I am trying to find a way to average an array column value with a condition on items from another column in that array - I am aware that a class or dictionary might be the best solution but I would like to stick to an array as in my real scenario I have to use an array.
In this case the data is as follows
Risk ID Data set 1 Data set 2
23359720 1154 587
23359720 1254 658
23359720 854 756
23293773 965 1456
20053692 1458 458
I would like to find the average of Data sets 1 and 2 per Risk ID, here is what I've tried but does not work - I have seen that this it's not possible to use for each and point it to a specific column, but not sure what else to do in the case of an array?
Edit: expected result data:
ArrayResultAverage()
Risk ID Avg Data set 1 Avg Data set 2
23359720 1087.33 667
23293773 965 1456
20053692 1458 458
Sub Test_Arr_Avg()
'
Dim TESTWB As Workbook
Dim TESTWS As Worksheet
Set TESTWB = ThisWorkbook
Set TESTWS = TESTWB.Worksheets("TEST")
'Array set up
Dim RngTest As Range
Dim ArrTestAvg As Variant
NbRowsTest = TESTWS.Range("A1").End(xlDown).Row
Set RngTest = TESTWS.Range(TESTWS.Cells(1, 1), TESTWS.Cells(NbRowsTest, 3))
ArrTestAvg = RangeToArray2D(RngTest)
'Find the average of Data Range 1 for each item in Risk ID
For k = 1 To UBound(ArrTestAvg, 1)
Dim Sum As Variant
Sum = 0
For Each Item In ArrTestAvg(k, 1)
Sum = Sum ArrTestAvg(k, 2)
Dim AverageDataSet1 As Variant
AverageDataSet1 = Sum / UBound(ArrTestAvg(Item)) 1
Debug.Print AverageDataSet1
Next Item
Next k
End Sub
Public Function RangeToArray2D(inputRange As Range) As Variant()
Dim size As Integer
Dim inputValue As Variant, outputArray() As Variant
inputValue = inputRange
On Error Resume Next
size = UBound(inputValue)
If Err.Number = 0 Then
RangeToArray2D = inputValue
Else
On Error GoTo 0
ReDim outputArray(1 To 1, 1 To 1)
outputArray(1, 1) = inputValue
RangeToArray2D = outputArray
End If
On Error GoTo 0
End Function
CodePudding user response:
It would be complicated to use a single Dictionary. Here I add a Sub-Dictionary for each Risk ID to the main Dictionary. The Sub-Dictionary is used to hold all the values for each ID. The final step is to create an array of averages for all the main Dictionary items.
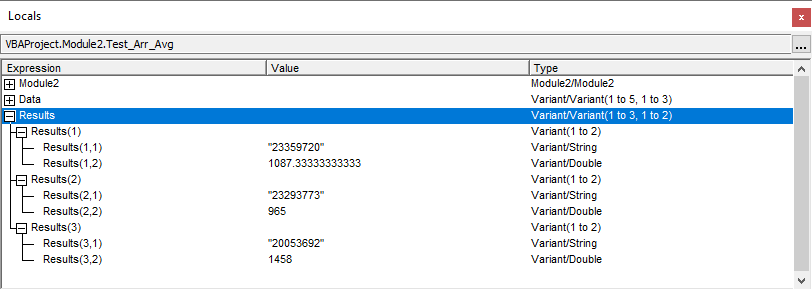
Sub Test_Arr_Avg()
Dim Data As Variant
With TestWS.Range("A1").CurrentRegion
Data = .Offset(1).Resize(.Rows.Count - 1, 3)
End With
Dim Results As Variant
Results = KeyedAverages(Data, 1, 2)
Stop
End Sub
Function KeyedAverages(Data As Variant, IDColumn As Long, ValueColumn As Long)
Dim Map As Object
Set Map = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
Dim Key As Variant
Dim r As Long
For r = 1 To UBound(Data)
Key = CStr(Data(r, IDColumn))
If Not Map.Exists(Key) Then Map.Add Key, CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
With Map(Key)
.Add CStr(.Count), Data(r, ValueColumn)
End With
Next
Dim Results As Variant
Dim Values As Variant
ReDim Results(1 To Map.Count, 1 To 2)
Dim n As Long
For Each Key In Map.Keys
n = n 1
Values = Map(Key).Items
Results(n, 1) = Key
Results(n, 2) = WorksheetFunction.Average(Values)
Next
KeyedAverages = Results
End Function
Public Function TestWB() As Workbook
Set TestWB = ThisWorkbook
End Function
Public Function TestWS() As Worksheet
Set TestWS = TestWB.Worksheets("Test")
End Function
CodePudding user response:
Get Averages of Unique Data
- Adjust the values in the constants section, especially the destination worksheet name (it's the same as the source worksheet name) and its first cell address.
- The dictionary's keys hold the unique risk ids, while its items (values) hold the associated destination rows.
- The result is written to the same array (which is too big) but with
drthe destination row size is tracked and only three columns will be copied. - Before the calculation of the averages, column 1 holds the unique risk ids (the same order as in the dictionary), columns 2 and 3 hold the sums while columns 4 and 5 hold the counts of the first and second data set respectively.
Option Explicit
Sub Test_Arr_Avg()
' Source
Const sName As String = "Sheet1"
' Destination
Const dName As String = "Sheet1"
Const dFirstCellAddress As String = "E1"
' Workbook
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook ' workbook containing this code
' Read from source.
Dim sws As Worksheet: Set sws = wb.Worksheets(sName)
Dim slRow As Long: slRow = sws.Cells(sws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
Dim srg As Range: Set srg = sws.Range("A1", sws.Cells(slRow, "C"))
Dim srCount As Long: srCount = srg.Rows.Count
' Write source range values to array.
Dim Data As Variant: Data = GetRange(srg)
' Add two helper columns for the count.
ReDim Preserve Data(1 To srCount, 1 To 5)
' Sum up and count uniques.
Dim dict As Object: Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
dict.CompareMode = vbTextCompare
Dim dr As Long: dr = 1 ' first row are headers
Dim sr As Long
Dim cr As Long
Dim c As Long
For sr = 2 To srCount
' Sum up.
If dict.Exists(Data(sr, 1)) Then
cr = dict(Data(sr, 1))
For c = 2 To 3
Data(cr, c) = Data(cr, c) Data(sr, c)
Next c
Else
dr = dr 1
cr = dr
dict(Data(sr, 1)) = cr
For c = 1 To 3
Data(cr, c) = Data(sr, c)
Next c
End If
' Count.
For c = 4 To 5
Data(cr, c) = Data(cr, c) 1
Next c
Next sr
' Calculate averages.
For cr = 2 To dr
For c = 2 To 3
Data(cr, c) = Data(cr, c) / Data(cr, c 2)
' You might want to round the results instead:
'Data(cr, c) = Round(Data(cr, c) / Data(cr, c 2), 2)
Next c
Next cr
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
' Write to destination.
Dim dws As Worksheet: Set dws = wb.Worksheets(dName)
With dws.Range(dFirstCellAddress).Resize(, 3)
.Resize(dr).Value = Data
' Clear below.
.Resize(dws.Rows.Count - .Row - dr 1).Offset(dr).Clear
' Apply various formatting.
.Font.Bold = True ' headers
.Resize(dr - 1, 2).Offset(1, 1).NumberFormat = "#0.00" ' averages
.EntireColumn.AutoFit ' columns
End With
'wb.Save
' Inform.
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
MsgBox "Risk ids averaged.", vbInformation
End Sub
''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
' Purpose: Returns the values of a range ('rg') in a 2D one-based array.
' Remarks: If ˙rg` refers to a multi-range, only its first area
' is considered.
''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
Function GetRange( _
ByVal rg As Range) _
As Variant
Const ProcName As String = "GetRange"
On Error GoTo ClearError
If rg.Rows.Count rg.Columns.Count = 2 Then ' one cell
Dim Data As Variant: ReDim Data(1 To 1, 1 To 1): Data(1, 1) = rg.Value
GetRange = Data
Else ' multiple cells
GetRange = rg.Value
End If
ProcExit:
Exit Function
ClearError:
Debug.Print "'" & ProcName & "' Run-time error '" _
& Err.Number & "':" & vbLf & " " & Err.Description
Resume ProcExit
End Function
