I have a file (file.xvg), of which I plot the result using matplotlib and numpy (version Python 3.9.12). here my script:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy
import numpy as np
from scipy import signal
x, y = numpy.loadtxt("file.xvg", unpack=True)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(13,8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x, y, color="k", linestyle='solid', linewidth=0.8)
ax.set_xlabel("Times (ps)", fontweight='bold', fontsize = 18, labelpad=3)
ax.set_ylabel("Pressures (bar)", fontweight='bold', fontsize = 18, labelpad=3)
plt.show()
and the file.xvg
0.0000000 0.0287198 0.0100000 0.0655187 0.0200000 0.0665948 0.0300000 0.0676697 0.0400000 0.0797021 0.0500000 0.0883750 0.0600000 0.0824649 0.0700000 0.0726798 0.0800000 0.0749663 0.0900000 0.0746549 0.1000000 0.0767466 0.1100000 0.1051620 0.1200000 0.0846607 0.1300000 0.0746683 0.1400000 0.0744862 0.1500000 0.0913541 0.1600000 0.0844304 0.1700000 0.0750595 0.1800000 0.0783450 0.1900000 0.0869718 0.2000000 0.0969575 0.2100000 0.0924280 0.2200000 0.0759971 0.2300000 0.0704025 . . .
I wanted to plot the running average as in the figure below:
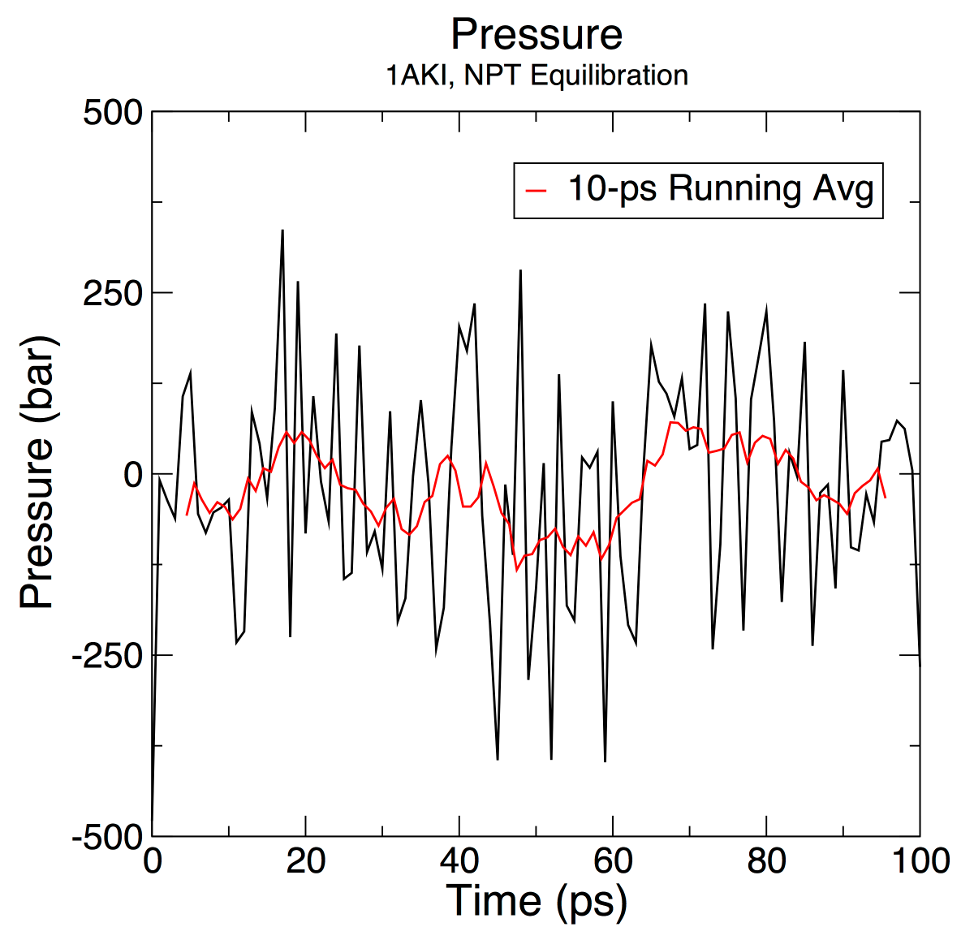
The average value of the plot figure is 7.5 ± 160.5 bar
CodePudding user response:
You have to calculate your running avg (selecting a window of values rang) for both your x and y array:
x_avg = []
y_avg = []
rang = 10
for ind in range(len(y)-rang 1):
y_avg.append(np.mean(y[ind:ind rang]))
x_avg.append(np.mean(x[ind:ind rang]))
ax.plot(x_avg, r_avg, color="red", linestyle='solid', linewidth=0.8)
PS: what a throwback, is that GROMACS? :)
CodePudding user response:
import numpy as np
from pandas import DataFrame as df
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
origin_data = np.array([
[0.0000000, 0.0287198],
[0.0100000, 0.0655187],
[0.0200000, 0.0665948],
[0.0300000, 0.0676697],
[0.0400000, 0.0797021],
[0.0500000, 0.0883750],
[0.0600000, 0.0824649],
[0.0700000, 0.0726798],
[0.0800000, 0.0749663],
[0.0900000, 0.0746549],
[0.1000000, 0.0767466],
[0.1100000, 0.1051620],
[0.1200000, 0.0846607],
[0.1300000, 0.0746683],
[0.1400000, 0.0744862],
[0.1500000, 0.0913541],
[0.1600000, 0.0844304],
[0.1700000, 0.0750595],
[0.1800000, 0.0783450],
[0.1900000, 0.0869718],
[0.2000000, 0.0969575],
[0.2100000, 0.0924280],
[0.2200000, 0.0759971],
[0.2300000, 0.0704025],
])
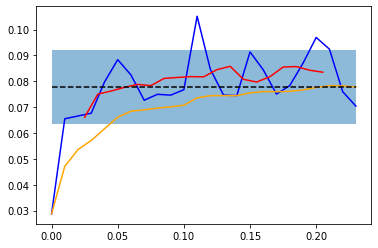
n = origin_data.shape[0]
data = df(origin_data, columns=['x', 'y'])
window = 6
roll_avg = data.rolling(window).mean()
roll_avg_cumulative = data['y'].cumsum()/np.arange(1, 25)
avg = data['y'].mean()
std_error = data['y'].std()
print('{:.2f} /- {:.2f}'.format(avg, std_error))
# all data
plt.plot(data['x'], data['y'], c='b')
# rolling avg by "window"
plt.plot(roll_avg['x'], roll_avg['y'], c='r')
# cumulative avg
plt.plot(data['x'], roll_avg_cumulative, c='orange')
# horizontal line at overall avg
plt.hlines(avg, data['x'].iloc[0], data['x'].iloc[-1],
ls='--',
colors=['k'])
# ymax - ymin band
plt.fill_between(data['x'], avg std_error, avg-std_error, alpha=0.5)