Let's say I have these two lists:
number_list_1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
number_list_2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
then let's say that I want to know if the two lists are equal (There are a lot of ways to do this in Python and it's not what I'm looking for, also this is not a good approach in Python to do this)
solution 1:
def list_equality_1(l1, l2):
# Assuming that two array like objects have the same length
length = len(l1)
for i in range(length):
if l1[i] == l2[i]:
continue
else:
return False
return True
solution 2:
def list_equality_1(l1, l2):
# Assuming that two array like objects have the same length
length = len(l1)
for i in range(length):
if l1[i] != l2[i]:
return False
return True
In both of these solutions, each time we loop, we are evaluating the if statement, for the first one we are evaluating for equality and for the second one we are evaluating for not equality of the elements in the ith place. My question is which one is better? evaluating for the 'equality' first and use else statement, or evaluating for the 'not equality'? I want to know how the compiler deals with this.
CodePudding user response:
My question is which one is better?
My answer is that the second one is better.
- You waste less lines
- Everybody knows the
continueis anyway implicit
I always use the second code when I have to, even thought as you said before there are several other ways to compare lists in Python, I'm talking of C/C .
length = len(l1)
for i in range(length):
if l1[i] != l2[i]:
return False
return True
This code is uselessy verbose, I would shorten it this way.
for first, second in zip(l1, l2):
if first != second:
return False
return True
It could be useful to you the reading of the documentation about built-in class 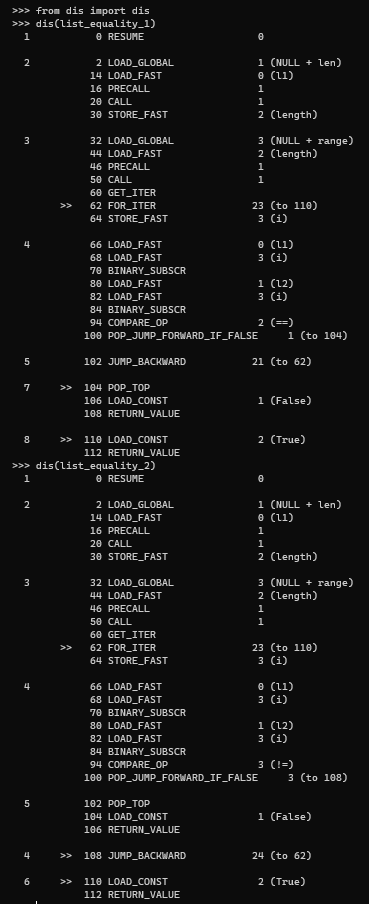
The two are equivalent, they generate almost the same set of instructions, except for a couple of things after line 100, but it won't affect the performance.
