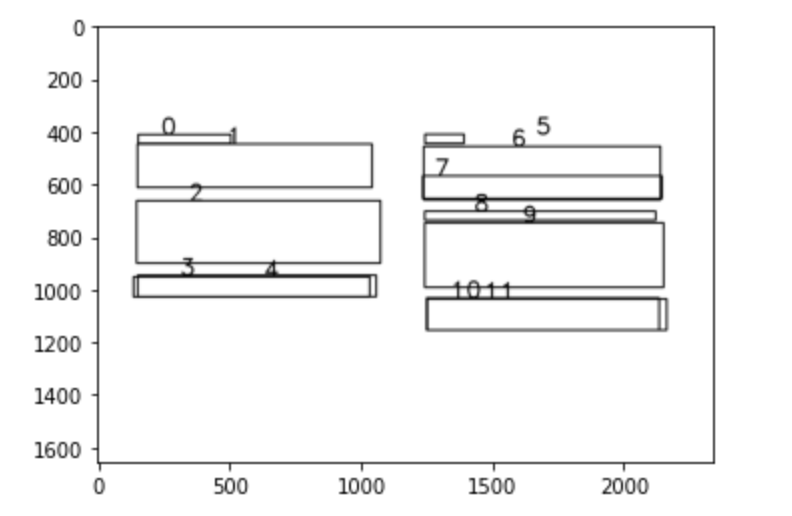
I have list of bounding boxes. When I plot them, there are some boxes overlapping with other. How can I identify them?
Here is attached example
Here we can see box 3,4 is overlapping, 10,11 is overlapping and box 7 is inside box 6. So I want to remove box which are 80% overlapping or 80% inside other box.
Here are the coordinates
boxes=[(0, (156.52566528320312, 411.3934326171875, 508.0946350097656, 445.0401611328125)),
(1, (153.34573364257812, 447.56744384765625, 1044.3194580078125, 612.4976196289062)),
(2, (150.6321258544922, 662.0474243164062, 1076.75439453125, 899.3271484375)),
(3, (154.38674926757812, 945.8661499023438, 1060.038330078125, 1026.8682861328125)),
(4, (138.6205596923828, 951.3151245117188, 1035.56884765625, 1027.590087890625)),
(5, (1245.50048828125, 410.4453430175781, 1393.0701904296875, 445.3376770019531)),
(6, (1240.206787109375, 456.7169189453125, 2139.934326171875, 659.1046752929688)),
(7, (1236.478759765625, 568.0098876953125, 2145.948486328125, 654.7606201171875)),
(8, (1244.784912109375, 702.7620239257812, 2121.079345703125, 736.1748046875)),
(9, (1244.885986328125, 746.2633666992188, 2151.534423828125, 991.8198852539062)),
(10, (1251.84814453125, 1031.8487548828125, 2134.333251953125, 1153.9320068359375)),
(11, (1254.38330078125, 1035.0196533203125, 2163.969970703125, 1153.2939453125))]
Here is the code, I used to generate above image
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
img = np.ones([1654,2339,3],dtype=np.uint8)*255
for i in boxes:
box=[int(i) for i in i[1]]
image = cv2.rectangle(img, (box[0],box[1]), (box[2],box[3]), (0,0,0), 5)
cv2.putText(
img = image,
text = str(i[0]),
org = (box[0] int(np.random.randint(0, high=500, size=1)),box[1]),
fontFace = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX,
fontScale = 3.0,
color = (0, 0, 0),
thickness = 3
)
plt.imshow(img)
The output I want is box 0,1,2,3 or 4 (the larger one), 5,6 ,8,9,10 or 11 (the larger one)
The solution I found work but not for all cases Here is my solution
#x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2
for i in range(len(boxes)-1):
x_min_1,y_min_1,x_max_1,y_max_1=boxes[i][1][0],boxes[i][1][1],boxes[i][1][2],boxes[i][1][3]
x_min_2,y_min_2,x_max_2,y_max_2=boxes[i 1][1][0],boxes[i 1][1][1],boxes[i 1][1][2],boxes[i 1][1][3]
box_1_in_box_2 = ((x_max_2> x_min_1 >= x_min_2) or \
(x_max_2>= x_max_1 >x_min_2)) and \
((y_max_2> y_min_1 >= y_min_2) or \
(y_max_2>= y_max_1 > y_min_2))
box_2_in_box_1 = ((x_max_1> x_min_2 >= x_min_1) or (x_max_1>= x_max_2 >x_min_1)) and ((y_max_1> y_min_2 >= y_min_1) or (y_max_1>= y_max_2 > y_min_1))
overlap = box_1_in_box_2 or box_2_in_box_1
print(i,overlap)
CodePudding user response:
For each box, calculate it's area. Then, for each other box, calculate how much that box overlaps in the x axis, and if it's greater than 0, calculate how much it overlaps in the y axis.
remove = []
areas = [(b[1][2] - b[1][0]) * (b[1][3] - b[1][2]) for b in boxes]
for i in range(len(boxes)-1):
if i in remove:
# don't check boxes you're already removing
continue
# Get x_1_1, y_1_1, x_2_1, y_2_1 for box i
j = i 1
while j < len(boxes):
if j in remove:
j = 1
continue
# Get x_1_2, y_1_2, x_2_2, y_2_2 for box i
x_overlap = min(x_2_1, x_2_2) - max(x_1_1, x_1_2)
# if there's no overlap, x_overlap will be negative or zero
x_overlap = max(0, x_overlap)
if not x_overlap:
j = 1
continue
y_overlap = min(y_2_1, y_2_2) - max(y_1_1, y_1_2)
# if there's no overlap, y_overlap will be negative or zero
y_overlap = max(0, y_overlap)
overlap_area = x_overlap * y_overlap
# if overlap area is greater than 90% of either box area
# add that index to remove
if overlap_area > areas[i] or overlap_area > areas[j]:
remove.append(i if areas[i] < areas[j] else j)
j = 1
CodePudding user response:
For this we can use the "non-maximum suppresion" method. We will iterate each box by comparing it with the others, calculating the air of each one, then calculating the air of a possible intersection. Then we will get their percenage of overlap and depending on the threshold we will delete them or not.
from typing import TypeAlias
Box: TypeAlias = tuple[float, float, float, float]
def calcul_area(box: Box):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box
return abs(x1 - x2) * abs(y1 - y2)
def nms_area(box_lhs: Box, box_rhs: Box, thresh_iou: float) -> float:
x1_lhs, y1_lhs, x2_lhs, y2_lhs = box_lhs
x1_rhs, y1_rhs, x2_rhs, y2_rhs = box_rhs
area_lhs = calcul_area(box_lhs)
area_rhs = calcul_area(box_rhs)
# Determines the coordinates of the intersection box
x1_inter = max(x1_lhs, x1_rhs)
y1_inter = max(y1_lhs, y1_rhs)
x2_inter = min(x2_lhs, x2_rhs)
y2_inter = min(y2_lhs, y2_rhs)
# Determines if the boxes overlap or not
# If one of the two is equal to 0, the boxes do not overlap
inter_w = max(0.0, x2_inter - x1_inter)
inter_h = max(0.0, y2_inter - y1_inter)
if inter_w == 0.0 or inter_h == 0.0:
return 0.0
intersection_area = inter_w * inter_h
union_area = area_lhs area_rhs - intersection_area
# See if the smallest box is not mostly in the largest one
if intersection_area / area_rhs >= thresh_iou:
return area_rhs / intersection_area
iou: float = intersection_area / union_area
return iou
# thresh_iou is a value between 0 and 1 determining the minimum percentage of overlap for a box to be deleted
# For example 90% = 0.9
def nms_algorithm(
boxes: list[tuple[int, Box]], thresh_iou: float
) -> list[tuple[int, Box]]:
if len(boxes) == 0:
return []
keeped_box_id, keeped_box = boxes.pop(0)
tmp_boxes: list[tuple[int, Box]] = []
for (id, box) in boxes:
if nms_area(keeped_box, box, thresh_iou) < thresh_iou:
tmp_boxes.append((id, box))
else:
print(f"Delete box {id}. Overlapping with {keeped_box_id}.")
return [
(keeped_box_id, keeped_box),
*nms_algorithm(tmp_boxes, thresh_iou),
]
boxes: list[tuple[int, Box]] = [
(0, (156.52566528320312, 411.3934326171875, 508.0946350097656, 445.0401611328125)),
(1, (153.34573364257812, 447.56744384765625, 1044.3194580078125, 612.4976196289062)),
(2, (150.6321258544922, 662.0474243164062, 1076.75439453125, 899.3271484375)),
(3, (154.38674926757812, 945.8661499023438, 1060.038330078125, 1026.8682861328125)),
(4, (138.6205596923828, 951.3151245117188, 1035.56884765625, 1027.590087890625)),
(5, (1245.50048828125, 410.4453430175781, 1393.0701904296875, 445.3376770019531)),
(6, (1240.206787109375, 456.7169189453125, 2139.934326171875, 659.1046752929688)),
(7, (1236.478759765625, 568.0098876953125, 2145.948486328125, 654.7606201171875)),
(8, (1244.784912109375, 702.7620239257812, 2121.079345703125, 736.1748046875)),
(9, (1244.885986328125, 746.2633666992188, 2151.534423828125, 991.8198852539062)),
(10, (1251.84814453125, 1031.8487548828125, 2134.333251953125, 1153.9320068359375)),
(11, (1254.38330078125, 1035.0196533203125, 2163.969970703125, 1153.2939453125)),
]
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(f"Entry boxes:{[id for id, _ in boxes]}\n")
# Sort the boxes from the largest to the smallest
# Will be useful to check if a smaller box is in the other one later
boxes.sort(key=lambda x: calcul_area(x[1]), reverse=True)
keeped_boxes = nms_algorithm(boxes, 0.9)
keeped_boxes.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])
print(f"\nKeeped boxes:{[id for id, _ in keeped_boxes]}")
And for your example I get:
Entry boxes:[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
Delete box 7. Overlapping with 6.
Delete box 11. Overlapping with 10.
Delete box 4. Overlapping with 3.
Keeped boxes:[0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10]