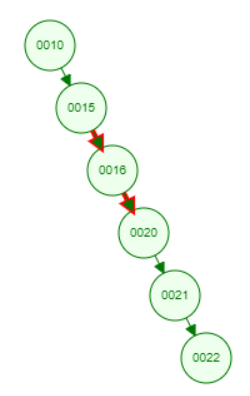
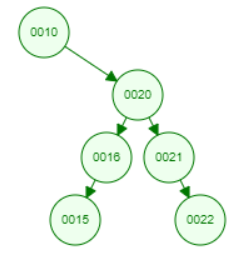
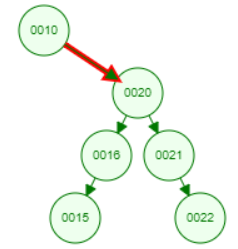
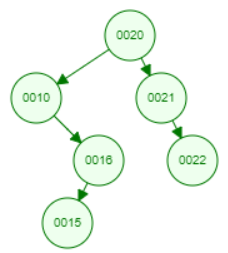
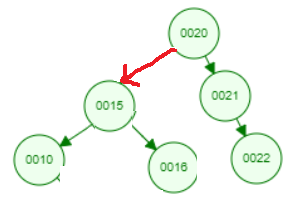
I am testing Zag-zag rotation with a right-skewed tree. Before that, I had tested Zig-zig, Zig-zag rotation with a left-skewed tree and OK.
Here is my code:
// An AVL tree node
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
function rightRotate(root) {
const rootLeft = root.left; // saving the reference
root.left = rootLeft.right;
rootLeft.right = root;
return rootLeft; // new root
}
function leftRotate(root) {
const rootRight = root.right;
root.right = rootRight.left;
rootRight.left = root;
return rootRight;
}
// This function modifies the tree and returns the new root
// - If has key, Brings the key at root
// - Else, brings the last accessed item at root.
function splay(root, key) {
// Base cases
if (root === null || root.key === key) return root; // bring last accessed element or founded element as root of left-left (sub)tree
// Grandparent start here
// Key lies in Left
if (key < root.key) {
// Key is not in tree
if (root.left === null) return root; // If not founded, Bring last accessed element root of left (sub)tree
// Parent start here
// Zig-Zig (Left Left)
if (key < root.left.key) {
root.left.left = splay(root.left.left, key);
// Do first rotation for root, brind child as parent of subtree
root = rightRotate(root);
}
// Zig-Zag (Left Right)
else if (key > root.left.key) {
root.left.right = splay(root.left.right, key);
// Do first rotation for root.left, brind child as parent of subtree
if (root.left.right != null) root.left = leftRotate(root.left);
}
// 1 cong 2 viec
// 1. Do second rotation, bring child as grandparent of subtree
// 2. Bring parent (level 2) as root of tree when last recursive splay() finish
return rightRotate(root);
// Parent end
}
// Key lies in Right
else {
if (root.right === null) return root;
// Parent start here
// Zag-Zag (Right Right)
if (key > root.right.key) {
root.right.right = splay(root.right.right, key);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
// Zag-Zig (Right Left)
else if (key < root.right.key) {
root.right.left = splay(root.right.left, key);
if (root.right.left != null) root.right = rightRotate(root.right);
}
return leftRotate(root);
// End parent
}
// Grandparent end
}
// The search function for Splay tree.
// This function returns the new root of Splay Tree.
// If key is present in tree then, it is moved to root.
// else, last accessed element is moved to root
function search(root, key) {
return splay(root, key);
}
// A utility function to print
// preorder traversal of the tree.
// The function also prints height of every node
function preOrder(root) {
if (root != null) {
console.log(root.key);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
// Right-skewed tree for Zag-zag and Zag-zig test
// Using root2 to console.log in other function like splay, search (because they have argument name "root")
let root2 = new Node(10);
root2.right = new Node(15);
root2.right.right = new Node(16);
root2.right.right.right = new Node(20);
root2.right.right.right.right = new Node(21);
root2.right.right.right.right.right = new Node(22);
root2 = splay(root2, 20);
console.log(root2)Assume we search for node 20. The rotation should happen as follow:
- Zag-zag rotation: Replace node 15 with 20.
- Zag rotation: Replace node 10 with 20
However, my code result is:
Demo of image used this
CodePudding user response:
Both your algorithm and the imaged algorithm perform double rotations correctly, every time taking a pair of edges on the path to the target node, and applying a double rotation on that pair.
However, when the path to the target node has an odd length, then there is one edge that will undergo a single rotation. The choice of this single edge is different:
your algorithm will "split" the path in pairs starting from the root node, treating the remaining single edge at the end of the path separately.
the imaged algorithm will "split" the path in pairs starting from the target node, treating the remaining single edge at the start of the path (at the root) separately.
Here is your code aligned with that second strategy:
function splay(root, key) {
function splaySub(root) {
if (!root) throw new RangeError; // Value not found in tree
if (root.key === key) return root;
let side = key < root.key ? "left" : "right";
root[side] = splaySub(root[side]);
// Check if odd: then caller to deal with rotation
if (root[side].key === key) return root;
// Apply a double rotation, top-down:
root = key < root.key ? rightRotate(root) : leftRotate(root);
return key < root.key ? rightRotate(root) : leftRotate(root);
}
try {
root = splaySub(root);
return !root || root.key === key
// Path had even length: all OK
? root
// Odd length: Perform a final, single rotation
: key < root.key ? rightRotate(root) : leftRotate(root);
} catch(e) {
if (!(e instanceof RangeError)) throw e;
return root; // Not found: return original tree
}
}
When the searched value is not in the tree, this code will trigger an Exception, so to exit quickly out of recursion without any update to the tree. In this case that approach makes the code a bit cleaner (fewer checks for null values...).
Addendum
As in comments you explained that the splay function should also bring a node to the top when it doesn't find the value, I provide here the updated code. I took the opportunity to turn the code into more OOP style, so you'll find here some of your functions turned into methods:
class Node {
constructor(key, left=null, right=null) {
this.key = key;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
* inOrder(depth=0) {
if (this.right) yield * this.right.inOrder(depth 1);
yield [depth, this.key];
if (this.left) yield * this.left.inOrder(depth 1);
}
_rotate(toRight) {
const [side, otherSide] = toRight ? ["right", "left"] : ["left", "right"];
const orig = this[otherSide];
this[otherSide] = orig[side];
orig[side] = this;
return orig;
}
rightRotate() {
return this._rotate(true);
}
leftRotate() {
return this._rotate(false);
}
insert(key) {
const side = key < this.key ? "left" : "right";
if (this[side]) return this[side].insert(key);
this[side] = new Node(key);
}
}
class SplayTree {
constructor(...values) {
this.root = null;
for (const value of values) this.insert(value);
}
insert(value) {
if (this.root) this.root.insert(value);
else this.root = new Node(value);
}
splay(key) {
if (!this.root) return;
function splaySub(root) {
if (root.key === key) return root;
const side = key < root.key ? "left" : "right";
// Not found? Then do as if we looked for current node's key
if (!root[side]) {
key = root.key; // Modifies the outer-scoped variable
return root;
}
root[side] = splaySub(root[side]);
// Check if odd: then caller to deal with rotation
if (root[side].key === key) return root;
// Apply a double rotation, top-down:
root = root._rotate(key < root.key);
return root._rotate(key < root.key);
}
this.root = splaySub(this.root);
if (this.root.key !== key) this.root = this.root._rotate(key < this.root.key);
}
search(key) {
this.splay(key);
}
* inOrder() {
if (this.root) yield * this.root.inOrder();
}
toString() {
return Array.from(tree.inOrder(), ([depth, key]) => " ".repeat(depth) key).join("\n");
}
}
const tree = new SplayTree(10, 15, 16, 20, 21, 22);
console.log("Initial tree:");
console.log(tree.toString());
tree.search(19); // Not found, so it splays 20.
console.log("Final tree:");
console.log(tree.toString());