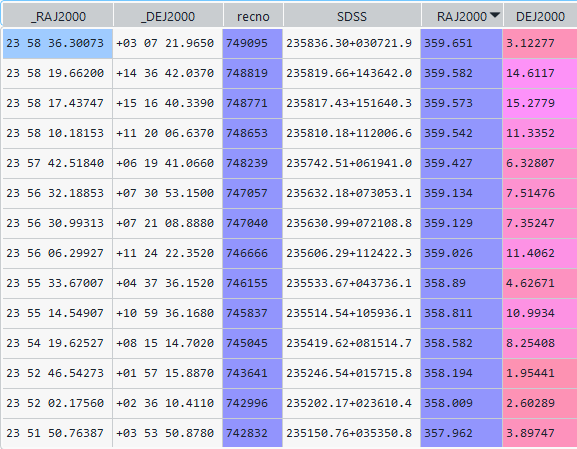
I have a pandas dataframe that includes the columns _RA2000 and _DEJ2000, thus:
and I'd like to convert them to degrees, as they appear in the RAJ2000 and DEJ2000 columns. I should be able to do it with astropy, but if I try the first one:
from astropy import units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
c = SkyCoord('23 58 36.30073', 'icrs', unit=(u.hourangle))
I get
ValueError: Invalid character at col 0 in angle 'icrs'
So my questions are:
- why is the string I've inputted causing the error, and
- how can I apply
SkyCoordto thepandascolumns?
CodePudding user response:
You need to do the conversion for both coords simultaneously and supply the frame as a keyword argument:
import pandas as pd
from astropy import units as u
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
df = pd.DataFrame({'_RAJ2000': ['23 58 36.30073 ', '23 58 19.66200 ', '23 58 17.43747 ', '23 58 10.18153 ',
'23 57 42.51840 ', '23 56 32.18853 ', '23 56 30.99313 ', '23 56 06.29927 ',
'23 55 33.67007 ', '23 55 14.54907 ', '23 54 19.62527 ', '23 52 46.54273 ',
'23 52 02.17560 ', '23 51 50.76387 '],
'_DEJ2000': [' 03 07 21.9650', ' 14 36 42.0370', ' 15 16 40.3390', ' 11 20 06.6370',
' 06 19 41.0660', ' 07 30 53.1500', ' 07 21 08.8880', ' 11 24 22.3520',
' 04 37 36.1520', ' 10 59 36.1680', ' 08 15 14.7020', ' 01 57 15.8870',
' 02 36 10.4110', ' 03 53 50.8780']})
df = pd.concat(
(df, SkyCoord(df._RAJ2000, df._DEJ2000, frame='icrs', unit=(u.hourangle, u.deg)).to_table().to_pandas()),
axis=1).rename(columns={'ra': 'RAJ2000', 'dec': 'DEJ2000'})
Result:
_RAJ2000 _DEJ2000 RAJ2000 DEJ2000
0 23 58 36.30073 03 07 21.9650 359.651253 3.122768
1 23 58 19.66200 14 36 42.0370 359.581925 14.611677
2 23 58 17.43747 15 16 40.3390 359.572656 15.277872
3 23 58 10.18153 11 20 06.6370 359.542423 11.335177
4 23 57 42.51840 06 19 41.0660 359.427160 6.328074
5 23 56 32.18853 07 30 53.1500 359.134119 7.514764
6 23 56 30.99313 07 21 08.8880 359.129138 7.352469
7 23 56 06.29927 11 24 22.3520 359.026247 11.406209
8 23 55 33.67007 04 37 36.1520 358.890292 4.626709
9 23 55 14.54907 10 59 36.1680 358.810621 10.993380
10 23 54 19.62527 08 15 14.7020 358.581772 8.254084
11 23 52 46.54273 01 57 15.8870 358.193928 1.954413
12 23 52 02.17560 02 36 10.4110 358.009065 2.602892
13 23 51 50.76387 03 53 50.8780 357.961516 3.897466
CodePudding user response:
You can also do this using the Angle class if you just want to use astropy to parse the coordinate strings
>>> from astropy.coordinates import Angle
>>> Angle(['23 58 36.30073 ', '23 58 19.66200 '], unit='hourangle').to_value('deg')
array([359.65125304, 359.581925 ])
>>> Angle([' 03 07 21.9650', ' 14 36 42.0370'], unit='deg').to_value('deg')
array([ 3.12276806, 14.61167694])