Sorry if my question is too stupid, but I can't figure out how to solve my problem.
I have a motor with a gearbox and I also have an absolute encoder mounted on the gearbox shaft. I need to make the output shaft rotate in a range from -90 to 90 and it is centered in 0°.
Now, when the shaft is in 0°, then the encoder outputs 1010, when it is at -90°, the encoder outputs 1120 and when it is in 90° it outputs 900.
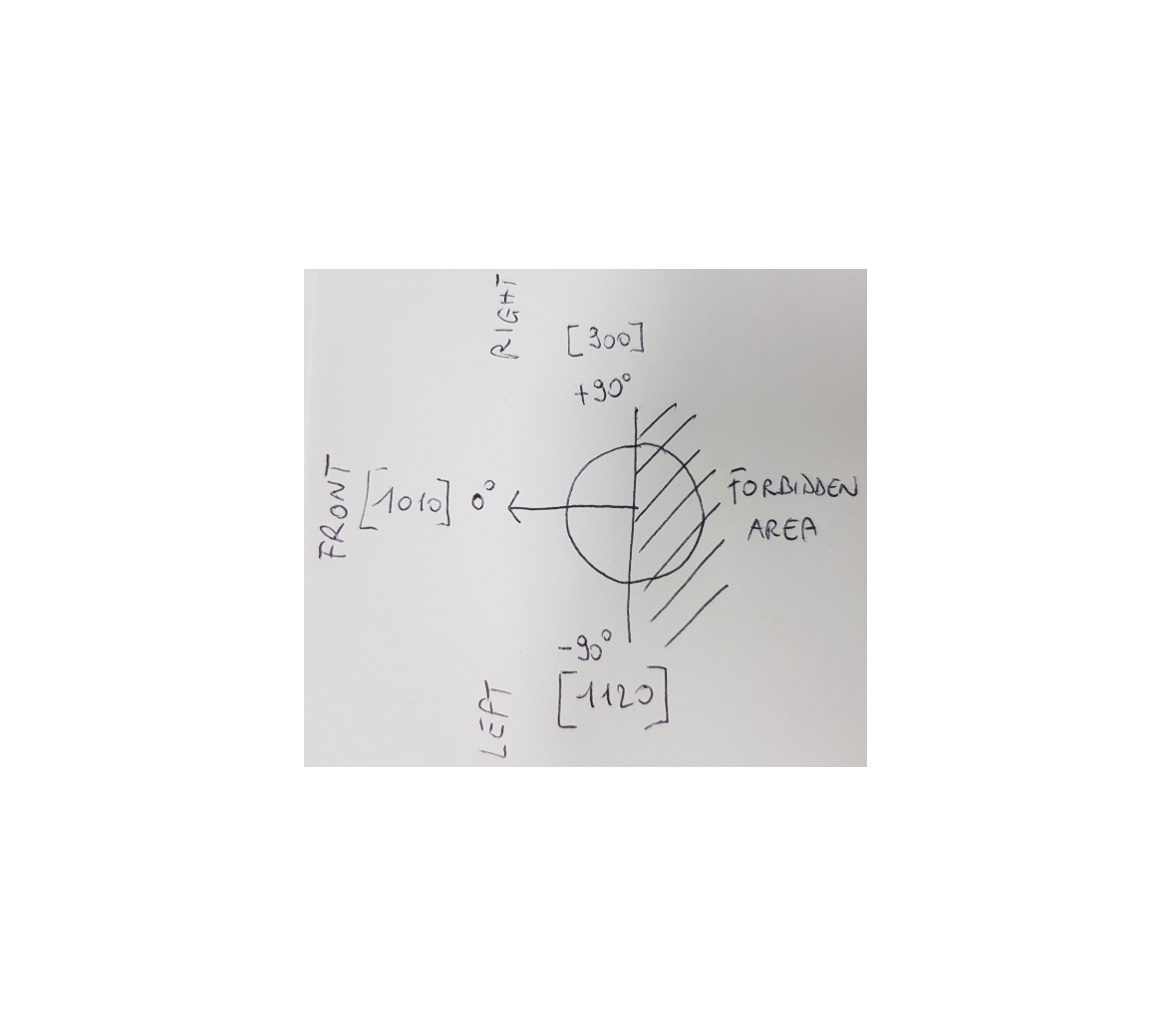
When the shaft is in 0° and has to reach 90°, the motor must rotate clockwise and when it needs to reach -90°, it needs to rotate counterclockwise.
I would like to command the motor by only giving it the position in degree. For example, I'd like to have a function like:
move_motor(1, 45°)
int move_motor(id_motor, pos){
read current motor position
// motor is at 0°
make motor #1 spins clockwise until encoder returns 955
}
I think that a PID controller would be a smart solution, but I really do not know how to implement it in C , sorry, I'm not a developer. Or do you suggest just to use if/else statements?
EDIT:
In order to make the motor move, I use this function:
void move_motor(motor_id, direction)
and it makes the motor spin in counterclockwise or clockwise depending on the second parameter To stop the motors:
void stop_motor(motor_id, 0)
and this other function:
int get_enc(encoder1)
returns an integer depending on the encoder1 readings.
So for example, to reach the desired position it should be:
while (get_enc != desired_position){
move_motor(motor_id, direction)
}
but the direction should be handled, too.
CodePudding user response:
Here's how I've understood it:
input output
----------------
<= -90° 1120
-45° 1065
0° 1010
45° 955
>= 90° 900
Then this function would do that:
#include <algorithm>
unsigned angle2pid(float angle_in_degrees) {
return std::clamp(1010 - angle_in_degrees * 55 / 45, 900.f, 1120.f);
}
std::clamp is used to limit the output between 900 and 1120.
CodePudding user response:
Here you go:
unsigned angle2pid(double angle_in_degrees)
{
return 1010 - angle_in_degrees * 55 / 45;
}
void move_motor(int motor_id, double angle)
{
static const int CLOSE_ENOUGH = 10;
int currentPosition = get_enc(motor_id);
int desiredPosition = angle2pid(angle);
// IF WE ARE CLOSE ENOUGH, DO NOTHING...
if(std::abs(currentPosition - desiredPosition) <= CLOSE_ENOUGH)
{
return;
}
if(desiredPosition > currentPosition)
{
move_motor(motor_id, CLOCKWISE);
while(desiredPosition > currentPosition)
{
currentPosition = get_enc(motor_id);
}
stop_motor(motor_id);
}
else if(desiredPosition < currentPosition)
{
move_motor(motor_id, COUNTER_CLOCKWISE);
while(desiredPosition < currentPosition)
{
currentPosition = get_enc(motor_id);
}
stop_motor(motor_id, 0);
}
}
Note that the motor_id might be a different type which you'll have to slightly adjust. And perhaps the get_enc requires a different argument, but this is the idea.
Credit goes to @TedLyngmo who provided the angle2pid function.
