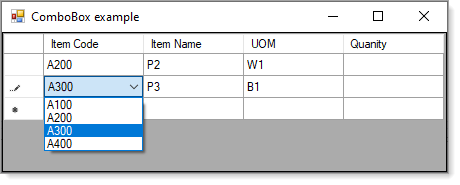
I am designing a winform in which I have a datagridview with predefined columns, the first column is a combobox and rest 3 columns are textboxes.
I am not binding datagridview to any datasource since the user is going to fill the last column "Qty", all I want to achieve is, when user clicks on the combobox it should show 3 columns from the database table (item code, item name and uom) and when user select any particular "item code" corresponding "item name" and "uom" should be displayed in second column and third column of the datagridview. Likewise the user should be able to enter as many row as he require. After data entry the data will be saved in a table named "purchase requisition".
I have not done any coding so far and have designed only the form.
CodePudding user response:
See if the following will provide base code to roll with. There are several classes to mock up data and a extension method which should be move to own files.
DataGridView was not configured in the designer, just in code.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace UnboundDataGridViewComboBox
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private ComboBox _cbo;
private string _comboColumnName = "ItemCodeColumn";
private List<Item> _items => Mocked.Items;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
Shown = OnShown;
}
private void OnShown(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var column1 = new DataGridViewComboBoxColumn
{
DataSource = _items.Select(x => x.ItemCode).ToArray(),
DisplayStyle = DataGridViewComboBoxDisplayStyle.Nothing,
Name = _comboColumnName,
HeaderText = "Item Code",
SortMode = DataGridViewColumnSortMode.NotSortable
};
var column2 = new DataGridViewTextBoxColumn
{
Name = "ItemNameColumn",
HeaderText = "Item Name"
};
var column3 = new DataGridViewTextBoxColumn
{
Name = "UomColumn",
HeaderText = "UOM"
};
var column4 = new DataGridViewTextBoxColumn
{
Name = "QuanityColumn",
HeaderText = "Quanity"
};
ItemsDataGridView.Columns.AddRange(column1, column2, column3, column4);
ItemsDataGridView.EditingControlShowing = DataGridView1OnEditingControlShowing;
}
private void DataGridView1OnEditingControlShowing(object sender, DataGridViewEditingControlShowingEventArgs e)
{
if (!ItemsDataGridView.CurrentCell.IsComboBoxCell()) return;
if (ItemsDataGridView.Columns[ItemsDataGridView.CurrentCell.ColumnIndex].Name != _comboColumnName) return;
_cbo = e.Control as ComboBox;
_cbo.SelectedIndexChanged -= ItemCodeColumnComboSelectionChanged;
_cbo.SelectedIndexChanged = ItemCodeColumnComboSelectionChanged;
}
private void ItemCodeColumnComboSelectionChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DataGridViewComboBoxEditingControl control = sender as DataGridViewComboBoxEditingControl;
Item item = _items.FirstOrDefault(x => x.ItemCode == control.EditingControlFormattedValue.ToString());
if (item == null)
{
return;
}
ItemsDataGridView.CurrentRow.Cells[1].Value = item.Name;
ItemsDataGridView.CurrentRow.Cells[2].Value = item.UOM;
}
}
#region Place classes into their own files
public static class Extensions
{
public static bool IsComboBoxCell(this DataGridViewCell sender)
=> sender.EditType != null &&
sender.EditType == typeof(DataGridViewComboBoxEditingControl);
}
// represents a table in a database
public class Item
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string ItemCode { get; set; }
public string UOM { get; set; }
public override string ToString() => ItemCode;
}
class Mocked
{
// simulate data from database
public static List<Item> Items => new List<Item>()
{
new Item() {Id = 1,Name = "P1", ItemCode = "A100", UOM = "Q1"},
new Item() {Id = 2,Name = "P2", ItemCode = "A200", UOM = "W1"},
new Item() {Id = 3,Name = "P3", ItemCode = "A300", UOM = "B1"},
new Item() {Id = 4,Name = "P4", ItemCode = "A400", UOM = "H1"}
};
}
#endregion
}