import json
dataframe1 = pd.read_csv(r'/data.txt', sep="|")
# storing this dataframe in a csv file
dataframe1.to_csv('CSV_CONVERTED.csv',
index = None)
def csv_to_json(event=None, context=None ):
jsonArray = []
csvFilePath = r'/CSV_CONVERTED.csv'
jsonFilePath = r'/data.json'
#read the csv file
with open(csvFilePath, encoding='utf-8') as csvf:
#load csv file data using csv library's dictionary reader
csvReader = csv.DictReader(csvf)
#convert each csv row into python dict
for row in csvReader:
#add this python dict to json array
jsonArray.append(row)
#convert python jsonArray to JSON String and write to file
with open(jsonFilePath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as jsonf:
jsonString = json.dumps(jsonArray, indent=4)
jsonf.write(jsonString)
return{
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'Success'
}
print(csv_to_json())
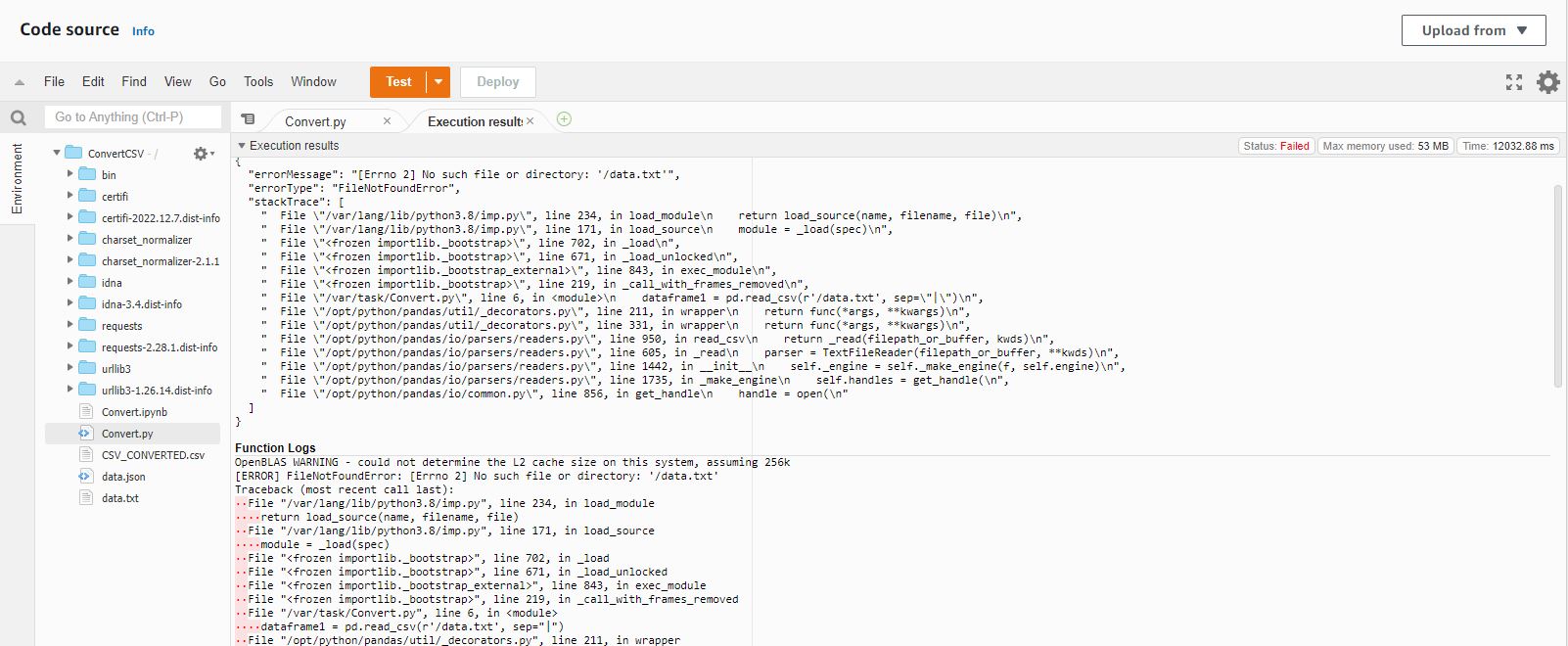
Here is the error response
{ "errorMessage": "[Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/data.txt'", "errorType": "FileNotFoundError", "stackTrace": [ " File "/var/lang/lib/python3.8/imp.py", line 234, in load_module\n return load_source(name, filename, file)\n", " File "/var/lang/lib/python3.8/imp.py", line 171, in load_source\n module = _load(spec)\n", " File "", line 702, in _load\n", " File "", line 671, in _load_unlocked\n", " File "", line 843, in exec_module\n", " File "", line 219, in _call_with_frames_removed\n", " File "/var/task/Convert.py", line 6, in \n dataframe1 = pd.read_csv(r'/data.txt', sep="|")\n", " File "/opt/python/pandas/util/_decorators.py", line 211, in wrapper\n return func(*args, **kwargs)\n", " File "/opt/python/pandas/util/_decorators.py", line 331, in wrapper\n return func(*args, **kwargs)\n", " File "/opt/python/pandas/io/parsers/readers.py", line 950, in read_csv\n return _read(filepath_or_buffer, kwds)\n", " File "/opt/python/pandas/io/parsers/readers.py", line 605, in _read\n parser = TextFileReader(filepath_or_buffer, **kwds)\n", " File "/opt/python/pandas/io/parsers/readers.py", line 1442, in init\n self._engine = self._make_engine(f, self.engine)\n", " File "/opt/python/pandas/io/parsers/readers.py", line 1735, in _make_engine\n self.handles = get_handle(\n", " File "/opt/python/pandas/io/common.py", line 856, in get_handle\n handle = open(\n" ] }
CodePudding user response:
In Lambda, you can only write to /tmp/ directory. The Lambda deployment package is deployed onto /var/task/ directory.
Hence use /tmp/ directory to write your files to.
data_file_path = f"/var/task/data.txt"
csvFilePath = f"/tmp/CSV_CONVERTED.csv"
dataframe1 = pd.read_csv(data_file_path, sep="|")
# storing this dataframe in a csv file
dataframe1.to_csv(csvFilePath, index = None)
def csv_to_json(event=None, context=None ):
jsonArray = []
jsonFilePath = f"/tmp/data.json"
#read the csv file
with open(csvFilePath, encoding='utf-8') as csvf:
#load csv file data using csv library's dictionary reader
csvReader = csv.DictReader(csvf)
#convert each csv row into python dict
for row in csvReader:
#add this python dict to json array
jsonArray.append(row)
#convert python jsonArray to JSON String and write to file
with open(jsonFilePath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as jsonf:
jsonString = json.dumps(jsonArray, indent=4)
jsonf.write(jsonString)
return{
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'Success'
}
print(csv_to_json())
