I have a date in string format with zulu time zone. I tried to get rid of the "Z" character with regular expression, but I guess there is a more efficient way.
input:
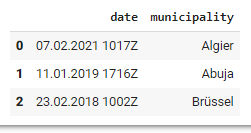
|index | date | municipality
|------| --------------------|--------------
| 0 | 07.02.2021 1017Z | Algier
| 1 | 11.01.2019 1716Z | Abuja
| 2 | 23.02.2018 1002Z | Brüssel
| 3 | 19.07.2021 1459Z | Brüssel
| 4 | 26.11.2019 1049Z | Berlin
desired outcome:
|index | date | municipality
|------| --------------------|--------------
| 0 | 2021-02-17 | Algier
| 1 | 2019-01-11 | Abuja
| 2 | 2018-02-23 | Bruxelles
| 3 | 2021-07-19 | Bruxelles
| 4 | 2019-11-26 | Berlin
CodePudding user response:
Instead of getting rid of the Z character, parse it correctly. EX:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'date': ['07.02.2021 1017Z', '11.01.2019 1716Z']})
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'], format='%d.%m.%Y %H%M%z')
# df['date']
# Out[19]:
# 0 2021-02-07 10:17:00 00:00
# 1 2019-01-11 17:16:00 00:00
# Name: date, dtype: datetime64[ns, UTC]
Note that setting the format keyword is optional, but it helps for general reliability to specify it explicitly.
You can also floor the hours if you don't want them:
df['date'] = df['date'].dt.floor('D')
# df['date']
# Out[21]:
# 0 2021-02-07 00:00:00 00:00
# 1 2019-01-11 00:00:00 00:00
# Name: date, dtype: datetime64[ns, UTC]
...or format to string:
df['date'].dt.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# 0 2021-02-07
# 1 2019-01-11
# Name: date, dtype: object
CodePudding user response:
This will works fine, I think. Additionally you can make some calculations with dates during transformation.
from datetime import datetime as dt
# specify input and output formats
input_format = '%d.%m.%Y %H%MZ'
output_format = '%Y-%m-%d'
# input date
input_date = '07.02.2021 1017Z'
# convert input date to datetime object
date = dt.strptime(input_date, input_format)
# convert datetime object to string with output format
output_date = dt.strftime(date, output_format)
print(output_date)
# output: 2021-02-07
CodePudding user response:
Alexei's method is a great solution also, we can switch its code into a function and use it example :
from datetime import datetime as dt
df=pd.DataFrame()
dates=['07.02.2021 1017Z','11.01.2019 1716Z','23.02.2018 1002Z']
municipality=['Algier','Abuja','Brüssel' ]
df['date']=dates
df['municipality']=municipality
# specify input and output formats
input_format = '%d.%m.%Y %H%M%z'
output_format = '%Y-%m-%d'
# input date
input_date = '07.02.2021 1017Z'
def convert(input_date):
# convert input date to datetime object
date = dt.strptime(input_date, input_format)
# convert datetime object to string with output format
output_date = dt.strftime(date, output_format)
return(output_date)
df.date.apply(convert)
df