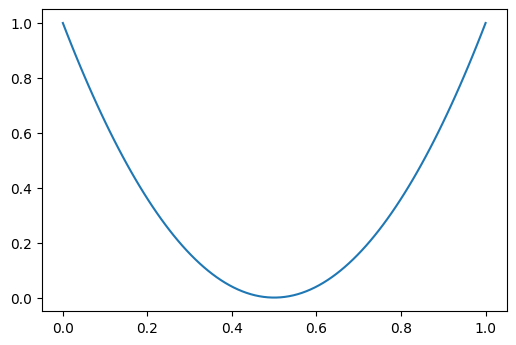
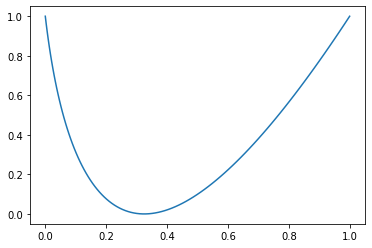
I'm having a curve as follows:
The curve is generated with the following code:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# normalize array
def min_max_scale_array(arr):
arr = np.array(arr)
return (arr - arr.min())/(arr.max()-arr.min())
x = np.linspace(-50,48,100)
y = x**2 2*x 2
x = min_max_scale_array(x)
y = min_max_scale_array(y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
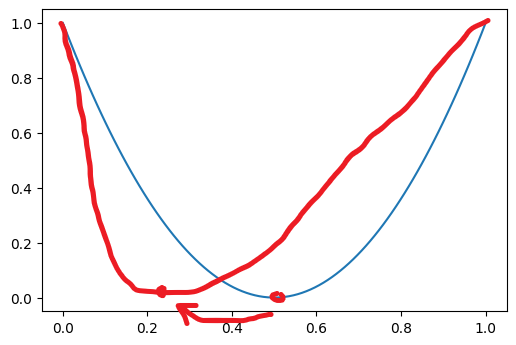
How can I generate a new curve by moving only the bottom left (or right) and keeping both ends the same like this? Thank you!
Edit: any curve generating algorithm is appreciated, as long as it works!
CodePudding user response:
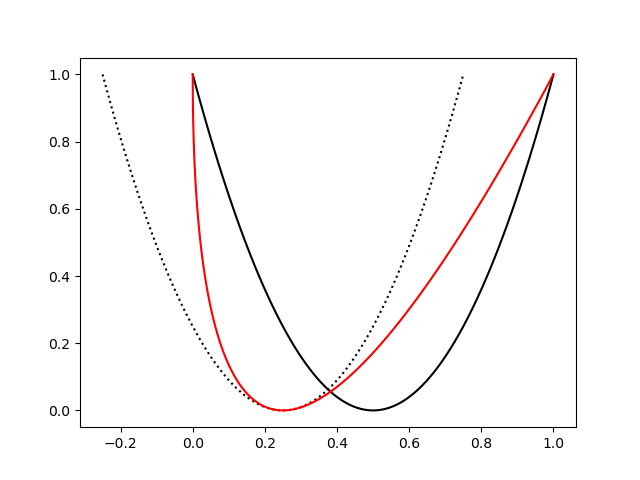
One way of doing so is defining x,y as before, but applying a shift. The dotted line shows if you just shift it. But now at the top most y we don't want to shift it, so we'd like to weight the shifted version on the bottom (y=0) by 1 but on the top (y=1) by 0 such that we get a gradual interpolation. We can do this by multiplying the shift by (1-y):
a = 0.25 # how far to shift left
plt.plot(x, y, 'k')
plt.plot(x-a, y, 'k:')
plt.plot(x-a*(1-y), y, 'r')
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
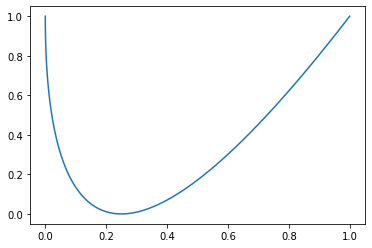
Easiest solution: apply a sublinear transformation to x - a quadratic function will work.
x = x**2 # works because x is scaled to 0-1
ax.plot(x, y)
UPD: as requested, a scaling factor would look something like:
scaling_factor = 0.7
x = scaling_factor*(x**2) (1-scaling_factor)*x