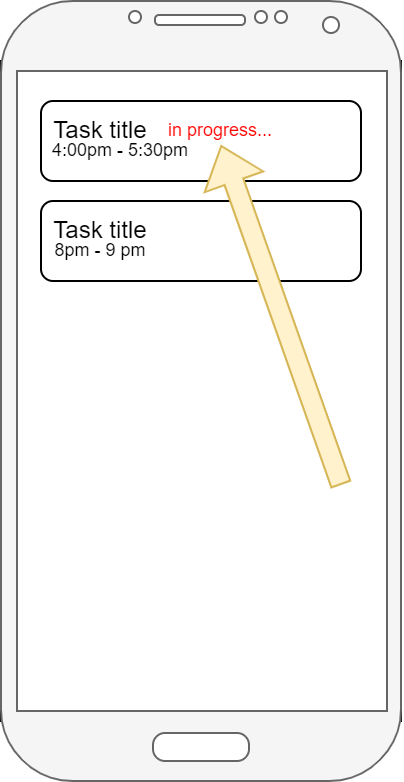
I have a simple app with list of Tasks. Each Task is time bound.
@freezed
class Task with _$Task {
const factory Task({
@Default('') String title,
required DateTime start,
required DateTime end,
}) = _Task;
}
Then I display the tasks using provider, e.g.:
class TasksController extends StateNotifier<List<Task>> {
TasksController()
: super(const []) {
init();
}
Future<void> init() async {
state = await GetTasksFromSomeRepo();
}
}
I would like to show indicator that task is happening now, e.g.:
There exists a simple solution, where I do rebuild entire list of Task's widgets every 1 second, using:
Timer.periodic(Duration(seconds: 1), (Timer t) {
setState(() {
// this calls build method
});
});
and in build method itself I check if DateTime.now() is within each Task "start/end" bounds.
This however seems like an inefficient approach.
Question:
- How to do it with in more efficient way, ideally with help of a Riverpod?
CodePudding user response:
Since you do not comunicate with any API the only way to check for something in progress is, as you mention in the question, with a timer.
What you can do however is, instead of calling setState, change something in task (you could would create a new variable state) by accessing the TasksController.
If implemented correctly, that should trigger a state change that rebuilds only the right widgets, instead of the whole widget tree.
CodePudding user response:
task_resolver.dart :
enum TaskEvent {
onProgrees,
completed,
}
class TaskResolver {
final Ref ref;
TaskResolver(this.ref);
Stream<TaskEvent> taskEvent() async* {
// get from your provider,
//ref.watch(taskController);
//for simulation i just assign next day
final taskDateCompleted = DateTime(2022, 12, 8);
TaskEvent? current;
while (true){
final now = DateTime.now();
if(current == null){
//default value
current = TaskEvent.onProgrees;
yield current;
}
if(taskDateCompleted.isBefore(now) && current != TaskEvent.onProgrees){
current = TaskEvent.onProgrees;
yield TaskEvent.onProgrees;
}
if(taskDateCompleted.isAfter(now) && current != TaskEvent.completed){
current = TaskEvent.completed;
yield TaskEvent.completed;
}
await Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1));
}
}
}
final taskResolver = StreamProvider.autoDispose<TaskEvent>((ref) => TaskResolver(ref).taskEvent());
on ui.dart:
class TaskPage extends ConsumerWidget {
const TaskPage({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, ref) {
final status = ref.watch(taskResolver);
return status.when(
data: (taskEvent){
print(taskEvent);
return Text(taskEvent.name);
},
error: (_,__)=> const Text('error'),
loading: ()=> const Text('loading')
);
}
}
CodePudding user response:
A more efficient solution using setState, here the TaskContainer widget is rebuilt at most twice.
class TaskContainer extends StatefulWidget {
const TaskContainer({
required this.task,
Key? key,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<TaskContainer> createState() => _TaskContainerState();
final Task task;
}
class _TaskContainerState extends State<TaskContainer> {
bool _inProgress = false;
void updateProgress() {
final now = DateTime.now();
setState(() {
_inProgress = now.compareTo(widget.task.start) >= 0 &&
now.compareTo(widget.task.end) <= 0;
});
}
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
updateProgress();
final nowFromEpoch = DateTime
.now()
.microsecondsSinceEpoch;
final timeToStart = widget.task.start.microsecondsSinceEpoch - nowFromEpoch;
final timeToEnd = widget.task.end.microsecondsSinceEpoch - nowFromEpoch;
if (timeToStart > 0) {
Future.delayed(Duration(microseconds: timeToStart), updateProgress);
}
if (timeToEnd > 0) {
Future.delayed(Duration(microseconds: timeToEnd), updateProgress);
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final task = widget.task;
final formatter = DateFormat('HH:mm');
return Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10),
border: Border.all(color: Colors.black),
),
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(10),
child: Column(
children: [
Row(
children: [
Text(task.title),
const SizedBox(
width: 20,
),
if (_inProgress) const Text('In Progress...'),
],
),
Row(
children: [
Text(formatter.format(task.start)),
const SizedBox(
width: 20,
),
Text(formatter.format(task.end)),
],
)
],
),
);
}
}
An example page for testing it.
class Home extends StatelessWidget {
const Home({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final now = DateTime.now();
final repository = <Task>[
Task(
title: 'First',
start: now,
end: DateTime(now.year, now.month, now.day, now.hour, now.minute 1),
),
Task(
title: 'Second',
start: DateTime(now.year, now.month, now.day, now.hour, now.minute 1),
end: DateTime(now.year, now.month, now.day, now.hour, now.minute 2),
),
];
return Scaffold(
body: ListView.separated(
itemBuilder: (context, index) => TaskContainer(task: repository[index]),
separatorBuilder: (context, index) =>
const SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
itemCount: repository.length,
),
);
}
}