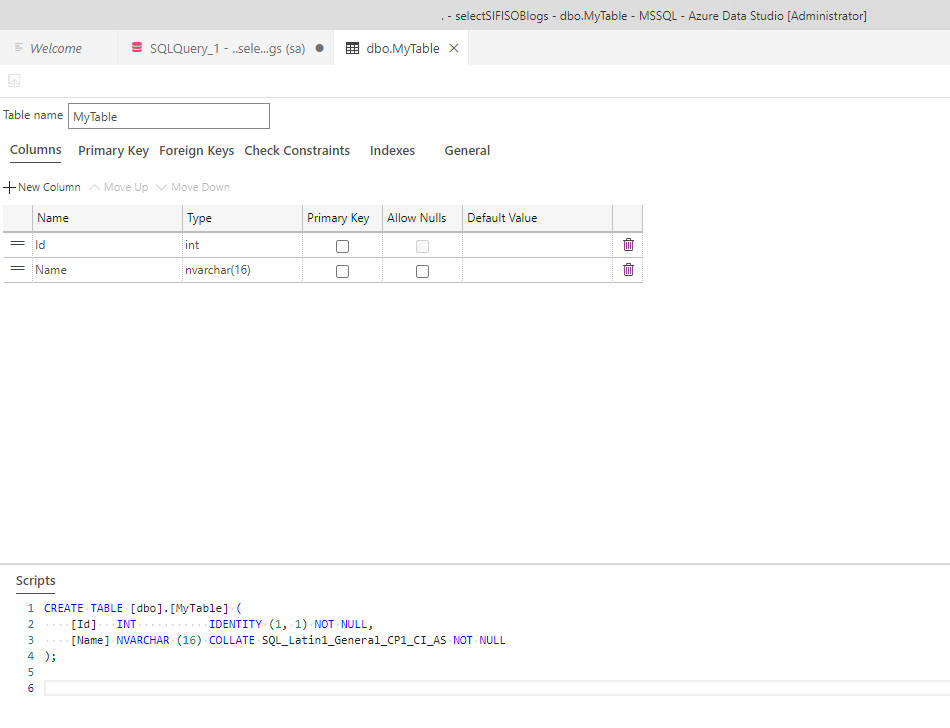
I created a table using the following SQL command:
CREATE TABLE [my-azure-db].dbo.MyTable (
Id int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
Name nvarchar(32) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL,
);
When I check the table with DBeaver, it looks like this:

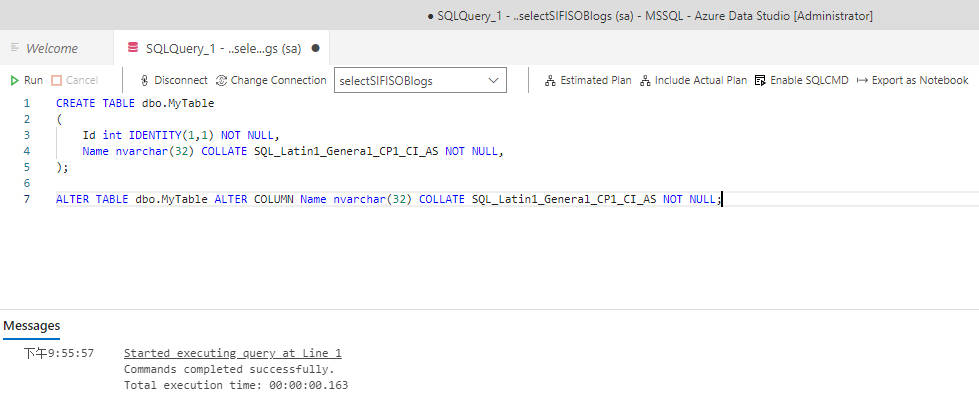
Therefore, I tried to alter the table and change the size of the field with the following script.
ALTER TABLE [my-azure-db].dbo.MyTable ALTER COLUMN Name nvarchar(32) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL;
The script runs through and the varchar size is still stuck at 16. When I try to do this directly in the Azure Query Editor, it also does nothing.
CodePudding user response:
CREATE TABLE dbo.MyTable
(
Id int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
Name nvarchar(32) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL,
);
ALTER TABLE dbo.MyTable ALTER COLUMN Name nvarchar(16) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL;
CodePudding user response:
I reproduced this in Azure SQL Database, and there is no change in the nvarchar size, and I am able to change it using query.
I created the above table with the name of reprotable and this is my table description with nvarchar(32).
The code for table description below is taken from this article of dataedo by Bart Gawrych.
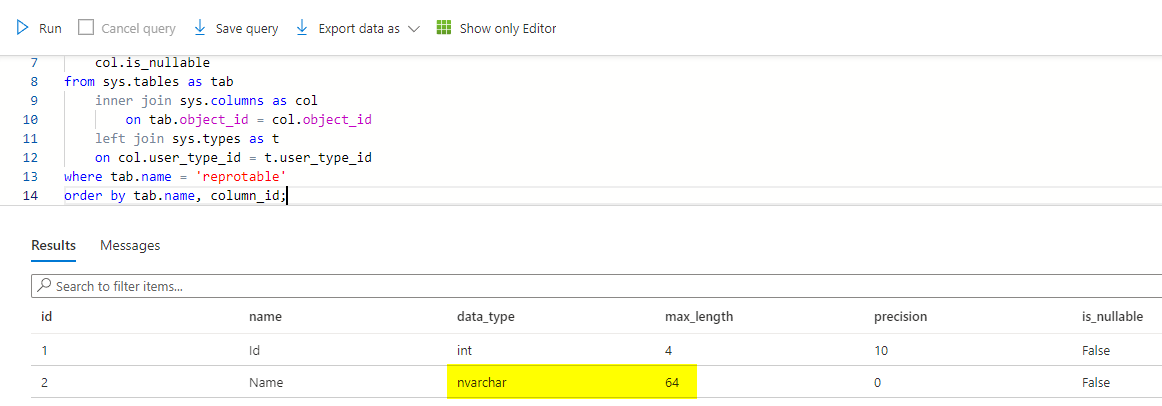
You can see the max_length is 64 above which means it is nvarchar(32).
Change to nvarchar(16) using your code.
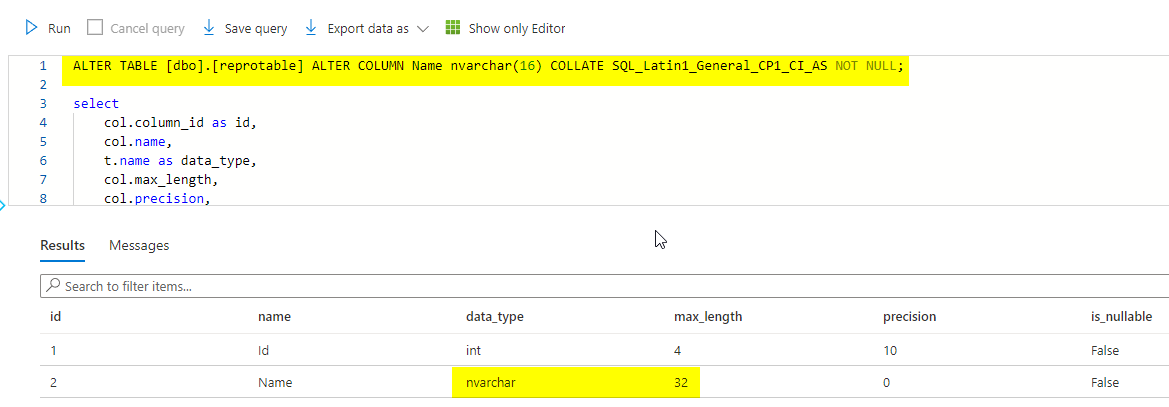
Try to use [dbo].[tablename] and check the result as suggested by Courser Xu.
And I suggest you try to create the table and Azure SQL DB and SSMS also if possible and check whether still you are getting the same.