If I want to have two tables with many-to-many relationship, how do I create models and seed the database?
For example classic tables Actors and Movies. I tried it like this
public class Actor
{
public Actor()
{
this.Movies = new HashSet<Movies>;
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Surname { get; set;}
public virtual ICollection<Movie> Movies { get; set; }
}
public class Movie
{
public Movie()
{
this.Actors = new HashSet<Actors>;
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Actor> Actors { get; set; }
}
As I understood Entity Framework creates automatically new table ActorMovies with two columns with IDs of Actor and Movie.
How I seed it:
Actor actor = new Actor { Name="John", Surname="Doe" };
Movie movie = new Movie { Name="John Doe and his garden hoe" };
actor.Movies.Add(movie);
dbContext.Add(movie); ( call from separate repository )
This automatically seeds Actor table as well and pretty much duplicates all data in both tables. Every time I add new Actor with same Movie, it creates new row in Movie table with same Name but just different ID, which is completely wrong.
My ApplicationDbContext is standard :
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
public DbSet<Actor> Actors { get; set; }
public DbSet<Movie> Movies { get; set; }
}
So what is the proper way of creating, initializing and seeding many-to-many relationship?
CodePudding user response:
You need to access the "Shadow Entity". By "convention" the joining table is the concatenation of the two names (ActorMovie). With the modelbuilder I can use the .HasData method to seed the data. Also by convention the foreign keys in the joining table is the plural name of the Entity "Id" (ActorsId and MoviesId)
public class SomeDbContext : DbContext
{
public SomeDbContext (DbContextOptions<SomeDbContext > options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Actor> Actors { get; set; }
public DbSet<Movie> Movies { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
var actorBuilder = builder.Entity<Actor>();
var movieBuilder = builder.Entity<Movie>();
actorBuilder
.HasMany(actor => actor.Movies)
.WithMany(movie => movie.Actors);
var actorMovieBuilder = builder.Entity("ActorMovie");
// Seed Actors
actorBuilder.HasData(new { Id = 1, Name = "Margot", Surname = "Robbie" });
// Seed Movies
movieBuilder.HasData(new { Id = 1, Name = "Suicide Squad" });
// Seed ActorMovies
actorMovieBuilder.HasData(new { ActorsId = 1, MoviesId = 1 });
}
}
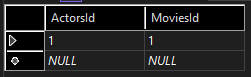
Seeded data in table
Note: You can override the "Convention" names.
CodePudding user response:
You need to specify an Id to avoid duplicates, or let the database assign Id for you by changing the Id properties of both classes to the following:
[Key]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
As for seeding initial data to database, this is one of the ways to do it:
public class ApplicationDbContext : DbContext
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Actor> Actors { get; set; }
public DbSet<Movie> Movies { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
var actor = new Actor { Id = 1, Name = "John", Surname = "Doe" };
var movie = new Movie { Id = 1, Name = "John Doe and his garden hoe" };
builder.Entity<Actor>().HasData(actor);
builder.Entity<Movie>().HasData(movie);
// Add relation data
// Column id = the collection property name "Id"
// e.g. public virtual ICollection<Movie> Films { get; set; }
// column id = FilmsId
builder
.Entity<Actor>()
.HasMany(p => p.Movies)
.WithMany(p => p.Actors)
.UsingEntity(j => j.HasData(new
{
ActorsId = actor.Id,
MoviesId = movie.Id
}));
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
}
}
Entity Classes:
public class Actor
{
public Actor()
{
Movies = new HashSet<Movie>();
}
[Key]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Surname { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Movie> Movies { get; set; }
}
public class Movie
{
public Movie()
{
Actors = new HashSet<Actor>();
}
[Key]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.Identity)]
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<Actor> Actors { get; set; }
}
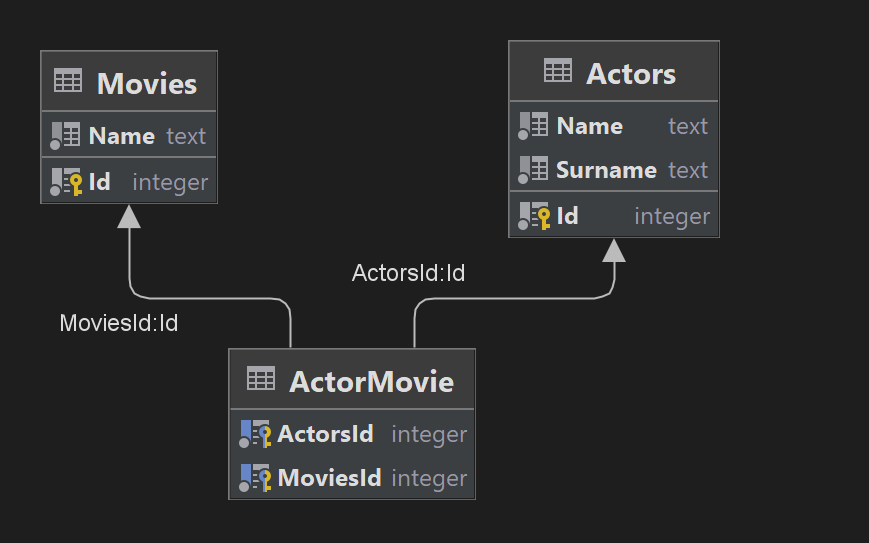
Visualization:
ActorMovie table is auto-generated by Entity Framework for many-to-many relationship between Actor and Movie entities.