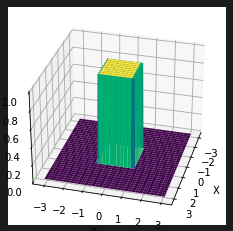
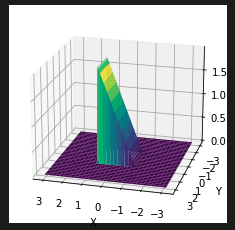
I have a 2D grid with shape [sampling_size* sampling_size, 2]. I'm using it to generatd 3D surfaces in Tensorflow as follows:
def cube(G):
res = []
for (X, Y) in G:
if X >= -1 and X < 1 and Y >= -1 and Y < 1:
res.append(1.)
else:
res.append(0.)
return tf.convert_to_tensor(res)
Z_cube = cube(grid)
cube_2d = tf.reshape(Z_cube, [sampling_size, sampling_size])
plot_surface(X, Y, cube_2d)
Here is another example:
def prism(G):
res = []
for (X, Y) in G:
if X >= -1 and X < 1 and Y >= -1 and Y < 1:
res.append(X 1.)
else:
res.append(0.)
return tf.convert_to_tensor(res)
Z_prism = prism(grid)
prism_2d = tf.reshape(Z_prism, [sampling_size, sampling_size])
My problem is: since this uses loops, this approach is not efficient, taking 10 seconds to generating a single cube.
I'm wondering if someone knows a more efficient vectorized way to generate those surfaces.
EDIT: I use the following code to generate the grid
sampling_size = 100
limit = math.pi
def generate_grid(_from, _to, _step):
range_ = tf.range(_from, _to, _step, dtype=float)
x, y = tf.meshgrid(range_, range_)
_x = tf.reshape(x, (-1,1))
_y = tf.reshape(y, (-1,1))
return tf.squeeze(tf.stack([_x, _y], axis=-1)), x, y
grid, X, Y = generate_grid(-limit, limit, 2*limit / sampling_size)
And for plotting:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
def plot_surface(X, Y, Z, a = 30, b = 15):
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=3, cstride=3, linewidth=1, antialiased=True,
cmap=cm.viridis)
ax.view_init(a, b)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
What you're looking for is the multiplexing mode of tf.where. Based on a condition, choose if the element should be taken from Tensor A or Tensor B.
You can then rewrite your prism function that way:
def tf_prism(G):
X,Y = tf.unstack(G, axis=-1)
# Here, the operator '&' replaces 'tf.math.logical_and'
# Do not use the keyword 'and' it will not work
return tf.where(
(X >= -1) & (X < 1) & (Y >= -1) & (Y < 1),
X 1,
0
)
Comparing execution speed with timeit:
[1]: %timeit tf_prism(grid)
373 µs ± 3.67 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
[2]: %timeit prism(grid)
6.47 s ± 127 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)