Currently I have achieved the title by using .apply() with a lambda function:
calFilteredDf['startTime'] = calFilteredDf['start'].apply(lambda x: x['dateTime'])
This is very slow and I was wondering how I could achieve the same results in less time. calFilteredDf['start'] is a Pandas Series and the data from the 'start' column looks like this:
1 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-11T15:00:0...
2 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-12T09:30:0...
3 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-12T10:00:0...
4 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-18T11:00:0...
...
1692 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-09T14:00:0...
1693 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-09T15:00:0...
1694 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T11:30:0...
1695 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T16:00:0...
1696 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T17:00:0...
Name: start, Length: 1697, dtype: object
and the data from the new 'startTime' column needs to look like this:
1 2021-08-11T15:00:00-04:00
2 2021-08-12T09:30:00-04:00
3 2021-08-12T10:00:00-04:00
4 2021-08-18T11:00:00-04:00
...
1692 2023-08-09T14:00:00-04:00
1693 2023-08-09T15:00:00-04:00
1694 2023-08-10T11:30:00-04:00
1695 2023-08-10T16:00:00-04:00
1696 2023-08-10T17:00:00-04:00
Name: startTime, Length: 1697, dtype: object
Is there a way to do this quickly? I have tried to set
calFilteredDf['startTime'] = calFilteredDf['startTime']['dateTime']
I've also tried using .loc which didn't work because the rows of 'start' aren't the right data type and I've tried using the swifter library to parallelize the process that .apply() is doing but since the dataset is not very large it actually made it slower because of the extra steps the library preforms to determine what the best way to process the data is.
CodePudding user response:
pd.json_normalize is more convenient to use, but it turns out to be the slowest. The list generator has become the fastest of all. Below is the pd.json_normalize code. And tests using different approaches.
import pandas as pd
aaa = [[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-12T09:30'}],
[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-12T10:00'}],
[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-18T11:00'}],
[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-09T14:00'}],
[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-09T15:00'}],
[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T11:30'}],
[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T16:00'}],
[{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T17:00'}]]
calFilteredDf = pd.DataFrame(aaa)
print(calFilteredDf)
calFilteredDf = pd.json_normalize(calFilteredDf[0])
calFilteredDf['startTime'] = calFilteredDf['dateTime']
print(calFilteredDf)
Input
0
0 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-12T09:30'}
1 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-12T10:00'}
2 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-18T11:00'}
3 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-09T14:00'}
4 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-09T15:00'}
5 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T11:30'}
6 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T16:00'}
7 {'date': None, 'dateTime': '2023-08-10T17:00'}
Output
date dateTime startTime
0 None 2021-08-12T09:30 2021-08-12T09:30
1 None 2021-08-12T10:00 2021-08-12T10:00
2 None 2021-08-18T11:00 2021-08-18T11:00
3 None 2023-08-09T14:00 2023-08-09T14:00
4 None 2023-08-09T15:00 2023-08-09T15:00
5 None 2023-08-10T11:30 2023-08-10T11:30
6 None 2023-08-10T16:00 2023-08-10T16:00
7 None 2023-08-10T17:00 2023-08-10T17:00
Yes, indeed json_normalize is twice as slow. Below is the code where apply, json_normalize, transform, list generator are used.
now = datetime.datetime.now()
for i in range(10000):
calFilteredDf[0].apply(lambda x: x['dateTime'])
time_ = datetime.datetime.now() - now
print('apply', time_)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
for i in range(10000):
pd.json_normalize(calFilteredDf[0])
time_ = datetime.datetime.now() - now
print('json_normalize', time_)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
for i in range(10000):
calFilteredDf[0].transform(lambda x: x['dateTime'])
time_ = datetime.datetime.now() - now
print('transform', time_)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
for i in range(10000):
a = [i['dateTime'] for i in calFilteredDf[0]]
time_ = datetime.datetime.now() - now
print('list generator', time_)
Output
apply 0:00:01.707580
json_normalize 0:00:03.666553
transform 0:00:01.896933
list generator 0:00:00.056657
The output is to use a list generator.
CodePudding user response:
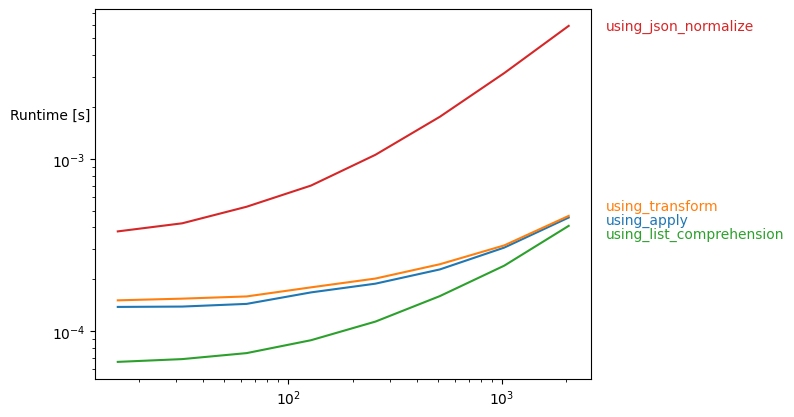
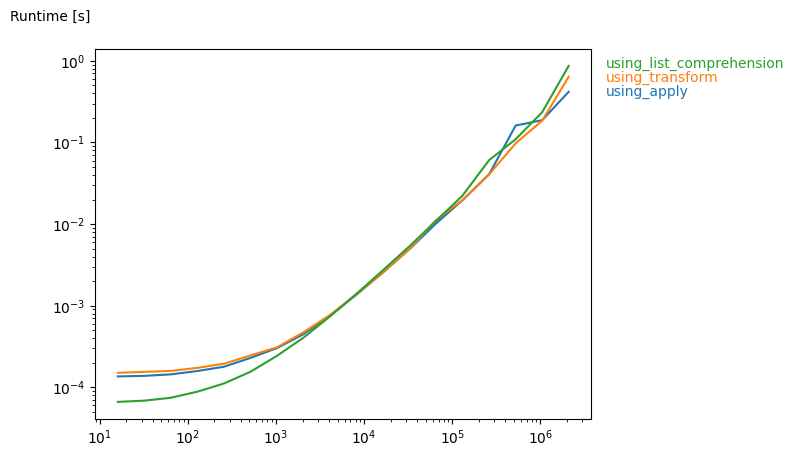
apply, transform and list comprehension methods produce similar speeds on large datasets (with more than 2000 rows), and they all are quite fast! On smaller datasets (especially < 1000 rows) list comprehension beats other methods.
Timings using the perfplot package:
def gen(n):
return pd.Series([{'date': None, 'dateTime': '2021-08-12T09:30'}] * n)
def using_apply(s):
return s.apply(lambda x: x['dateTime'])
def using_transform(s):
return s.transform(lambda x: x['dateTime'])
def using_list_comprehension(s):
return pd.Series([i['dateTime'] for i in s])
import perfplot
perfplot.plot(
setup=gen,
kernels=[using_apply, using_transform, using_list_comprehension],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(4, 22)],
equality_check=None
)
Comparison with ps.json_normalize() on smaller datasets:
def using_json_normalize(s):
return pd.json_normalize(s)['dateTime']
perfplot.plot(
setup=gen,
kernels=[using_apply, using_transform, using_list_comprehension, using_json_normalize],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(4, 12)],
equality_check=None
)