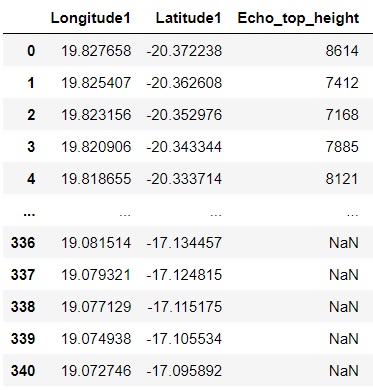
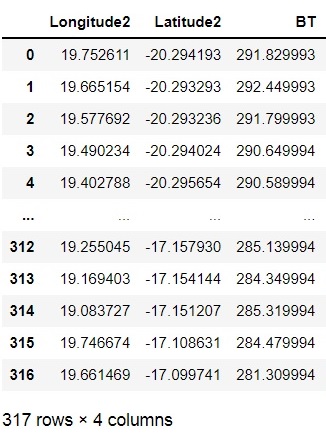
I have two data frames that have Longitude and Latitude columns. DF1 and DF2:
DF1 = pd.DataFrame([[19.827658,-20.372238,8614], [19.825407,-20.362608,7412], [19.081514,-17.134456,8121]], columns=['Longitude1', 'Latitude1','Echo_top_height'])
DF2 = pd.DataFrame([[19.083727, -17.151207, 285.319994], [19.169403, -17.154144, 284.349994], [19.081514,-17.154456, 285.349994]], columns=['Longitude2', 'Latitude2','BT'])
I need to find a match for long and lat in DF1 with a long and lat in DF2. And where data match, add the corresponding value from the BT column from DF2 to DF1.
I used the code from here and managed to check if there is a match:
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import haversine_distances
threshold = 5000 # meters
earth_radius = 6371000 # meters
DF1['nearby'] = (
# get the distance between all points of each DF
haversine_distances(
# note that you need to convert to radiant with *np.pi/180
X=DF1[['Latitude1','Longitude1']].to_numpy()*np.pi/180,
Y=DF2[['Latitude2','Longitude2']].to_numpy()*np.pi/180)
*earth_radius < threshold).any(axis=1).astype(int)
So the result I need would look like this:
Longitude1 Latitude1 Echo_top_height BT
19.82 -20.37 8614 290.345
19.82 -20.36 7412 289.235
and so on...
CodePudding user response:
It looks like you are comparing the dataframes by index, so you can use join and drop the unnecessary rows and columns:
DF3 = DF1.join(DF2[['BT']])
DF3 = DF3[DF3['nearby'].eq(1)].drop('nearby', axis=1)
DF3
full reproducible code:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import haversine_distances
DF1 = pd.DataFrame([[19.827658,-20.372238,8614], [19.825407,-20.362608,7412], [19.081514,-17.134456,8121]], columns=['Longitude1', 'Latitude1','Echo_top_height'])
DF2 = pd.DataFrame([[19.083727, -17.151207, 285.319994], [19.169403, -17.154144, 284.349994], [19.081514,-17.154456, 285.349994]], columns=['Longitude2', 'Latitude2','BT'])
DF1, DF2
threshold = 5000 # meters
earth_radius = 6371000 # meters
DF1['nearby'] = (
# get the distance between all points of each DF
haversine_distances(
# note that you need to convert to radiant with *np.pi/180
X=DF1[['Latitude1','Longitude1']].to_numpy()*np.pi/180,
Y=DF2[['Latitude2','Longitude2']].to_numpy()*np.pi/180)
*earth_radius < threshold).any(axis=1).astype(int)
DF3 = DF1.join(DF2[['BT']])
DF3 = DF3[DF3['nearby'].eq(1)].drop('nearby', axis=1)
DF3
Output:
Out[1]:
Longitude1 Latitude1 Echo_top_height BT
2 19.081514 -17.134456 8121 285.349994
CodePudding user response:
You can use BallTree:
from sklearn.neighbors import BallTree, DistanceMetric
# DF1
coords = np.radians(df2[['Latitude2', 'Longitude2']])
dist = DistanceMetric.get_metric('haversine')
tree = BallTree(coords, metric=dist)
# DF2
coords = np.radians(df1[['Latitude1', 'Longitude1']])
distances, indices = tree.query(coords, k=1)
df1['BT'] = df2['BT'].iloc[indices.flatten()].values
df1['Distance'] = distances.flatten()
Output:
| Longitude1 | Latitude1 | Echo_top_height | BT | Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19.8277 | -20.3722 | 8614 | 284.35 | 0.0572097 |
| 19.8254 | -20.3626 | 7412 | 284.35 | 0.0570377 |
| 19.0815 | -17.1345 | 8121 | 285.32 | 0.000294681 |