The question came into my mind when I've declared a final callback in a class, and the constructor can be declared as const, and trying to make a constant value of a function like so:
class MyClass {
final void Function() callback;
const MyClass(this.callback);
}
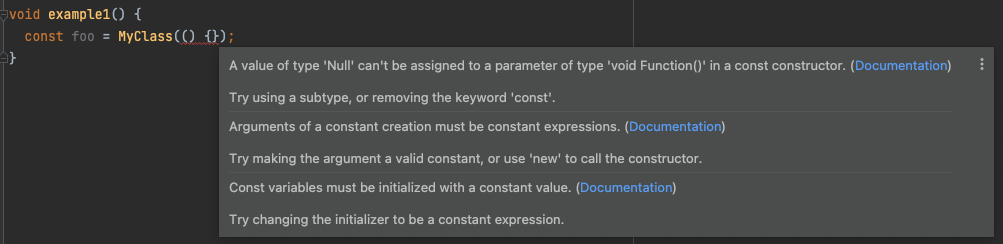
void example1() {
const foo = MyClass(() {});
}
This gives the error:
Why can I delcare a constant constructor in the first place? What would make an object of MyClass compile-time constant if no function value can be constant?
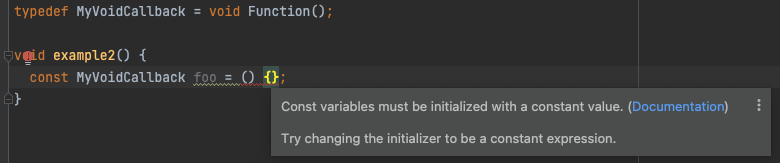
A simpler example:
typedef MyVoidCallback = void Function();
void example2() {
const MyVoidCallback bar = () {};
}
This gives the error:
Thank you in advance
CodePudding user response:
It is because () {} is not a constant value, it is rather creating a new instance every time. All functions in dart inherit Function class which doesn't have const constructor.
However, since functions are top-level members in dart, you can pass them by name (like a variable). So if you define your function outside of any class such that it is a global function, you can pass it as a parameter value in a const constructor.
UPDATE from
@randal-schwartzcomment: Static functions inside a class can also be passed into these const constructors as parameters.
Below code should work:
class MyClass {
final void Function() callback;
const MyClass(this.callback);
}
void example1() {
const foo = MyClass(doWork);
}
void doWork() {
// TODO: do work
}